The mysterious spokes in Saturn’s rings
Cool image time! When Voyager-1 did its fly-by of Saturn in December 1980, its cameras captured something in the gas giant’s rings that no one had predicted or expected, spokes of brightness pointing outward along the surface of the rings at right angles to the planet. Even more puzzling, these spokes actually appeared to rotate around Saturn, always pointing away from it.
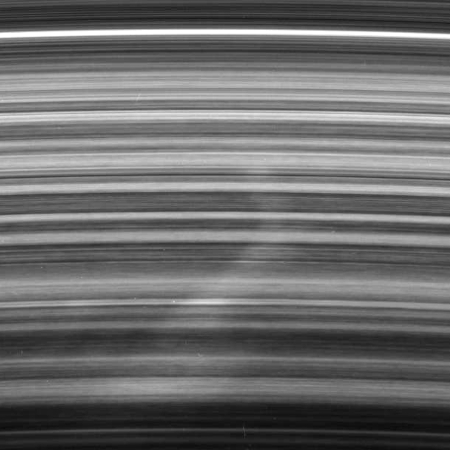
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on March 7, 2007 by the Saturn orbiter Cassini. It shows a close-up of one such spoke, though in this case it is bent. From the press release:
A bright spoke extends across the unilluminated side of Saturn’s B ring about the same distance as that from London to Cairo. The background ring material displays some azimuthal (i.e., left to right) asymmetry. The radial (outward from Saturn) direction is up in this view. A noticeable kink in the spoke occurs very close to the radius where ring particles orbit the planet at the speed of Saturn’s magnetic field. Such a connection is most intriguing to scientists studying these ghostly ring phenomena.
If gravity alone were affecting the spoke material, there would be no kink and the entire spoke would be angled toward right, like the bottom portion. That it bends to the left above the kink indicates that some other force, possibly related to the magnetic field, is acting on the spoke material. The shape might also indicate that the spoke did not form in a radial orientation, thus challenging scientists’ assumptions about these features.
In other words, the spokes exist because of multiple factors, some still unknown, that cause these streaks of brightness in the rings. For some reason, the millions of tiny ice particles that comprise the rings are brightened along these spokes, and it isn’t just gravity that is causing it.
Cool image time! When Voyager-1 did its fly-by of Saturn in December 1980, its cameras captured something in the gas giant’s rings that no one had predicted or expected, spokes of brightness pointing outward along the surface of the rings at right angles to the planet. Even more puzzling, these spokes actually appeared to rotate around Saturn, always pointing away from it.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on March 7, 2007 by the Saturn orbiter Cassini. It shows a close-up of one such spoke, though in this case it is bent. From the press release:
A bright spoke extends across the unilluminated side of Saturn’s B ring about the same distance as that from London to Cairo. The background ring material displays some azimuthal (i.e., left to right) asymmetry. The radial (outward from Saturn) direction is up in this view. A noticeable kink in the spoke occurs very close to the radius where ring particles orbit the planet at the speed of Saturn’s magnetic field. Such a connection is most intriguing to scientists studying these ghostly ring phenomena.
If gravity alone were affecting the spoke material, there would be no kink and the entire spoke would be angled toward right, like the bottom portion. That it bends to the left above the kink indicates that some other force, possibly related to the magnetic field, is acting on the spoke material. The shape might also indicate that the spoke did not form in a radial orientation, thus challenging scientists’ assumptions about these features.
In other words, the spokes exist because of multiple factors, some still unknown, that cause these streaks of brightness in the rings. For some reason, the millions of tiny ice particles that comprise the rings are brightened along these spokes, and it isn’t just gravity that is causing it.