Russia to build own space station; admits Zvezda is failing
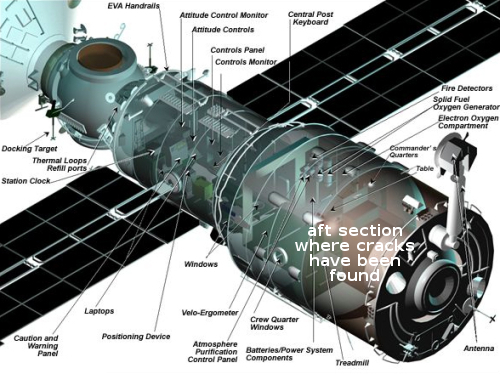
The Zvezda module, with aft section indicated
where the cracks have been found.
The new colonial movement: On April 12th, the 60th anniversary of the flight of Yuri Gagarin, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that Russia is going to build its own independent space station, dubbed the Russian Orbital Space Station (ROSS), to replace its half of ISS.
More important however was this carefully worded admission:
In recent years, the ISS has begun to fall apart, with astronauts now frequently discovering cracks. Last week, it was revealed that Russian cosmonauts were still working on plugging a leak first noticed in 2019. The ongoing problems with the international station have prompted Moscow to begin creating a replacement.
What this state-run news article failed to mention is that the cracks and leaks have only been found in Russia’s twenty-year-old Zvezda module, not the rest of ISS. What ISS faces is the failure of the core section of Russia’s half of the station.
This public statement however is the first from Russia that clearly admits that the cracks in Zvezda are likely systemic stress fractures, and the patches to seal them are mere bandaids on a much more fundamental problem that is certain to get worse over time.
The decision to build its own new station is however not really surprising. The American goals in space have been shifting from promoting the government’s program to stimulating the American commercial aerospace industry. International cooperation is no longer the primary goal. The American foreign aid to Russia’s space program from the early days of ISS’s construction has long ago dried up, and Russia is also no longer getting any cash from the U.S. to fly American astronauts to ISS. The incentive to remain a partner has vanished.
If successful this will make three national stations in orbit, ISS, China’s, and Russia’s. In addition, we should start seeing the launch of several private commercial stations sometime this decade.
The competition is going to be glorious, with the results fast-paced and exciting. The moribund days of boring international cooperation where everything was squeezed into a single project, the International Space Station, appear over.

The Zvezda module, with aft section indicated
where the cracks have been found.
The new colonial movement: On April 12th, the 60th anniversary of the flight of Yuri Gagarin, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that Russia is going to build its own independent space station, dubbed the Russian Orbital Space Station (ROSS), to replace its half of ISS.
More important however was this carefully worded admission:
In recent years, the ISS has begun to fall apart, with astronauts now frequently discovering cracks. Last week, it was revealed that Russian cosmonauts were still working on plugging a leak first noticed in 2019. The ongoing problems with the international station have prompted Moscow to begin creating a replacement.
What this state-run news article failed to mention is that the cracks and leaks have only been found in Russia’s twenty-year-old Zvezda module, not the rest of ISS. What ISS faces is the failure of the core section of Russia’s half of the station.
This public statement however is the first from Russia that clearly admits that the cracks in Zvezda are likely systemic stress fractures, and the patches to seal them are mere bandaids on a much more fundamental problem that is certain to get worse over time.
The decision to build its own new station is however not really surprising. The American goals in space have been shifting from promoting the government’s program to stimulating the American commercial aerospace industry. International cooperation is no longer the primary goal. The American foreign aid to Russia’s space program from the early days of ISS’s construction has long ago dried up, and Russia is also no longer getting any cash from the U.S. to fly American astronauts to ISS. The incentive to remain a partner has vanished.
If successful this will make three national stations in orbit, ISS, China’s, and Russia’s. In addition, we should start seeing the launch of several private commercial stations sometime this decade.
The competition is going to be glorious, with the results fast-paced and exciting. The moribund days of boring international cooperation where everything was squeezed into a single project, the International Space Station, appear over.