New research confirms the steady decline of Martian ice with each glacial cycle
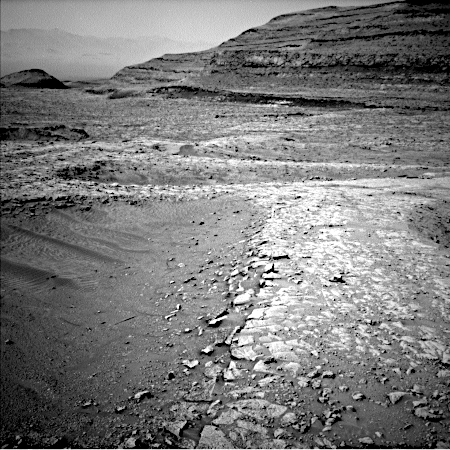
Using orbital data from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) of glaciers inside mid-latitude craters, scientists have concluded that there was a steady decline in the growth of those glaciers with each new glacial cycle.
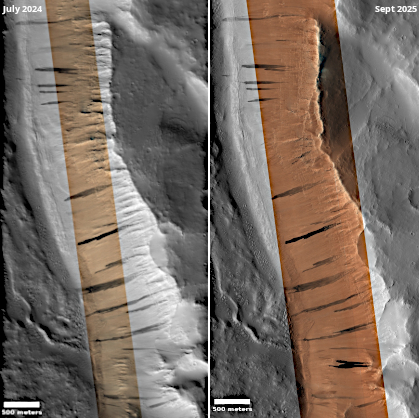
They focused on craters with indicative signs of glaciation, such as ridges, moraines (piles of debris left behind by glaciers), and brain terrain (a pitted, maze-like surface formed by ice-rich landforms). By comparing the shapes and orientations of these features with climate models, they found that ice consistently clustered in the colder, shadowed southwestern walls of craters. This trend was consistent across various glacial periods, ranging from approximately 640 million to 98 million years ago.
The results show that Mars didn’t just freeze once—it went through a series of ice ages driven by shifts in its axial tilt, also known as obliquity. Unlike Earth, Mars’ tilt can swing dramatically over millions of years, redistributing sunlight and triggering cycles of ice build-up and melting. These changes shaped where water ice could survive on the planet’s surface. Over time, however, each cycle stored less ice, pointing to a gradual planetary drying. [emphasis mine]
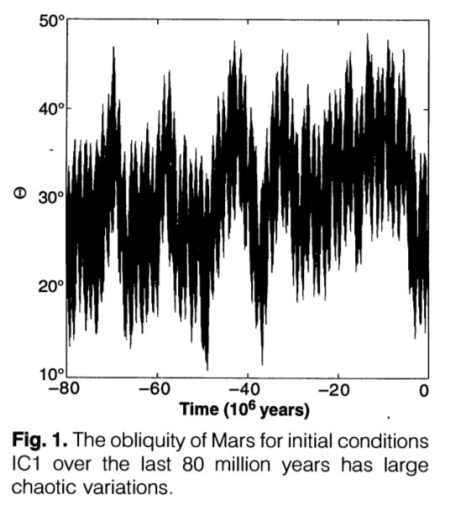
You can read the paper here [pdf]. This result is not new. Based on the orbital data scientists have theorized now for almost a decade that as Mars’ rotational tilt (its obliquity) swings from 11 to 60 degrees, it produces extreme climate cycles on the planet. Those swings are shown on the graph to the right, taken from this 1993 paper [pdf]. When the obliquity is low, the mid-latitudes are warm and the glaciers there shrink, with the snow falling at the poles. When obliquity is high, the poles are warmer and its ice sublimates away to fall as snow in the mid-latitudes, thus causing those glaciers to grow instead.
The orbital data has consistently shown that with each new cycle, the glaciers grew less, suggesting that less global water was available on the planet. This new study further confirms these conclusions.
One last point: Though the amount of water ice on Mars has declined, we mustn’t think the red planet now has none. The orbital data shows that there is a lot of near surface ice on Mars, covering the planet from 30 degrees latitude poleward. As I’ve noted numerous times, Mars is a desert like Antarctica.

Using orbital data from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) of glaciers inside mid-latitude craters, scientists have concluded that there was a steady decline in the growth of those glaciers with each new glacial cycle.
They focused on craters with indicative signs of glaciation, such as ridges, moraines (piles of debris left behind by glaciers), and brain terrain (a pitted, maze-like surface formed by ice-rich landforms). By comparing the shapes and orientations of these features with climate models, they found that ice consistently clustered in the colder, shadowed southwestern walls of craters. This trend was consistent across various glacial periods, ranging from approximately 640 million to 98 million years ago.
The results show that Mars didn’t just freeze once—it went through a series of ice ages driven by shifts in its axial tilt, also known as obliquity. Unlike Earth, Mars’ tilt can swing dramatically over millions of years, redistributing sunlight and triggering cycles of ice build-up and melting. These changes shaped where water ice could survive on the planet’s surface. Over time, however, each cycle stored less ice, pointing to a gradual planetary drying. [emphasis mine]
You can read the paper here [pdf]. This result is not new. Based on the orbital data scientists have theorized now for almost a decade that as Mars’ rotational tilt (its obliquity) swings from 11 to 60 degrees, it produces extreme climate cycles on the planet. Those swings are shown on the graph to the right, taken from this 1993 paper [pdf]. When the obliquity is low, the mid-latitudes are warm and the glaciers there shrink, with the snow falling at the poles. When obliquity is high, the poles are warmer and its ice sublimates away to fall as snow in the mid-latitudes, thus causing those glaciers to grow instead.
The orbital data has consistently shown that with each new cycle, the glaciers grew less, suggesting that less global water was available on the planet. This new study further confirms these conclusions.
One last point: Though the amount of water ice on Mars has declined, we mustn’t think the red planet now has none. The orbital data shows that there is a lot of near surface ice on Mars, covering the planet from 30 degrees latitude poleward. As I’ve noted numerous times, Mars is a desert like Antarctica.