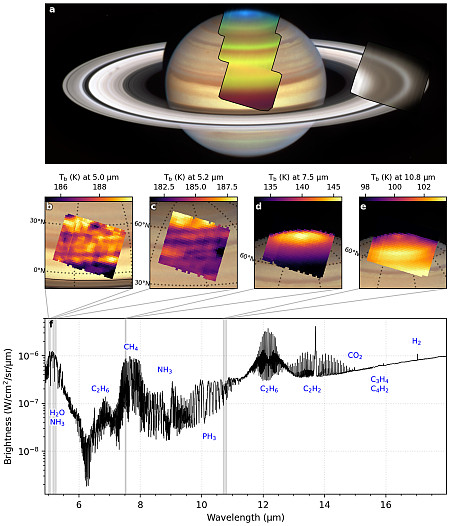
Hubble data shows expansion of supernova remnant
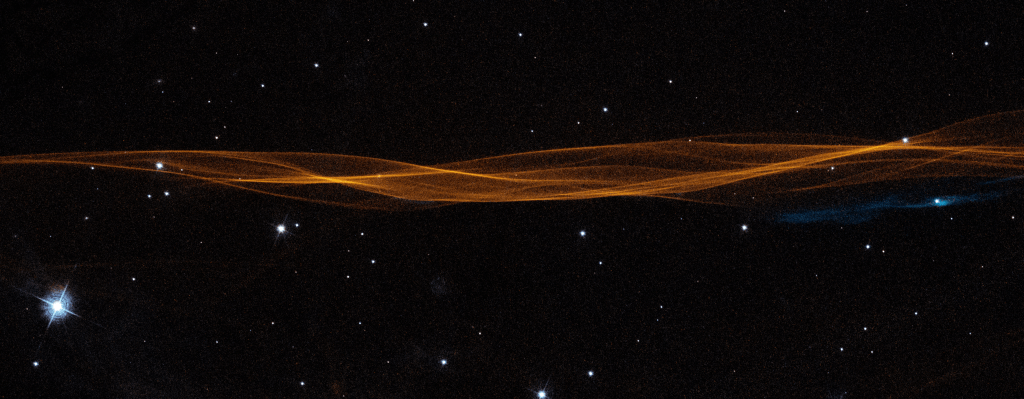
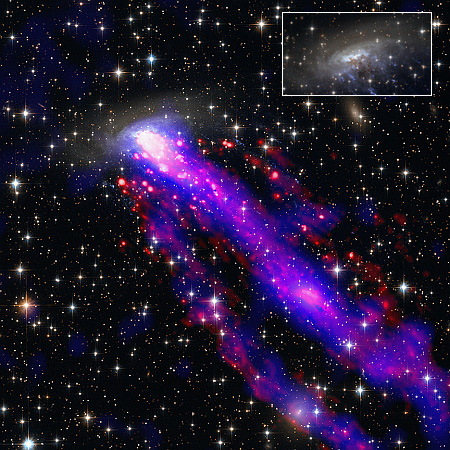
Astronomers have created a four-second long movie using Hubble images collected over twenty years that shows the expansion of one filament in the Cygnus Loop supernova remnant, the explosion of which is thought to have occurred 20,000 years ago.
The picture above is one frame of that movie. The filament is estimated to be two light years in length.
By analyzing the shock’s location, astronomers found that the shock hasn’t slowed down at all in the last 20 years, and is speeding into interstellar space at over half a million miles per hour – fast enough to travel from Earth to the Moon in less than half an hour. While this seems incredibly fast, it’s actually on the slow end for the speed of a supernova shock wave.
Two versions of the movie are at the link, with the longer providing excellent context.

Astronomers have created a four-second long movie using Hubble images collected over twenty years that shows the expansion of one filament in the Cygnus Loop supernova remnant, the explosion of which is thought to have occurred 20,000 years ago.
The picture above is one frame of that movie. The filament is estimated to be two light years in length.
By analyzing the shock’s location, astronomers found that the shock hasn’t slowed down at all in the last 20 years, and is speeding into interstellar space at over half a million miles per hour – fast enough to travel from Earth to the Moon in less than half an hour. While this seems incredibly fast, it’s actually on the slow end for the speed of a supernova shock wave.
Two versions of the movie are at the link, with the longer providing excellent context.