Looking down at Saturn’s rings
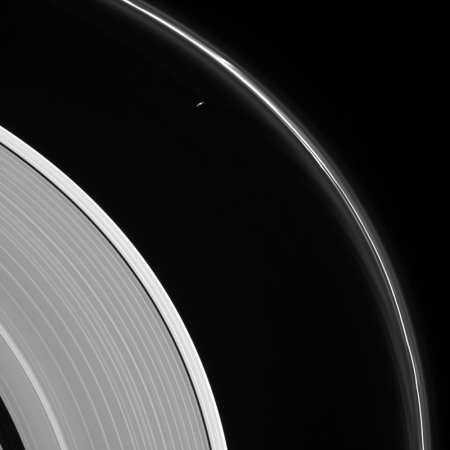
Cool image time! The image on the right, reduced in resolution to show here, was taken by Cassini in May and looks down at the outer rings of Saturn. The moon Prometheus can also be seen in the large gap between the main rings and the outermost F ring.
Most of the small moon’s surface is in darkness due to the viewing geometry here. Cassini was positioned behind Saturn and Prometheus with respect to the sun, looking toward the moon’s dark side and just a bit of the moon’s sunlit northern hemisphere.
Also visible here is a distinct difference in brightness between the outermost section of Saturn’s A ring (left of center) and rest of the ring, interior to the Keeler Gap (lower left).
The image clearly shows the gravitational influence of the moon on the outer ring. As Prometheus orbits past the F ring its mass creates waves through the ring’s materials.

Cool image time! The image on the right, reduced in resolution to show here, was taken by Cassini in May and looks down at the outer rings of Saturn. The moon Prometheus can also be seen in the large gap between the main rings and the outermost F ring.
Most of the small moon’s surface is in darkness due to the viewing geometry here. Cassini was positioned behind Saturn and Prometheus with respect to the sun, looking toward the moon’s dark side and just a bit of the moon’s sunlit northern hemisphere.
Also visible here is a distinct difference in brightness between the outermost section of Saturn’s A ring (left of center) and rest of the ring, interior to the Keeler Gap (lower left).
The image clearly shows the gravitational influence of the moon on the outer ring. As Prometheus orbits past the F ring its mass creates waves through the ring’s materials.