Engineers place Pragyan into sleep mode
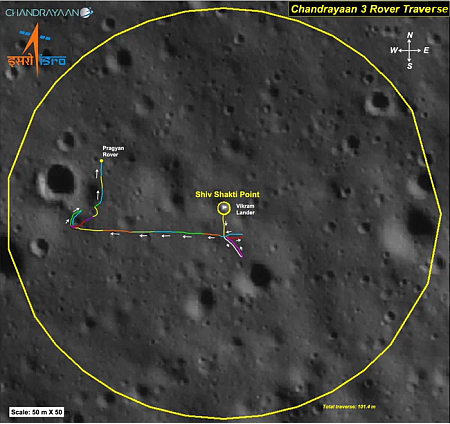
With lunar sunset looming, engineers have completed all work on both the lander Vikram and the rover Pragyan and have prepared Pragyan as best as possible to survive the long 14-Earth-day long lunar night.
Currently, the battery is fully charged. The solar panel is oriented to receive the light at the next sunrise expected on September 22, 2023. The receiver is kept on.
All data from Vikram’s instruments has been transmitted back to Earth, through the rover. It appears that the mission has been using the rover has the main communications relay, not the lander. It also appears there is no expectation of the lander surviving the lunar night.
With lunar sunset looming, engineers have completed all work on both the lander Vikram and the rover Pragyan and have prepared Pragyan as best as possible to survive the long 14-Earth-day long lunar night.
Currently, the battery is fully charged. The solar panel is oriented to receive the light at the next sunrise expected on September 22, 2023. The receiver is kept on.
All data from Vikram’s instruments has been transmitted back to Earth, through the rover. It appears that the mission has been using the rover has the main communications relay, not the lander. It also appears there is no expectation of the lander surviving the lunar night.