Bubbling but frozen terrain on Mars
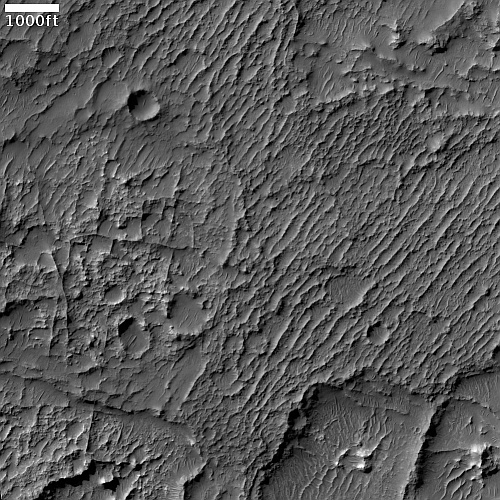
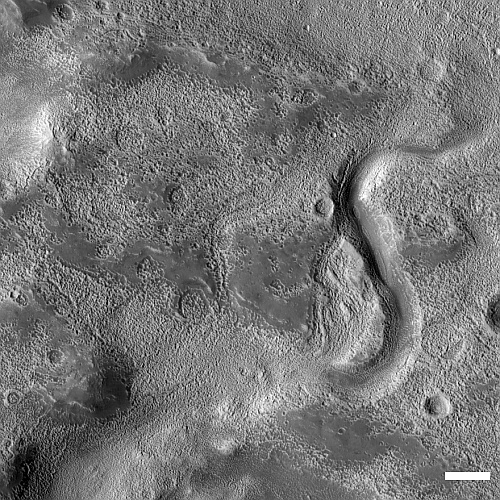
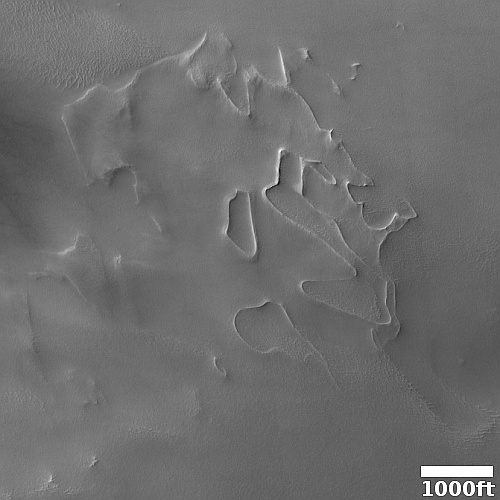
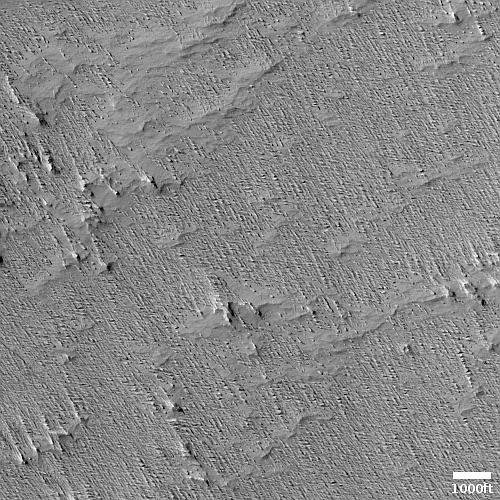
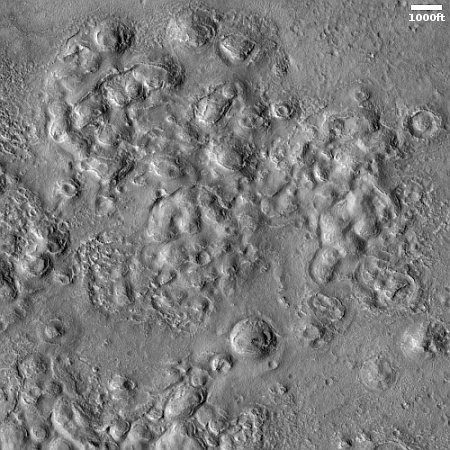
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on June 8, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows some of the more unusual terrain found at the higher latitudes in the Martian northern lowland plains.
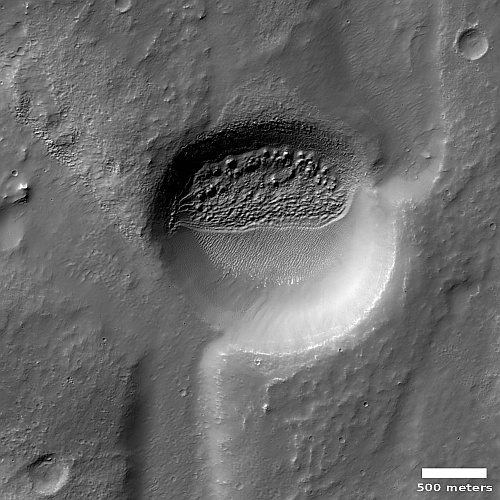
How do we explain this strange landscape? Based on what little we presently know about Mars, at 40 degrees north latitude this bubbly-looking surface probably indicates the presence of a lot of near-surface ice that at some time in the past was heated for some reason and thus bubbled upward to form these mounds. Think of tomato soup simmering.
Unlike simmering tomato soup, this terrain is solid and no longer bubbling. We are looking at a soup that has frozen even as it bubbled. The process could have been like an ice volcano, the ice turning to thick slurry that froze quickly, like lava. Or it could have happened fast, and then froze to remain unchanging in the eons since.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on June 8, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows some of the more unusual terrain found at the higher latitudes in the Martian northern lowland plains.
How do we explain this strange landscape? Based on what little we presently know about Mars, at 40 degrees north latitude this bubbly-looking surface probably indicates the presence of a lot of near-surface ice that at some time in the past was heated for some reason and thus bubbled upward to form these mounds. Think of tomato soup simmering.
Unlike simmering tomato soup, this terrain is solid and no longer bubbling. We are looking at a soup that has frozen even as it bubbled. The process could have been like an ice volcano, the ice turning to thick slurry that froze quickly, like lava. Or it could have happened fast, and then froze to remain unchanging in the eons since.
» Read more