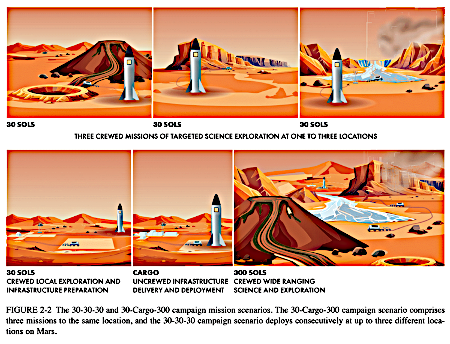
Figure 2-2 from the National Academies
of Science report
A new report released today by the National Academies of Science, entitled “Highest Priority Science for the First Human Missions to Mars,” is essentially the first attempt by the planetary science community to plan its future science missions to Mars using the gigantic capabilities that SpaceX’s Starship is expected to provide them.
You can download the report here.
Even though the report made the search for life on Mars its big priority — a bugaboo that NASA and the science community trots out repeatedly to garner clicks from the ignorant propaganda press — this report is radically different then all previous similar NASA studies proposing future Mars exploration, as indicated by the graphics from figure 2-2 of the report to the right. Unlike those past studies, which were badly limited by the inadequate capabilities of any spacecraft NASA could send to Mars, this new report recognizes how much the game is changed by SpaceX’s Starship.
First, the new panel did not attempt to place any limit on any landing zones. Earlier reports had forbidden landings in the high latitudes or high altitudes because of the risks to NASA’s proposed landers. Starship overcomes much of those risks, giving researchers much greater flexibility.
Second, the focus of the missions will not be solely devoted to scientific or geological research, as had been the case for all previous similar reports by NASA and the academic community. Instead, the proposed research goals includes important engineering and human exploration requirements outside of science, including efforts to use the resources on Mars itself as well as find locations better suited for human habitation. Once again, the vastly greater capabilities of Starship influenced this change.
Even more important, the study doesn’t assume the future missions will be unmanned, as all previous NASA reports have done. In fact, it does the opposite, proposing multiple 30-day manned missions, as shown in the graphic. One set of three missions would go to three different locations, while another set of three missions would focus on one place in particular.
Much of this shift towards manned flight I think stemmed from the presence on the panel of representatives from the private companies SpaceX and The Exploration Company (a French startup), as well as an engineer from the National Academy of Engineering. Previously studies were almost always entirely dominated by planetary scientists, so the goals outlined were always focused on their interests. Now the idea of human exploration has become prevalent.
The panel’s work was clearly also influenced by the realization that SpaceX’s Starship is not only far more capable, its first flights are just around the corner. SpaceX plans sending it numerous times to Mars in the very near future, as shown in the graphic below that Elon Musk released during a presentation in May 2025.
» Read more