Scientists pin down Venus’s most likely active volcanic regions
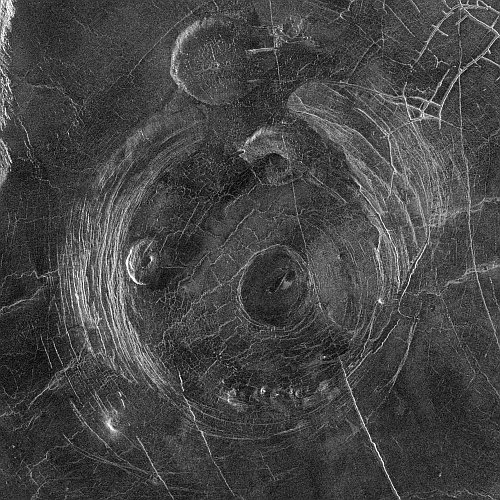
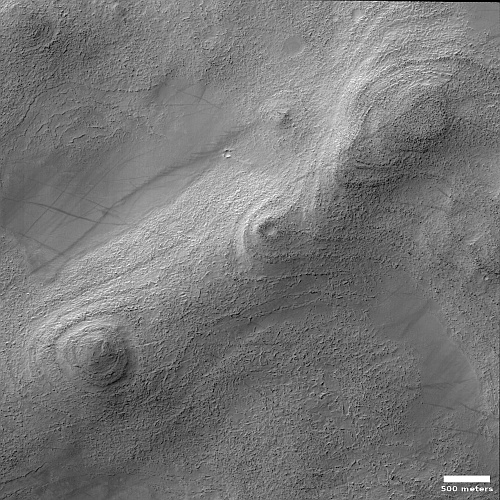
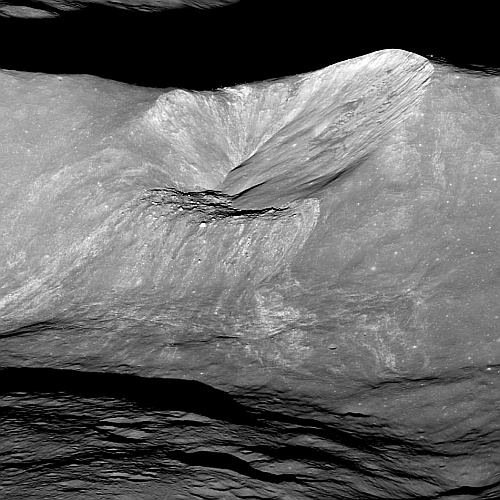
The Aine corona on Venus, about 124 miles in diameter.
Click for original image.
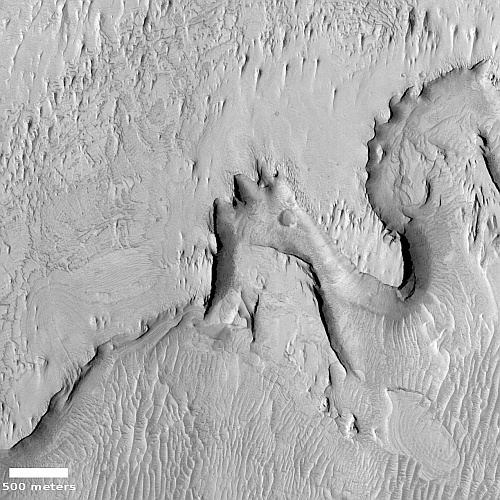
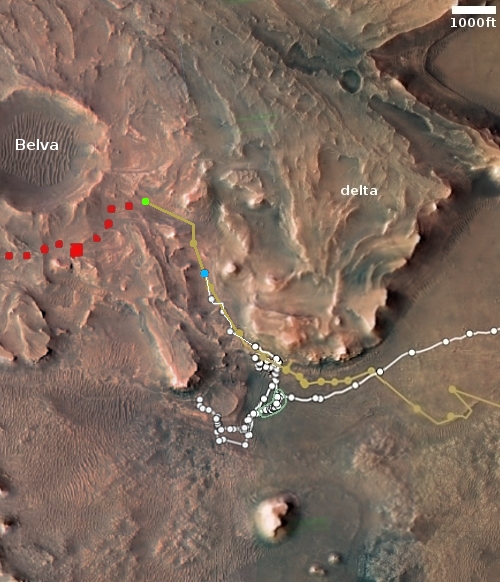
Using archival data from the Magellan radar imaging Venus orbiter from the early 1990s, scientists think they have identified the regions Venus that are most likely to have active volcanoes, places that have a unique Venusian circular feature called coronae.
The researchers focused on 65 previously unstudied coronae that are up to a few hundred miles across. To calculate the thickness of the lithosphere surrounding them, they measured the depth of the trenches and ridges around each corona. What they found is that ridges are spaced more closely together in areas where the lithosphere is more flexible, or elastic. By applying a computer model of how an elastic lithosphere bends, they determined that, on average, the lithosphere around each corona is about 7 miles (11 kilometers) thick – much thinner than previous studies suggest. These regions have an estimated heat flow that is greater than Earth’s average, suggesting that coronae are geologically active.
Thus, more volcanic activity, releasing the planet’s interior heat outward.
This research confirms other work done looking at coronae back in 2020.

The Aine corona on Venus, about 124 miles in diameter.
Click for original image.
Using archival data from the Magellan radar imaging Venus orbiter from the early 1990s, scientists think they have identified the regions Venus that are most likely to have active volcanoes, places that have a unique Venusian circular feature called coronae.
The researchers focused on 65 previously unstudied coronae that are up to a few hundred miles across. To calculate the thickness of the lithosphere surrounding them, they measured the depth of the trenches and ridges around each corona. What they found is that ridges are spaced more closely together in areas where the lithosphere is more flexible, or elastic. By applying a computer model of how an elastic lithosphere bends, they determined that, on average, the lithosphere around each corona is about 7 miles (11 kilometers) thick – much thinner than previous studies suggest. These regions have an estimated heat flow that is greater than Earth’s average, suggesting that coronae are geologically active.
Thus, more volcanic activity, releasing the planet’s interior heat outward.
This research confirms other work done looking at coronae back in 2020.