January 16, 2026 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Gravity – Rocket Size Comparison as of 2024
A evening pause: The list is not quite complete, but it does give a sense of the comparable sizes of the most important rockets flying today, with a few important historic examples thrown in for context.
Hat tip Edward Thelen.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
January 16, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Blue Origin completes direct field acoustic testing on its unmanned Blue Moon MK1 lunar lander
The launch date is presently set vaguely for the first quarter of 2026.
- Liechtenstein awards spectrum license to satellite startup Open Cosmos
The company will launch the first two satellites in its constellation in ’26, using Rocket Lab as its launch provider.
- On this day in 2005 Stardust’s sample return capsule returned to Earth,
It returned particles released from Comet Wild 2.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Blue Origin completes direct field acoustic testing on its unmanned Blue Moon MK1 lunar lander
The launch date is presently set vaguely for the first quarter of 2026.
- Liechtenstein awards spectrum license to satellite startup Open Cosmos
The company will launch the first two satellites in its constellation in ’26, using Rocket Lab as its launch provider.
- On this day in 2005 Stardust’s sample return capsule returned to Earth,
It returned particles released from Comet Wild 2.
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s high resolution camera is showing its age
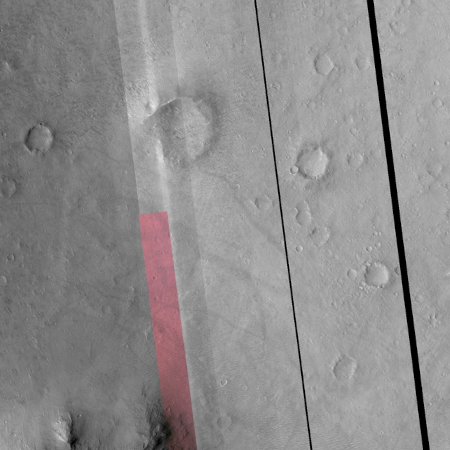
In a cool image earlier this week I noted that, in going through the archive of images most recently sent back from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s (MRO) high resolution camera, it appeared the camera was exhibiting more anomalies, and that we must therefore “be prepared for the loss of this camera and orbiter in the somewhat near future.”
In reviewing the archive again yesterday I noticed even more evidence of deterioration, as illustrated by the picture to the left. Not only are there blank vertical strips of no data, but the color drops out of the color strip halfway down, something I had never seen before. Nor was this the only picture with these issues.
I decided to email Alfred McEwen of the Lunar & Planetary Laboratory in Arizona. who until recently had been the camera’s principal investigator, to find out what is really going on. His answer:
Yes, HiRISE is getting old, just like us. There are 2 issues:
- 1. Sometimes RED4 fails, leaving a gap in the RED products and color.
- 2. Bit flips create bad pixels (zeros) in RED1_1 and RED3_1. This can still be mitigated by raising electronics temperatures, and we were just approved for an increase, so this problem should soon be reduced for a year or two. One problem with these increased temperatures is that our calibration isn’t correct, leading to the stripe-ing and strange colors that you noted, although dusty air can also create such issues. The calibration will eventually get updated, but funding is extremely tight.
The first issue explains the drop-out in the color strip. This appears to be a relatively new problem.
The second issue explains the two additional black strips to the right of the color strip. (Bit flips are cases where the radiation of space causes a binary bit to flip randomly from 0 to 1, or visa versa.) Bit flips are something engineers expect in spacecraft, but it appears on MRO they are occurring with more and more frequency.
A third issue, the failure of the electronics unit for CCD RED4 that occurred in August 2023, causes a loss of data in the color strip (see the b&w version of the image above for an example), which the camera team has compensated for using other color filters in that area.
According to McEwen, while the team seems confident the increased temperatures, combined with re-calibration, will fix or reduce issue #2, it is less confident about its impact on the camera’s lifespan.
We wish we knew. We’ve raised temperatures many times and it still works, so we keep raising temperatures incrementally just in case.
All in all, however, McEwen says he expects the high resolution camera to be able to produce images for at as long as MRO operates (at least a decade more), though with time we might be finding the images become narrower and narrower strips.
In a cool image earlier this week I noted that, in going through the archive of images most recently sent back from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s (MRO) high resolution camera, it appeared the camera was exhibiting more anomalies, and that we must therefore “be prepared for the loss of this camera and orbiter in the somewhat near future.”
In reviewing the archive again yesterday I noticed even more evidence of deterioration, as illustrated by the picture to the left. Not only are there blank vertical strips of no data, but the color drops out of the color strip halfway down, something I had never seen before. Nor was this the only picture with these issues.
I decided to email Alfred McEwen of the Lunar & Planetary Laboratory in Arizona. who until recently had been the camera’s principal investigator, to find out what is really going on. His answer:
Yes, HiRISE is getting old, just like us. There are 2 issues:
- 1. Sometimes RED4 fails, leaving a gap in the RED products and color.
- 2. Bit flips create bad pixels (zeros) in RED1_1 and RED3_1. This can still be mitigated by raising electronics temperatures, and we were just approved for an increase, so this problem should soon be reduced for a year or two. One problem with these increased temperatures is that our calibration isn’t correct, leading to the stripe-ing and strange colors that you noted, although dusty air can also create such issues. The calibration will eventually get updated, but funding is extremely tight.
The first issue explains the drop-out in the color strip. This appears to be a relatively new problem.
The second issue explains the two additional black strips to the right of the color strip. (Bit flips are cases where the radiation of space causes a binary bit to flip randomly from 0 to 1, or visa versa.) Bit flips are something engineers expect in spacecraft, but it appears on MRO they are occurring with more and more frequency.
A third issue, the failure of the electronics unit for CCD RED4 that occurred in August 2023, causes a loss of data in the color strip (see the b&w version of the image above for an example), which the camera team has compensated for using other color filters in that area.
According to McEwen, while the team seems confident the increased temperatures, combined with re-calibration, will fix or reduce issue #2, it is less confident about its impact on the camera’s lifespan.
We wish we knew. We’ve raised temperatures many times and it still works, so we keep raising temperatures incrementally just in case.
All in all, however, McEwen says he expects the high resolution camera to be able to produce images for at as long as MRO operates (at least a decade more), though with time we might be finding the images become narrower and narrower strips.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
Conscious Choice: The origins of slavery in America and why it matters today and for our future in outer space, is a riveting page-turning story that documents how slavery slowly became pervasive in the southern British colonies of North America, colonies founded by a people and culture that not only did not allow slavery but in every way were hostile to the practice.
Conscious Choice does more however. In telling the tragic history of the Virginia colony and the rise of slavery there, Zimmerman lays out the proper path for creating healthy societies in places like the Moon and Mars.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
Astronomers detect a bar of iron in the center of the Ring Nebula
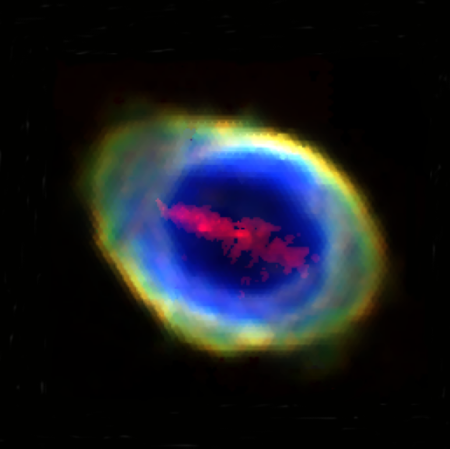
Composite image showing iron bar inside Ring Nebula.
Click for original.
The uncertainty of science: Using a new instrument on the Herschel Telescope in Chile, astronomers have detected a bar of iron cutting across the hole in the center of the Ring Nebula. You can read their paper here.
The cloud of iron atoms, described for the first time in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, is in the shape of a bar or strip: it just fits inside the inner layer of the elliptically shaped nebula, familiar from many images including those obtained by the James Webb Space Telescope at infrared wavelengths. The bar’s length is roughly 500 times that of Pluto’s orbit around the Sun and, according to the team, its mass of iron atoms is comparable to the mass of Mars.
The bar does not cross the nebula’s central star, nor does it exhibit the kind of motion seen by jets flowing outward from such stars. From the paper’s conclusion:
At present, there seem to be no obvious explanations that can account for the presence of the narrow ‘bar’ of [Fe v] and [Fe vi] emission seen in our WEAVE spectra to extend across the central regions of the Ring Nebula. Fresh observations of this newly uncovered feature at much higher spectral resolution seem essential to make progress
The scientists toss out the possibility that the bar is the remains of a rocky planet vaporized at some point in the system’s past, but that is simply a wild guess.

Composite image showing iron bar inside Ring Nebula.
Click for original.
The uncertainty of science: Using a new instrument on the Herschel Telescope in Chile, astronomers have detected a bar of iron cutting across the hole in the center of the Ring Nebula. You can read their paper here.
The cloud of iron atoms, described for the first time in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, is in the shape of a bar or strip: it just fits inside the inner layer of the elliptically shaped nebula, familiar from many images including those obtained by the James Webb Space Telescope at infrared wavelengths. The bar’s length is roughly 500 times that of Pluto’s orbit around the Sun and, according to the team, its mass of iron atoms is comparable to the mass of Mars.
The bar does not cross the nebula’s central star, nor does it exhibit the kind of motion seen by jets flowing outward from such stars. From the paper’s conclusion:
At present, there seem to be no obvious explanations that can account for the presence of the narrow ‘bar’ of [Fe v] and [Fe vi] emission seen in our WEAVE spectra to extend across the central regions of the Ring Nebula. Fresh observations of this newly uncovered feature at much higher spectral resolution seem essential to make progress
The scientists toss out the possibility that the bar is the remains of a rocky planet vaporized at some point in the system’s past, but that is simply a wild guess.
The recent computer hack of the European Space Agency was bigger than it admitted
After the European Space Agency (ESA) claimed in December that a computer hack that stole about 200 gigabytes of data was “limited,” it turns out that the agency had been hacked more than once preveious this past fall, and that the data stolen was far larger and apparently not limited at all.
The European Space Agency on Wednesday confirmed yet another massive security breach, and told The Register that the data thieves responsible will be subject to a criminal investigation. And this could be a biggie.
Earlier in the week, Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters told us that they gained initial access to ESA’s servers back in September by exploiting a public CVE, and stole 500 GB of very sensitive data. This, we’re told, includes operational procedures, spacecraft and mission details, subsystems documentation, and proprietary contractor data from ESA partners including SpaceX, Airbus Group, and Thales Alenia Space, among others.
And, according to the crims, the security hole remains open, giving them continued access to the space agency’s live systems.
“ESA is in the process of informing the judicial authorities having jurisdiction over this cyber incident to initiate a criminal inquiry,” an ESA spokesperson said via email. The agency declined to answer The Register’s specific questions about the intruders’ claims.
The article at the link outlines a slew of other hacks at ESA over the last decade. The agency seems unable to clean up its act.
After the European Space Agency (ESA) claimed in December that a computer hack that stole about 200 gigabytes of data was “limited,” it turns out that the agency had been hacked more than once preveious this past fall, and that the data stolen was far larger and apparently not limited at all.
The European Space Agency on Wednesday confirmed yet another massive security breach, and told The Register that the data thieves responsible will be subject to a criminal investigation. And this could be a biggie.
Earlier in the week, Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters told us that they gained initial access to ESA’s servers back in September by exploiting a public CVE, and stole 500 GB of very sensitive data. This, we’re told, includes operational procedures, spacecraft and mission details, subsystems documentation, and proprietary contractor data from ESA partners including SpaceX, Airbus Group, and Thales Alenia Space, among others.
And, according to the crims, the security hole remains open, giving them continued access to the space agency’s live systems.
“ESA is in the process of informing the judicial authorities having jurisdiction over this cyber incident to initiate a criminal inquiry,” an ESA spokesperson said via email. The agency declined to answer The Register’s specific questions about the intruders’ claims.
The article at the link outlines a slew of other hacks at ESA over the last decade. The agency seems unable to clean up its act.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
Winner of the 2003 Eugene M. Emme Award of the American Astronautical Society.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
China launches four satellites for another Chinese constellation
The Chinese pseudo-company Galactic Energy early today successfully launched another four satellites in the Tianqi satellite constellation, its Ceres-1 solid-fueled rocket lifting off from a sea platform off the northeast coast of China.
This was the sixth launch for the Tianqi constellation, which apparently is an internet-of-things constellation. It has launched 41 satellites so far, though only 29 are presently operational, with 12 having had their orbits decay.
The 2026 launch race:
6 SpaceX
4 China
The Chinese pseudo-company Galactic Energy early today successfully launched another four satellites in the Tianqi satellite constellation, its Ceres-1 solid-fueled rocket lifting off from a sea platform off the northeast coast of China.
This was the sixth launch for the Tianqi constellation, which apparently is an internet-of-things constellation. It has launched 41 satellites so far, though only 29 are presently operational, with 12 having had their orbits decay.
The 2026 launch race:
6 SpaceX
4 China
French rocket startup MaiaSpace wins ten-launch contract from Eutelsat
The French rocket startup MaiaSpace, which has not yet launched anything, has won a ten-launch contract from Eutelsat to place an unspecified number of its next generation OneWeb satellites into orbit.
Eutelsat has ordered around ten launches from MaiaSpace to launch some of the 440 new OneWeb satellites. These launches are scheduled from late 2027 to 2029. MaiaSpace has thus secured 50% of the launches planned for this period.
MaiaSpace is a wholly owned subsidiary of ArianeGroup, the company that builds Arianespace’s Ariane-6 rocket. ArianeGroup created it when it realized the expendable Ariane-6 rocket was not going to do well competing with the new reusable rockets. MaiaSpace’s Maia rocket will launch from French Guiana, and is being designed to eventually be reusable.
What makes this deal puzzling is that MaiaSpace is far behind at least thee other rocket startups in Europe, Germany’s Isar Aerospace and Rocket Factory Augsburg, and Spain’s PLD, all of which are much closer to an orbital launch. I suspect ArianeGroup used its clout to win the contract.
The French rocket startup MaiaSpace, which has not yet launched anything, has won a ten-launch contract from Eutelsat to place an unspecified number of its next generation OneWeb satellites into orbit.
Eutelsat has ordered around ten launches from MaiaSpace to launch some of the 440 new OneWeb satellites. These launches are scheduled from late 2027 to 2029. MaiaSpace has thus secured 50% of the launches planned for this period.
MaiaSpace is a wholly owned subsidiary of ArianeGroup, the company that builds Arianespace’s Ariane-6 rocket. ArianeGroup created it when it realized the expendable Ariane-6 rocket was not going to do well competing with the new reusable rockets. MaiaSpace’s Maia rocket will launch from French Guiana, and is being designed to eventually be reusable.
What makes this deal puzzling is that MaiaSpace is far behind at least thee other rocket startups in Europe, Germany’s Isar Aerospace and Rocket Factory Augsburg, and Spain’s PLD, all of which are much closer to an orbital launch. I suspect ArianeGroup used its clout to win the contract.
Chris Rea – The Road To Hell
An evening pause: Performed live 2006.
Hat tip Alec Gimarc, who adds these details: “Chris Rea passed away last week. About our age. Over 30 studio albums. British. Very much an acquired taste. Been listening to him for nearly 40 years. Smooth, smoky voice. He specialized in slide guitar. Road to Hell is probably his greatest hit.”
January 15, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Airspace closure notice suggests the damaged Shenzhou-20 crew spacecraft will attempt reentry and landing on January 19, 2026
I wonder if the Chinese will finally release an image of its damaged window, should it survive re-entry.
- On this date in 2005 the Huygens probe landed on Saturn’s moon Titan
The tweet includes the best picture taken from the surface. Huygens sent back data for 72 minutes.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Airspace closure notice suggests the damaged Shenzhou-20 crew spacecraft will attempt reentry and landing on January 19, 2026
I wonder if the Chinese will finally release an image of its damaged window, should it survive re-entry.
- On this date in 2005 the Huygens probe landed on Saturn’s moon Titan
The tweet includes the best picture taken from the surface. Huygens sent back data for 72 minutes.
Martian glacier flowing past small peak
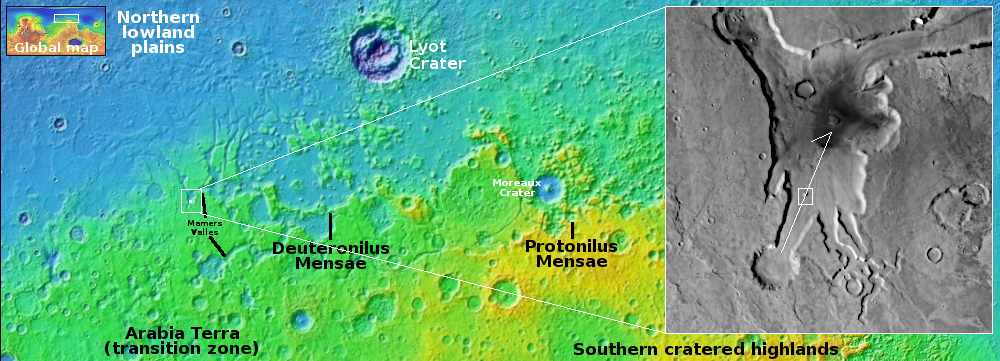
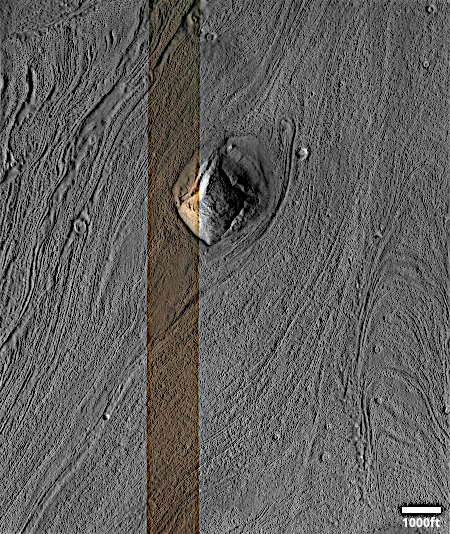
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on November 24, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
As is proper, the science team labels this vaguely as a “flow obstacle in lobate debris apron.” The obstacle is that small peak. The lobate debris apron is the material flowing past, resembling in almost all details what a glacier looks like on Earth. The scientists use vague terms because they don’t want to trap themselves into a conclusion before it is confirmed.
Nonetheless, based on all the data MRO and other Mars orbiters have been gathering for the past decade, we are almost certainly looking at near-surface ice flowing downhill and past that peak.
The white dot in the overview map above marks the location, on the western end of the 2,000-mile-long mid-latitude strip I label “glacier country,” because practically every image from this region shows features such as this.
The arrow in the inset shows the direction of the downhill grade, dropping from 2,000 to 3,000 feet from the surrounding plateau. The peak itself rises about 130 feet above the flow on the uphill side, but 650 feet above on the downhill side. Apparently the flow piled up somewhat as it hit the peak.
That flow however is likely inactive at this time. Though the researchers have repeatedly monitored the many glacial flows they have found on Mars in the decade since MRO arrived in Mars orbit, so far I have heard of no example showing any movement. And that covers about five Martian years.
These images do prove one thing: Mars is not dry. It has plenty of water near the surface, though locked in ice.

Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on November 24, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
As is proper, the science team labels this vaguely as a “flow obstacle in lobate debris apron.” The obstacle is that small peak. The lobate debris apron is the material flowing past, resembling in almost all details what a glacier looks like on Earth. The scientists use vague terms because they don’t want to trap themselves into a conclusion before it is confirmed.
Nonetheless, based on all the data MRO and other Mars orbiters have been gathering for the past decade, we are almost certainly looking at near-surface ice flowing downhill and past that peak.
The white dot in the overview map above marks the location, on the western end of the 2,000-mile-long mid-latitude strip I label “glacier country,” because practically every image from this region shows features such as this.
The arrow in the inset shows the direction of the downhill grade, dropping from 2,000 to 3,000 feet from the surrounding plateau. The peak itself rises about 130 feet above the flow on the uphill side, but 650 feet above on the downhill side. Apparently the flow piled up somewhat as it hit the peak.
That flow however is likely inactive at this time. Though the researchers have repeatedly monitored the many glacial flows they have found on Mars in the decade since MRO arrived in Mars orbit, so far I have heard of no example showing any movement. And that covers about five Martian years.
These images do prove one thing: Mars is not dry. It has plenty of water near the surface, though locked in ice.
Lockheed Martin and General Electric complete tests of a rotating-detonation engine
Lockheed Martin and General Electric announced this week that they have successfully tested a rotating-detonation engine using complimentary technology developed by each company.
GE Aerospace and Lockheed Martin completed a series of engine tests demonstrating the viability of a liquid-fueled rotating detonation ramjet for use in hypersonic missiles, the first initiative between the companies under a broader joint technology development arrangement.
This fuel-efficient rotating detonation ramjet promises to fly missiles faster—including at hypersonic speeds—and farther while decreasing costs compared to other ramjet options. … The rotating detonation ramjet combusts fuel and air through detonation waves instead of the traditional combustion methods used in ramjet engines today. This propulsion system generates high thrust for super- and hypersonic speeds to engage high-value, time-sensitive targets, with a smaller engine size and weight that boosts range.
In October Lockheed Martin’s venture capital division announced it was investing in a startup, Venus Aerospace, that was developing its own rotating detonation engines. One now wonders, based on today’s story, if that investment might have been a purchase of the technology itself.
Either way, the Pentagon’s program to develop hypersonic missile capability has blossomed in the past two years, since it stopped trying to build the technology itself and has instead been hiring private aerospace companies to do the research for it. Ain’t capitalism wonderful?
Lockheed Martin and General Electric announced this week that they have successfully tested a rotating-detonation engine using complimentary technology developed by each company.
GE Aerospace and Lockheed Martin completed a series of engine tests demonstrating the viability of a liquid-fueled rotating detonation ramjet for use in hypersonic missiles, the first initiative between the companies under a broader joint technology development arrangement.
This fuel-efficient rotating detonation ramjet promises to fly missiles faster—including at hypersonic speeds—and farther while decreasing costs compared to other ramjet options. … The rotating detonation ramjet combusts fuel and air through detonation waves instead of the traditional combustion methods used in ramjet engines today. This propulsion system generates high thrust for super- and hypersonic speeds to engage high-value, time-sensitive targets, with a smaller engine size and weight that boosts range.
In October Lockheed Martin’s venture capital division announced it was investing in a startup, Venus Aerospace, that was developing its own rotating detonation engines. One now wonders, based on today’s story, if that investment might have been a purchase of the technology itself.
Either way, the Pentagon’s program to develop hypersonic missile capability has blossomed in the past two years, since it stopped trying to build the technology itself and has instead been hiring private aerospace companies to do the research for it. Ain’t capitalism wonderful?
The European Space Agency and China hold the first joint meeting in almost a decade

The European Space Agency (ESA) this week hosted the leaders of the China National Space Administration (CNSA) in Paris, the first such joint meeting since 2017.
The meeting was co-chaired by ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher and CNSA Administrator Shan Zhongde. Both ESA and CNSA had unique achievements to share and discuss since the last time the heads of agencies met in person.
Both highlighted joint successes in space science, notably the Tianguan (Einstein Probe) launch with ESA hardware, and progress on the joint Smile mission, set to launch this year. Similarly, the two sides addressed the successful Chang’e-6 mission carrying ESA’s NILS instrument, ESA’s first experiment on the lunar surface. In the field of telemetry and tracking, both looked back on their long-term cooperation in supporting science and exploration missions. In discussing their respective space safety and Earth observation related programmes, the importance of cooperation to protect our planet and climate was recognised on both sides.
It was discussed, that building past progress, both sides in their respective institutional contexts would explore potential opportunities for further collaboration in areas such as Earth and space science.
Let me translate: We in Europe have found that our cooperative Soviet-style government-run projects with NASA (ISS, Mars Sample Return, and Lunar Gateway) are going away, and we need to find some other authoritarian nation we can partner with.
You see, the bureaucrats in Europe like their Soviet-style government-run space program, and are actually offended that the U.S. is shifting from that approach to the capitalism model, an independent industry run by private enterprise. Moreover, these bureaucrats at ESA are finding their own political support dwindling within the ESA’s member nations, many of whom are adopting the same private industry approach as the U.S.
Thus, rather than embrace freedom, competition, and capitalism — the principles that once made Europe great — they look to China now to help fund their government projects. How so very governmental of them!
It is likely some space projects will come of this, but if the U.S. remains steadfast in support of freedom and private enterprise, it will flow like a tidal wave over anything ESA and China develop.

The European Space Agency (ESA) this week hosted the leaders of the China National Space Administration (CNSA) in Paris, the first such joint meeting since 2017.
The meeting was co-chaired by ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher and CNSA Administrator Shan Zhongde. Both ESA and CNSA had unique achievements to share and discuss since the last time the heads of agencies met in person.
Both highlighted joint successes in space science, notably the Tianguan (Einstein Probe) launch with ESA hardware, and progress on the joint Smile mission, set to launch this year. Similarly, the two sides addressed the successful Chang’e-6 mission carrying ESA’s NILS instrument, ESA’s first experiment on the lunar surface. In the field of telemetry and tracking, both looked back on their long-term cooperation in supporting science and exploration missions. In discussing their respective space safety and Earth observation related programmes, the importance of cooperation to protect our planet and climate was recognised on both sides.
It was discussed, that building past progress, both sides in their respective institutional contexts would explore potential opportunities for further collaboration in areas such as Earth and space science.
Let me translate: We in Europe have found that our cooperative Soviet-style government-run projects with NASA (ISS, Mars Sample Return, and Lunar Gateway) are going away, and we need to find some other authoritarian nation we can partner with.
You see, the bureaucrats in Europe like their Soviet-style government-run space program, and are actually offended that the U.S. is shifting from that approach to the capitalism model, an independent industry run by private enterprise. Moreover, these bureaucrats at ESA are finding their own political support dwindling within the ESA’s member nations, many of whom are adopting the same private industry approach as the U.S.
Thus, rather than embrace freedom, competition, and capitalism — the principles that once made Europe great — they look to China now to help fund their government projects. How so very governmental of them!
It is likely some space projects will come of this, but if the U.S. remains steadfast in support of freedom and private enterprise, it will flow like a tidal wave over anything ESA and China develop.
China launches classified military satellite in partnership with Algeria
China today successfully placed a classified military remote sensing satellite into orbit, its Long March 2C rocket lifting off from its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China.
China’s state-run press provided no update on where the rocket’s lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China. The story at the link, from China’s military, did provide this information about the satellite:
Developed by China Academy of Space Technology under China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the satellite will be used for land planning and disaster prevention and mitigation. The launch is part of the Algeria remote sensing satellite system program, a joint project between China Great Wall Industry Corporation, a subsidiary of CASC, and the Algerian Space Agency. Signed in July 2023, the agreement includes two optical remote sensing satellites, ground systems, training, and related support services.
The 2026 launch race:
6 SpaceX
3 China
China today successfully placed a classified military remote sensing satellite into orbit, its Long March 2C rocket lifting off from its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China.
China’s state-run press provided no update on where the rocket’s lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China. The story at the link, from China’s military, did provide this information about the satellite:
Developed by China Academy of Space Technology under China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the satellite will be used for land planning and disaster prevention and mitigation. The launch is part of the Algeria remote sensing satellite system program, a joint project between China Great Wall Industry Corporation, a subsidiary of CASC, and the Algerian Space Agency. Signed in July 2023, the agreement includes two optical remote sensing satellites, ground systems, training, and related support services.
The 2026 launch race:
6 SpaceX
3 China
Indian startup raises seed money to build robotic satellite servicing “jetpacks”
An Indian startup, Aule Space, has now raised $2 million in seed money to begin development of a robot servicing spacecraft it intends to call “jetpacks”, designed to attach to satellites and provide them fuel and power.
The seed funding will allow Aule Space to being work on a demonstration mission planned for launch next year to test its docking capabilities. That will involve two satellites, each weighing about 30 kilograms, but Panchal said one option is to instead use an orbital transfer vehicle as the client for the docking demonstration.
The 11-person company, which plans to grow to 20 people by the end of the quarter, is working on ground tests of its rendezvous and docking technology. It has access to facilities used by the Indian space agency ISRO for testing SPADEX, a docking demonstration mission flown a year ago.
This “jetpack” concept is very similar to Northrop Grumman’s Mission Extension Vehicles (MEV), several of which have already flown and extended the life of several satellites.
Aule is exactly the type of Indian satellite startup that India’s rocket startups, Agnikul and Skyroot, are being built to serve. The problem is that all of these startups, both satellite and rocket, are literally all startups. None has flown. India’s private space sector won’t really take off until its private rocket companies get off the ground, as its government space agency, ISRO, has done a very poor job launching its PSLV and SSLV rockets (both designed for smallsats). The PSLV has failed on its last two launches, and the SSLV has been in limbo now for years.
An Indian startup, Aule Space, has now raised $2 million in seed money to begin development of a robot servicing spacecraft it intends to call “jetpacks”, designed to attach to satellites and provide them fuel and power.
The seed funding will allow Aule Space to being work on a demonstration mission planned for launch next year to test its docking capabilities. That will involve two satellites, each weighing about 30 kilograms, but Panchal said one option is to instead use an orbital transfer vehicle as the client for the docking demonstration.
The 11-person company, which plans to grow to 20 people by the end of the quarter, is working on ground tests of its rendezvous and docking technology. It has access to facilities used by the Indian space agency ISRO for testing SPADEX, a docking demonstration mission flown a year ago.
This “jetpack” concept is very similar to Northrop Grumman’s Mission Extension Vehicles (MEV), several of which have already flown and extended the life of several satellites.
Aule is exactly the type of Indian satellite startup that India’s rocket startups, Agnikul and Skyroot, are being built to serve. The problem is that all of these startups, both satellite and rocket, are literally all startups. None has flown. India’s private space sector won’t really take off until its private rocket companies get off the ground, as its government space agency, ISRO, has done a very poor job launching its PSLV and SSLV rockets (both designed for smallsats). The PSLV has failed on its last two launches, and the SSLV has been in limbo now for years.
Expedition-11 crew splashdowns safely
SpaceX’s Endeavour capsule has safely splashed down and been recovered off the coast of California, returning the four Expedition-11 astronauts several weeks early from ISS due to an as-yet undisclosed medical issue with one astronaut.
Crew-11 returned home about a month earlier than planned because of a medical concern teams are monitoring with one of the crew members, who remains stable. Due to medical privacy, it is not appropriate for NASA to share more details about the crew member. Prior to return, NASA previously coordinated for all four crew members to be transported to a local hospital for additional evaluation, taking advantage of medical resources on Earth to provide the best care possible.
Following the planned overnight hospital stay, the crew members will return to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston and undergo standard postflight reconditioning and evaluations.
This hospital visit for all four astronauts is simply a cover to hide which astronaut has the medical issue. At some point this information must be revealed, simply because it impacts how future space travel will be planned.
SpaceX’s Endeavour capsule has safely splashed down and been recovered off the coast of California, returning the four Expedition-11 astronauts several weeks early from ISS due to an as-yet undisclosed medical issue with one astronaut.
Crew-11 returned home about a month earlier than planned because of a medical concern teams are monitoring with one of the crew members, who remains stable. Due to medical privacy, it is not appropriate for NASA to share more details about the crew member. Prior to return, NASA previously coordinated for all four crew members to be transported to a local hospital for additional evaluation, taking advantage of medical resources on Earth to provide the best care possible.
Following the planned overnight hospital stay, the crew members will return to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston and undergo standard postflight reconditioning and evaluations.
This hospital visit for all four astronauts is simply a cover to hide which astronaut has the medical issue. At some point this information must be revealed, simply because it impacts how future space travel will be planned.
January 14, 2026 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Endeavour undocks from ISS, carrying the Expedition-11 crew
SpaceX’s Endeavour Dragon capsule undocked from ISS late this afternoon, carrying its four Expedition-11 crew who are coming home a few weeks early because of a medical issue with one crew person.
Live return coverage will resume at 2:15 a.m. Thursday, Jan. 15 on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and the agency’s YouTube channel until Dragon splashes down at approximately 3:41 a.m. off the coast of California and crew members are safely recovered.
It has been speculated by several sources, based on several NASA updates, that the crewman with the medical issues is Mike Finke, 58, who had flown in space three times previously.
Note that the only reason most major news sources are covering this crew return is because of the medical emergency. Normally, SpaceX has made this process so routine few pay attention any longer.
SpaceX’s Endeavour Dragon capsule undocked from ISS late this afternoon, carrying its four Expedition-11 crew who are coming home a few weeks early because of a medical issue with one crew person.
Live return coverage will resume at 2:15 a.m. Thursday, Jan. 15 on NASA+, Amazon Prime, and the agency’s YouTube channel until Dragon splashes down at approximately 3:41 a.m. off the coast of California and crew members are safely recovered.
It has been speculated by several sources, based on several NASA updates, that the crewman with the medical issues is Mike Finke, 58, who had flown in space three times previously.
Note that the only reason most major news sources are covering this crew return is because of the medical emergency. Normally, SpaceX has made this process so routine few pay attention any longer.
Anabasis – Dead Can Dance
Because Boeing did nothing to replace a defective part, an airplane crashed killing fifteen
Despite previously identifying stress fractures in a part that held the engines to the wing on three different MD-11 airplanes, Boeing did nothing to replace the part, and so fifteen people died when the engine fell off a UPS cargo plane at take-off in November 2025.
The sequence of images to the right, which I have annotated to show the engine breaking free from the wing, comes from the NTSB preliminary investigation report [pdf]. From the article at the link above:
In an update to its ongoing investigation into the crash of UPS Flight 2976, the National Transportation Safety Board [NTSB] said its team found fatigue cracking and overstress failure across much of the bearing race inside the area that attached the plane’s left engine to its wing. NTSB investigators then went back into Boeing service data and confirmed the design of the bearing assembly was consistent with the original design of that part.
[A] Boeing Service Letter dated Feb. 7, 2011 [and found by the NTSB], told operators the company was aware of four previous bearing race failures on three different airplanes. Boeing had seen the fractures of the bearing race, with the parts splitting in two and moving out of place. However, Boeing told operators its review of the bearing failure “would not result in a safety of flight condition.”
Boeing said further regular inspection of MD-11 airplanes would include a look at this bearing assembly, something scheduled for 60-month service intervals. And while Boeing used that service letter to discuss a new bearing assembly configuration, the installation of the original parts “was not prohibited.”
The plane itself had been built by McDonnell-Douglas, prior to its merger with Boeing. Nonetheless, Boeing engineers and managers were aware of this issue and did nothing to inform the owners of this plane so they could take action. In fact, Boeing apparently continued to ship out the original parts to airlines as replacement spares.
This is another example of a serious quality control problem at Boeing, where engineers no longer view serious engineering failures as serious engineering failures.
Despite previously identifying stress fractures in a part that held the engines to the wing on three different MD-11 airplanes, Boeing did nothing to replace the part, and so fifteen people died when the engine fell off a UPS cargo plane at take-off in November 2025.
The sequence of images to the right, which I have annotated to show the engine breaking free from the wing, comes from the NTSB preliminary investigation report [pdf]. From the article at the link above:
In an update to its ongoing investigation into the crash of UPS Flight 2976, the National Transportation Safety Board [NTSB] said its team found fatigue cracking and overstress failure across much of the bearing race inside the area that attached the plane’s left engine to its wing. NTSB investigators then went back into Boeing service data and confirmed the design of the bearing assembly was consistent with the original design of that part.
[A] Boeing Service Letter dated Feb. 7, 2011 [and found by the NTSB], told operators the company was aware of four previous bearing race failures on three different airplanes. Boeing had seen the fractures of the bearing race, with the parts splitting in two and moving out of place. However, Boeing told operators its review of the bearing failure “would not result in a safety of flight condition.”
Boeing said further regular inspection of MD-11 airplanes would include a look at this bearing assembly, something scheduled for 60-month service intervals. And while Boeing used that service letter to discuss a new bearing assembly configuration, the installation of the original parts “was not prohibited.”
The plane itself had been built by McDonnell-Douglas, prior to its merger with Boeing. Nonetheless, Boeing engineers and managers were aware of this issue and did nothing to inform the owners of this plane so they could take action. In fact, Boeing apparently continued to ship out the original parts to airlines as replacement spares.
This is another example of a serious quality control problem at Boeing, where engineers no longer view serious engineering failures as serious engineering failures.
January 14, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- War Department will invest in L3Harris’s missile division
This is a strange deal. Instead of buying solid-rockets from L3Harris, the government appears to be buying part of the company, now called Missile Solutions. Not a good plan in the long run.
- Firefly unveils the upgraded Block II version of its Alpha rocket
The final launch of Block 1 is tentatively scheduled “in a few weeks” and “will test some Block II subsystems.” As Block I had a poor launch record, the sooner it is replaced with an upgrade the better.
- Nimbus Power Systems successfully completes simulated launch test of its fuel cell system
This power system will be used on Blue Origin’s lunar landers, both manned and unmanned.
- A review of historical records finds the pulse of a variable star has shortened by three days
The Space.com headline at the link is garbage, pure clickbait that does not reflect the basic research.
- NASA official admits it is “unlikely” the MAVEN Mars orbiter will be recovered
Engineers will resume their effort to restore contact later this week, after the solar conjunction ends that is presently blocking communications with Mars.
- NASA’s IMAP space telescope reaches its planned L1 position
From here it will study the edge of the solar system and the local space weather produced by the Sun
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- War Department will invest in L3Harris’s missile division
This is a strange deal. Instead of buying solid-rockets from L3Harris, the government appears to be buying part of the company, now called Missile Solutions. Not a good plan in the long run.
- Firefly unveils the upgraded Block II version of its Alpha rocket
The final launch of Block 1 is tentatively scheduled “in a few weeks” and “will test some Block II subsystems.” As Block I had a poor launch record, the sooner it is replaced with an upgrade the better.
- Nimbus Power Systems successfully completes simulated launch test of its fuel cell system
This power system will be used on Blue Origin’s lunar landers, both manned and unmanned.
- A review of historical records finds the pulse of a variable star has shortened by three days
The Space.com headline at the link is garbage, pure clickbait that does not reflect the basic research.
- NASA official admits it is “unlikely” the MAVEN Mars orbiter will be recovered
Engineers will resume their effort to restore contact later this week, after the solar conjunction ends that is presently blocking communications with Mars.
- NASA’s IMAP space telescope reaches its planned L1 position
From here it will study the edge of the solar system and the local space weather produced by the Sun
Axiom has delayed the launch of its first space station module to ’28

Axiom’s module assembly sequence
When Axiom announced in September 2025 that Redwire would be building the solar panels for the first module of its space station, dubbed the PPTM, it also said that module would launch in late 2027, which was a delay of one year from the original launch date of 2026.
That schedule has now apparently been delayed again. In an interview yesterday, the company’s vice president of human spaceflight, former NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson, indicated the launch was now targeting 2028.
Plans call for the initial Axiom Station to be comprised of two modules, the PPTM — short for Payload Power Thermal Module — and a habitat module. The PPTM, which is to be shipped shortly to Houston for final assembly and integration, is slated to be launched in early 2028, with the second module following just months later. From there, Axiom aims to swiftly begin welcoming crew, Peggy Whitson, the company’s vice president of human spaceflight, told me in an interview.
This schedule almost guarantees that the Axiom station will not detach from ISS as quickly as originally intended. PPTM has a large hatch opening connecting it to ISS, allowing for the easy transfer of much of the research racks held on ISS. Before Axiom can become a free-flying station that ISS equipment must be moved, a process that will take time, likely months. To get it done the company will probably have to also attach its second habitation module so that crews can arrive and begin this transfer process.
In other words, Axiom’s schedule margins for getting its station launched, docked to ISS, loaded with ISS equipment, and then separated before ISS retires in 2030 are shrinking. It can ill afford further delays.
Below are my rankings of the five American space stations presently under development. Note that I now consider Axiom and Starlab tied for second.
» Read more

Axiom’s module assembly sequence
When Axiom announced in September 2025 that Redwire would be building the solar panels for the first module of its space station, dubbed the PPTM, it also said that module would launch in late 2027, which was a delay of one year from the original launch date of 2026.
That schedule has now apparently been delayed again. In an interview yesterday, the company’s vice president of human spaceflight, former NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson, indicated the launch was now targeting 2028.
Plans call for the initial Axiom Station to be comprised of two modules, the PPTM — short for Payload Power Thermal Module — and a habitat module. The PPTM, which is to be shipped shortly to Houston for final assembly and integration, is slated to be launched in early 2028, with the second module following just months later. From there, Axiom aims to swiftly begin welcoming crew, Peggy Whitson, the company’s vice president of human spaceflight, told me in an interview.
This schedule almost guarantees that the Axiom station will not detach from ISS as quickly as originally intended. PPTM has a large hatch opening connecting it to ISS, allowing for the easy transfer of much of the research racks held on ISS. Before Axiom can become a free-flying station that ISS equipment must be moved, a process that will take time, likely months. To get it done the company will probably have to also attach its second habitation module so that crews can arrive and begin this transfer process.
In other words, Axiom’s schedule margins for getting its station launched, docked to ISS, loaded with ISS equipment, and then separated before ISS retires in 2030 are shrinking. It can ill afford further delays.
Below are my rankings of the five American space stations presently under development. Note that I now consider Axiom and Starlab tied for second.
» Read more
SpaceX launches 29 more Starlink satellites
SpaceX today successfully placed another 29 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The first stage completed its 13th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The 2026 launch race:
6 SpaceX
2 China
SpaceX today successfully placed another 29 Starlink satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The first stage completed its 13th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The 2026 launch race:
6 SpaceX
2 China
Update on Starship launchpad construction in Texas and Florida
Link here. First, it appears construction of a second launch tower in Florida is about to begin. Second, the launchpad needed for the next orbital test flight of Starship/Superheavy is nearing completion.
Not only does this suggest the next test flight is only a matter of weeks away, the first launch out of Florida is not far in the future.
Link here. First, it appears construction of a second launch tower in Florida is about to begin. Second, the launchpad needed for the next orbital test flight of Starship/Superheavy is nearing completion.
Not only does this suggest the next test flight is only a matter of weeks away, the first launch out of Florida is not far in the future.
Another ESA rendezvous demo mission proposed
The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Luxembourg startup ClearSpace yesterday announced a new demo mission to test autonomous rendezvous and proximity maneuvers, scheduled to launch in 2027.
PRELUDE aims to validate autonomous rendezvous and proximity operations in real flight conditions. The mission will test high-accuracy tracking, navigation and maneuvering using a combination of vision-based and complementary sensors feeding onboard algorithms and autonomous, fault-tolerant guidance, navigation and control (GNC) software. The goal is to demonstrate full freedom of movement and safe, repeatable maneuvers around another spacecraft.
Sounds good, eh? Not so fast. ClearSpace has had a bunch of these missions proposed, and none has yet flown. In 2019 ClearSpace won an ESA contract to de-orbit an old piece of space junk by 2025. In 2023 however that mission was stymied when that space junk, a payload adapter from a 2013 launch of Vega rocket launch, was hit by another piece of space junk.
Both ESA and ClearSpace apparently had difficulties re-designing the mission. In 2024, the ESA forced a major shake-up in ClearSpace’s management and missions, with the established company OHB taking over the startup. Subsequently the mission was redesigned to de-orbit a different defunct satellite, but delayed until 2029.
In 2024 the United Kingdom gave ClearSpace and Japan’s Astroscale a contract to de-orbit two satellites in ’26. It is however not clear at this time whether that mission will launch as planned.
This new PRECLUDE mission is interesting in that it will test the rendezvous and proximity technology that ClearSpace must have for all the other de-orbit missions. In other words, those other missions were never possible, because ClearSpace didn’t have the capability to do them. This new mission appears designed to develop that capability.
I ask: Why wasn’t PRECLUDE scheduled first, in the first place? That it wasn’t reflects very badly on both ClearSpace and the ESA.
The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Luxembourg startup ClearSpace yesterday announced a new demo mission to test autonomous rendezvous and proximity maneuvers, scheduled to launch in 2027.
PRELUDE aims to validate autonomous rendezvous and proximity operations in real flight conditions. The mission will test high-accuracy tracking, navigation and maneuvering using a combination of vision-based and complementary sensors feeding onboard algorithms and autonomous, fault-tolerant guidance, navigation and control (GNC) software. The goal is to demonstrate full freedom of movement and safe, repeatable maneuvers around another spacecraft.
Sounds good, eh? Not so fast. ClearSpace has had a bunch of these missions proposed, and none has yet flown. In 2019 ClearSpace won an ESA contract to de-orbit an old piece of space junk by 2025. In 2023 however that mission was stymied when that space junk, a payload adapter from a 2013 launch of Vega rocket launch, was hit by another piece of space junk.
Both ESA and ClearSpace apparently had difficulties re-designing the mission. In 2024, the ESA forced a major shake-up in ClearSpace’s management and missions, with the established company OHB taking over the startup. Subsequently the mission was redesigned to de-orbit a different defunct satellite, but delayed until 2029.
In 2024 the United Kingdom gave ClearSpace and Japan’s Astroscale a contract to de-orbit two satellites in ’26. It is however not clear at this time whether that mission will launch as planned.
This new PRECLUDE mission is interesting in that it will test the rendezvous and proximity technology that ClearSpace must have for all the other de-orbit missions. In other words, those other missions were never possible, because ClearSpace didn’t have the capability to do them. This new mission appears designed to develop that capability.
I ask: Why wasn’t PRECLUDE scheduled first, in the first place? That it wasn’t reflects very badly on both ClearSpace and the ESA.
A small European prototype re-entry capsule survived PSLV launch failure
A small prototype re-entry demonstration capsule, built by the Spanish startup Orbital Paradigm and dubbed the Kestrel Initial Demonstrator (KID), apparently survived for a short period the failure of the third stage of India’s PSLV rocket early this week.
According to an Orbital Paradigm press release, the survival of its little demonstrator came as a surprise. “When we understood that the launch was non-nominal it was a bit of a hit for us,” explained Orbital Paradigm CEO Francesco Cacciatore. … “I think the launch livestream was still ongoing when the team saw that we had 190 seconds of flight data transmitted and received. We needed a few minutes to realize it was real data and not a glitch.”
…“KID was tested beyond its design envelope, and it worked. Separation, power-on, and data transmission, even after reentry, all performed well despite degraded conditions,” explained the company in a 13 January update. “Based on initial analysis, it seems that we achieved 4 out of 5 launch milestones, albeit through an off-nominal profile. The failure to deliver customers’ data prevents us from declaring the mission a success.”
The company considers the mission a failure because it did not get the re-entry data back that it really needed. It says however it is moving forward on a more advanced demonstrator it hopes to launch in 2027. I suspect it will not hire India’s space agency ISRO to launch it.
A small prototype re-entry demonstration capsule, built by the Spanish startup Orbital Paradigm and dubbed the Kestrel Initial Demonstrator (KID), apparently survived for a short period the failure of the third stage of India’s PSLV rocket early this week.
According to an Orbital Paradigm press release, the survival of its little demonstrator came as a surprise. “When we understood that the launch was non-nominal it was a bit of a hit for us,” explained Orbital Paradigm CEO Francesco Cacciatore. … “I think the launch livestream was still ongoing when the team saw that we had 190 seconds of flight data transmitted and received. We needed a few minutes to realize it was real data and not a glitch.”
…“KID was tested beyond its design envelope, and it worked. Separation, power-on, and data transmission, even after reentry, all performed well despite degraded conditions,” explained the company in a 13 January update. “Based on initial analysis, it seems that we achieved 4 out of 5 launch milestones, albeit through an off-nominal profile. The failure to deliver customers’ data prevents us from declaring the mission a success.”
The company considers the mission a failure because it did not get the re-entry data back that it really needed. It says however it is moving forward on a more advanced demonstrator it hopes to launch in 2027. I suspect it will not hire India’s space agency ISRO to launch it.
ULA loses another launch contract to SpaceX
The Space Force yesterday announced it has switched rocket companies for its next GPS satellite launch, taking the launch away from ULA and its Vulcan rocket and giving it to SpaceX.
SpaceX could launch the GPS III Space Vehicle 09 (SV09) within the next few weeks, as the satellite was entering the final stages of pre-flight preparations. As part of the swap, United Launch Alliance (ULA) will instead launch the third of the next generation of Global Positioning System satellites. The GPS III Follow-on (GPS IIIF) SV13 satellite was originally scheduled to launch on a Falcon Heavy, but will now fly on Vulcan.
“SV09 and SV13 were traded between ULA and SpaceX to get capability to orbit as soon as possible, for the same reason as the prior swap, which resulted in the last GPS launch in May 2025,” the spokesperson said in a statement. “The trade results in an overall net cost savings to the government and again demonstrates our sustained commitment to moving at speed to deliver combat-credible capabilities on orbit to meet warfighter needs.”
While at first glance it appears ULA has lost nothing, the military’s decision here bodes ill for the company. First, it indicates ULA has been unable to get Vulcan ready on time, forcing the Space Force to look to someone who could.
Second, this is the second time the Pentagon has taken a launch from ULA for these reasons. Increasingly it appears the military is losing patience with ULA’s inability to launch on time. For example, in awarding its most recent set of nine launches, it gave them all to SpaceX, bypassing ULA entirely.
In the past the Space Force tolerated ULA’s delays and high launch cost in order to guarantee the military had more than one launch provider. It now appears it is placing more importance on reliability and cost savings. And as I say, this bodes ill for ULA, which has not done a good job of providing either.
The Space Force yesterday announced it has switched rocket companies for its next GPS satellite launch, taking the launch away from ULA and its Vulcan rocket and giving it to SpaceX.
SpaceX could launch the GPS III Space Vehicle 09 (SV09) within the next few weeks, as the satellite was entering the final stages of pre-flight preparations. As part of the swap, United Launch Alliance (ULA) will instead launch the third of the next generation of Global Positioning System satellites. The GPS III Follow-on (GPS IIIF) SV13 satellite was originally scheduled to launch on a Falcon Heavy, but will now fly on Vulcan.
“SV09 and SV13 were traded between ULA and SpaceX to get capability to orbit as soon as possible, for the same reason as the prior swap, which resulted in the last GPS launch in May 2025,” the spokesperson said in a statement. “The trade results in an overall net cost savings to the government and again demonstrates our sustained commitment to moving at speed to deliver combat-credible capabilities on orbit to meet warfighter needs.”
While at first glance it appears ULA has lost nothing, the military’s decision here bodes ill for the company. First, it indicates ULA has been unable to get Vulcan ready on time, forcing the Space Force to look to someone who could.
Second, this is the second time the Pentagon has taken a launch from ULA for these reasons. Increasingly it appears the military is losing patience with ULA’s inability to launch on time. For example, in awarding its most recent set of nine launches, it gave them all to SpaceX, bypassing ULA entirely.
In the past the Space Force tolerated ULA’s delays and high launch cost in order to guarantee the military had more than one launch provider. It now appears it is placing more importance on reliability and cost savings. And as I say, this bodes ill for ULA, which has not done a good job of providing either.
NASA and Department of Energy agree to place nuclear reactor on Moon by ’30
NASA and Department of Energy have signed an agreement to develop nuclear power stations for NASA lunar base, and are targeting 2030 for placing a nuclear reactor on Moon.
NASA, along with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), announced Tuesday a renewed commitment to their longstanding partnership to support the research and development of a fission surface power system for use on the Moon under the Artemis campaign and future NASA missions to Mars.
A recently signed memorandum of understanding between the agencies solidifies this collaboration and advances President Trump’s vision of American space superiority by deploying nuclear reactors on the Moon and in orbit, including the development of a lunar surface reactor by 2030. This effort ensures the United States leads the world in space exploration and commerce. [emphasis mine]
Wanna bet? I’m laying odds that this joint government effort will end up being delayed and overbudget. In fact, the highlighted phrase suggests this work is already experiencing delays and budget overruns. Why else make a big deal about “a renewed commitment”?
NASA and Department of Energy have signed an agreement to develop nuclear power stations for NASA lunar base, and are targeting 2030 for placing a nuclear reactor on Moon.
NASA, along with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), announced Tuesday a renewed commitment to their longstanding partnership to support the research and development of a fission surface power system for use on the Moon under the Artemis campaign and future NASA missions to Mars.
A recently signed memorandum of understanding between the agencies solidifies this collaboration and advances President Trump’s vision of American space superiority by deploying nuclear reactors on the Moon and in orbit, including the development of a lunar surface reactor by 2030. This effort ensures the United States leads the world in space exploration and commerce. [emphasis mine]
Wanna bet? I’m laying odds that this joint government effort will end up being delayed and overbudget. In fact, the highlighted phrase suggests this work is already experiencing delays and budget overruns. Why else make a big deal about “a renewed commitment”?
HotPlays – Beethoven’s 5th Symphony
An evening pause: It isn’t what you expect. More from this group here.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
This a cappella group performs Beethoven’s 5th Symphony. 👏🏻👏🏻👏🏻
Credit: HotPlaysMusic YT pic.twitter.com/GB6NRQaOvs
— Juanita Broaddrick (@atensnut) December 18, 2025
China launches twice from today different spaceports
China finally entered the 2026 launch race today with two launches from two of its spaceports.
First, it placed a classified remote sensing satellite into orbit, its Long March 6A rocket lifting off from its Taiyuan spaceport in northeast China.
No word on where the rocket’S lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
About an hour later it launched the 18th group of Guowang (also Satnet) satellites into orbit, its Long March 8A lifting off from its coastal Wenchang spaceport in south China.
Though the lower stages of this rocket fell in the ocean, they did so in the territorial waters of the Philippines, forcing its government to issue a warning to its citizens.
Though China’s state-run press provided no information about the number of Guowang satellites launched, all previous launches using the Long March 8A placed nine in orbit. Based on this guess, this internet-of-things constellation now has 137 satellites in orbit out of a planned 13,000.
The 2026 launch race:
5 SpaceX
2 China
China finally entered the 2026 launch race today with two launches from two of its spaceports.
First, it placed a classified remote sensing satellite into orbit, its Long March 6A rocket lifting off from its Taiyuan spaceport in northeast China.
No word on where the rocket’S lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
About an hour later it launched the 18th group of Guowang (also Satnet) satellites into orbit, its Long March 8A lifting off from its coastal Wenchang spaceport in south China.
Though the lower stages of this rocket fell in the ocean, they did so in the territorial waters of the Philippines, forcing its government to issue a warning to its citizens.
Though China’s state-run press provided no information about the number of Guowang satellites launched, all previous launches using the Long March 8A placed nine in orbit. Based on this guess, this internet-of-things constellation now has 137 satellites in orbit out of a planned 13,000.
The 2026 launch race:
5 SpaceX
2 China






