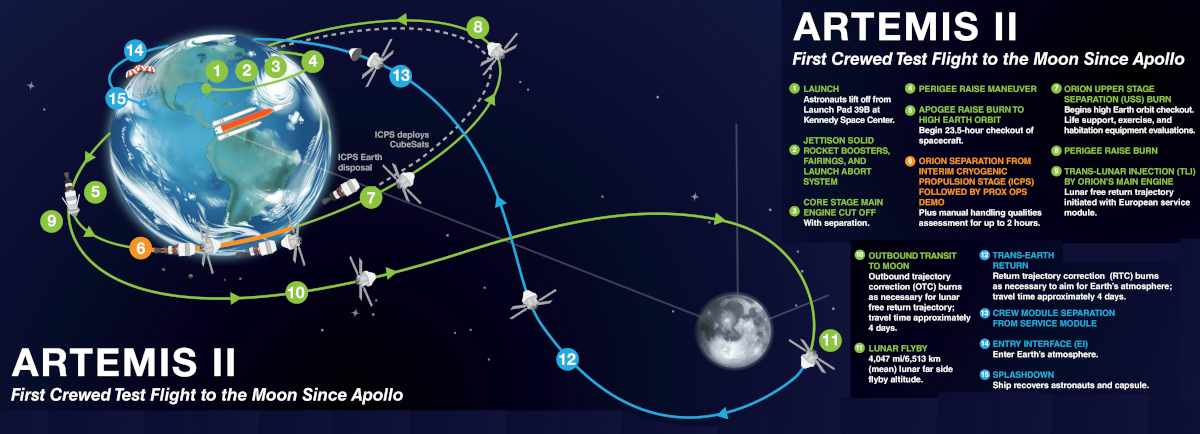
January 29, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Blue Origin successfully completes soft capture test of docking system to be used on its manned lunar lander and Orbital Reef space station
As far as I know, this could be the first real hardware Blue Origin has built for Orbital Reef.
- Declassifying JUMPSEAT, a surveillance satellite program from the ’70s and ’80s
The satellites used a high elliptical orbit that favored high latitude observations, excellent for monitoring Soviet military operations.
- I bought “Remove Before Flight” tags on eBay in 2010—it turns out they’re from Challenger’s final flight
Very interesting story about collecting miscellaneous space memorabilia that turns out to come from a very significant space mission.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Blue Origin successfully completes soft capture test of docking system to be used on its manned lunar lander and Orbital Reef space station
As far as I know, this could be the first real hardware Blue Origin has built for Orbital Reef.
- Declassifying JUMPSEAT, a surveillance satellite program from the ’70s and ’80s
The satellites used a high elliptical orbit that favored high latitude observations, excellent for monitoring Soviet military operations.
- I bought “Remove Before Flight” tags on eBay in 2010—it turns out they’re from Challenger’s final flight
Very interesting story about collecting miscellaneous space memorabilia that turns out to come from a very significant space mission.