Watching Elon Musk’s update on Starship tonight
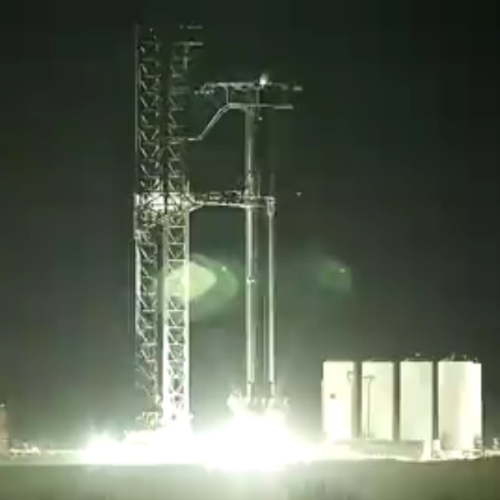

Tonight at 8 pm (central) Elon Musk is going to give a presentation updating the world on the status of SpaceX’s Starship project, with the fully stacked Starship/Superheavy as his backdrop. The photo to the right is a screen capture showing that stacking.
I have embedded the live stream below. Or you can watch it on SpaceX’s website or on its youtube channel.
The biggest question is the regulatory situation for Boca Chica. Will Musk report progress in getting operations approved there by the federal government, or will he outline how the federal government is acting as a barrier to progress? Or will he sidestep the issue (for diplomatic reasons) and focus his talk entirely on technical issues?
We can only wait and see.

Tonight at 8 pm (central) Elon Musk is going to give a presentation updating the world on the status of SpaceX’s Starship project, with the fully stacked Starship/Superheavy as his backdrop. The photo to the right is a screen capture showing that stacking.
I have embedded the live stream below. Or you can watch it on SpaceX’s website or on its youtube channel.
The biggest question is the regulatory situation for Boca Chica. Will Musk report progress in getting operations approved there by the federal government, or will he outline how the federal government is acting as a barrier to progress? Or will he sidestep the issue (for diplomatic reasons) and focus his talk entirely on technical issues?
We can only wait and see.