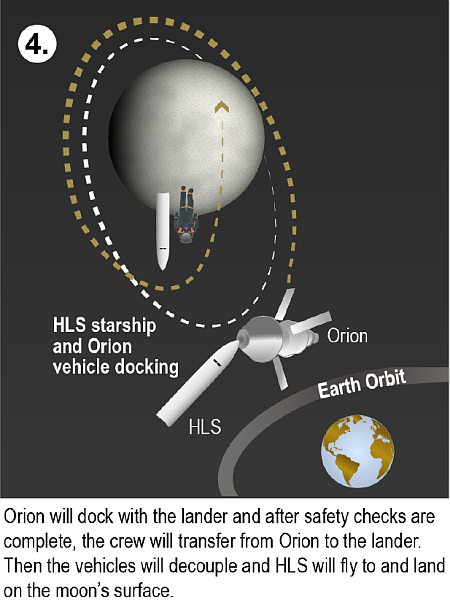
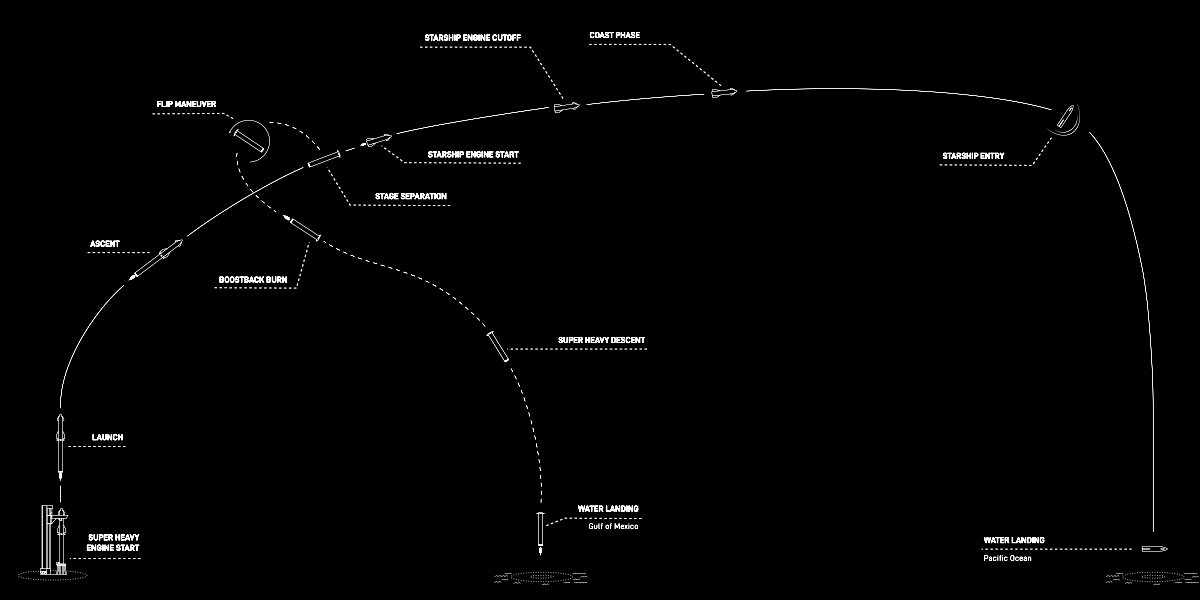
SpaceX launches 25 payloads, including South Korea’s first five homebuilt surveillance satellites
SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to launch 25 payloads into orbit, including first five homebuilt surveillance satellites by South Korea, lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The first stage successfully completed its seventeenth flight, landing back at Vandenberg. The fairings completed their fifth and sixth flights respectively. As of posting not all the payloads had been deployed.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
88 SpaceX
53 China
16 Russia
7 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise now leads China in successful launches, 100 to 53, and the entire world combined 100 to 85. SpaceX by itself now leads the entire world (excluding other American companies) 88 to 85.
SpaceX still has one more launch scheduled for today, from Cape Canaveral at 11 pm (Eastern). The link goes to the live stream.
This launch was significant for the United States. For the first time the U.S. has reached 100 launches in a single year, something that only the Soviet Union previously achieved, with 100 launches in 1982. With SpaceX’s launch tonight the U.S. will thus set a new record for the most launches in a single year by any nation.
SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to launch 25 payloads into orbit, including first five homebuilt surveillance satellites by South Korea, lifting off from Vandenberg in California.
The first stage successfully completed its seventeenth flight, landing back at Vandenberg. The fairings completed their fifth and sixth flights respectively. As of posting not all the payloads had been deployed.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
88 SpaceX
53 China
16 Russia
7 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise now leads China in successful launches, 100 to 53, and the entire world combined 100 to 85. SpaceX by itself now leads the entire world (excluding other American companies) 88 to 85.
SpaceX still has one more launch scheduled for today, from Cape Canaveral at 11 pm (Eastern). The link goes to the live stream.
This launch was significant for the United States. For the first time the U.S. has reached 100 launches in a single year, something that only the Soviet Union previously achieved, with 100 launches in 1982. With SpaceX’s launch tonight the U.S. will thus set a new record for the most launches in a single year by any nation.