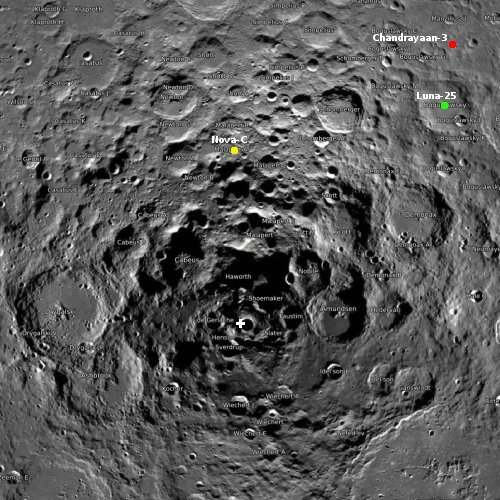
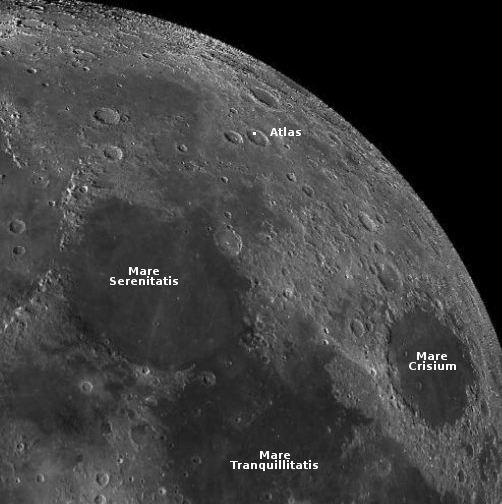
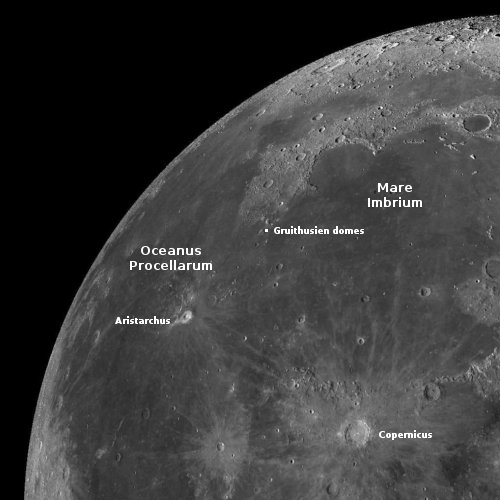
South Korean researchers turn simulated lunar soil into building blocks
Using simulated lunar soil, South Korean researchers have developed the engineering that turns that soil into building blocks shaped as needed.
The researchers first produce simulated moon soil by grinding black volcanic rock from Cheorwon County bordering the North. They then use a microwave to turn the sand-like simulant into solidified blocks. Lee said the team has developed a technique to make blocks by heating the soil in a mold to more than 1,000 degrees Celsius in two to three hours and cooling them. In space, the process could be powered by nuclear energy.
The article at the link also provides a nice summary of the status of South Korea’s entire space effort.
Using simulated lunar soil, South Korean researchers have developed the engineering that turns that soil into building blocks shaped as needed.
The researchers first produce simulated moon soil by grinding black volcanic rock from Cheorwon County bordering the North. They then use a microwave to turn the sand-like simulant into solidified blocks. Lee said the team has developed a technique to make blocks by heating the soil in a mold to more than 1,000 degrees Celsius in two to three hours and cooling them. In space, the process could be powered by nuclear energy.
The article at the link also provides a nice summary of the status of South Korea’s entire space effort.