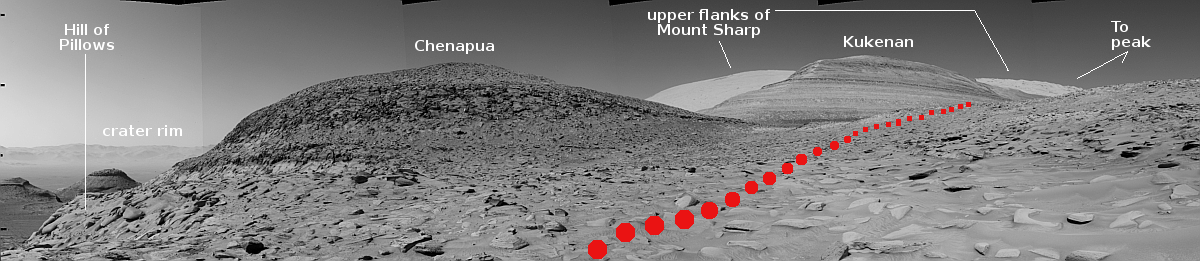
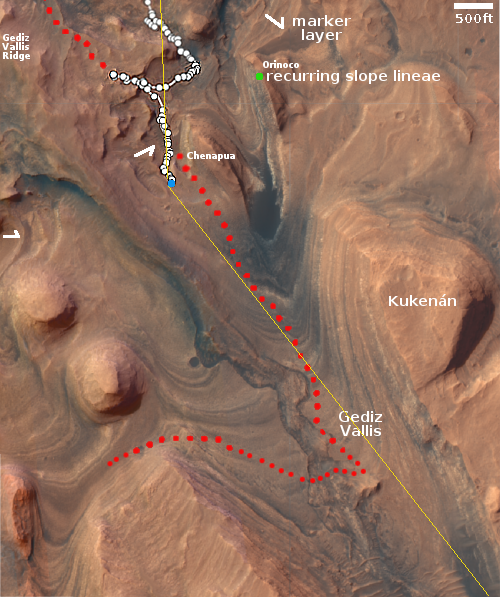
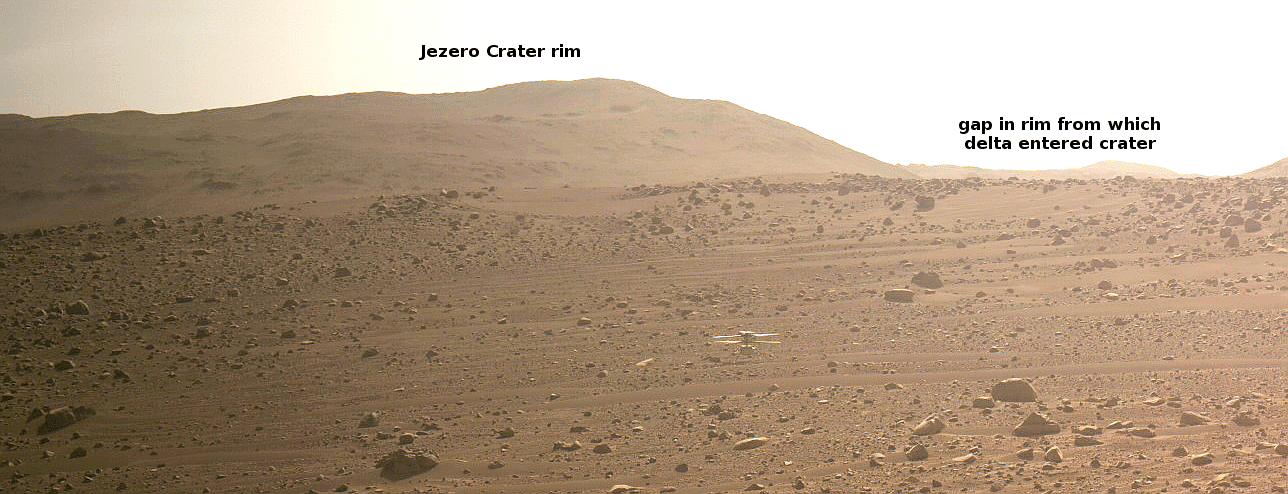
Radar antenna on Europe’s JUICE probe to Jupiter stuck
European Space Agency officials revealed yesterday that the 52-foot radar antenna on its JUICE probe to Jupiter has failed to deploy as planned, and that they are attempting to shake what they think is a small pin free that is in the way.
Engineers suspect a tiny pin may be protruding. Flight controllers in Germany plan to fire the spacecraft’s engine in hopes of shaking the pin loose. If that doesn’t work, they said they have plenty of time to solve the problem.
Juice, short for Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer, won’t reach the giant planet until 2031. It’s taking a roundabout path to get there, including gravity-assist flybys of Earth and our moon, and Venus.
The radar antenna is needed to peer beneath the icy crust of three Jupiter moons suspected of harboring underground oceans and possibly life, a major goal of the nearly $1.8 billion mission. Its targets include Callisto, Europa and Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system.
If this antenna cannot be freed, it will prevent JUICE from doing one of its prime missions.
European Space Agency officials revealed yesterday that the 52-foot radar antenna on its JUICE probe to Jupiter has failed to deploy as planned, and that they are attempting to shake what they think is a small pin free that is in the way.
Engineers suspect a tiny pin may be protruding. Flight controllers in Germany plan to fire the spacecraft’s engine in hopes of shaking the pin loose. If that doesn’t work, they said they have plenty of time to solve the problem.
Juice, short for Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer, won’t reach the giant planet until 2031. It’s taking a roundabout path to get there, including gravity-assist flybys of Earth and our moon, and Venus.
The radar antenna is needed to peer beneath the icy crust of three Jupiter moons suspected of harboring underground oceans and possibly life, a major goal of the nearly $1.8 billion mission. Its targets include Callisto, Europa and Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system.
If this antenna cannot be freed, it will prevent JUICE from doing one of its prime missions.