Pentagon getting serious of hauling cargo with Starship
Capitalism in space: In the budget proposal submitted by the Biden administration the Pentagon included a request for $47.9 million to help develop the infrastructure it will need to use SpaceX’s Starship rocket as a method for transporting cargo point-to-point on Earth.
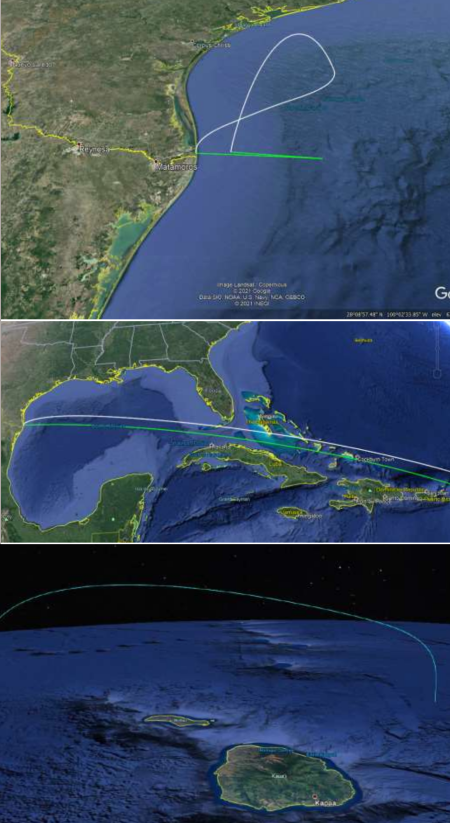
“The Department of the Air Force seeks to leverage the current multi-billion dollar commercial investment to develop the largest rockets ever, and with full reusability to develop and test the capability to leverage a commercial rocket to deliver AF cargo anywhere on the Earth in less than one hour, with a 100-ton capacity,” the document states.
Although this does not refer to Starship by name, this is the only vehicle under development in the world with this kind of capability. The Air Force does not intend to invest directly into the vehicle’s development, the document says. However, it proposes to fund science and technology needed to interface with the Starship vehicle so that the Air Force might leverage its capabilities.
Clearly, some Air Force officials are intrigued by the possibility of launching 100 tons of cargo from the United States and having the ability to land it anywhere in the world about an hour later.
The proposal is calling for a fourfold increase in funding for this work, as the Air Force is already spending slightly less than $10 million this year on this work.
The bottom line is that it appears SpaceX already has at least one real customer for its giant rocket. And if the military is that interested now, it likely means many more private customers are beginning to line up.
Capitalism in space: In the budget proposal submitted by the Biden administration the Pentagon included a request for $47.9 million to help develop the infrastructure it will need to use SpaceX’s Starship rocket as a method for transporting cargo point-to-point on Earth.
“The Department of the Air Force seeks to leverage the current multi-billion dollar commercial investment to develop the largest rockets ever, and with full reusability to develop and test the capability to leverage a commercial rocket to deliver AF cargo anywhere on the Earth in less than one hour, with a 100-ton capacity,” the document states.
Although this does not refer to Starship by name, this is the only vehicle under development in the world with this kind of capability. The Air Force does not intend to invest directly into the vehicle’s development, the document says. However, it proposes to fund science and technology needed to interface with the Starship vehicle so that the Air Force might leverage its capabilities.
Clearly, some Air Force officials are intrigued by the possibility of launching 100 tons of cargo from the United States and having the ability to land it anywhere in the world about an hour later.
The proposal is calling for a fourfold increase in funding for this work, as the Air Force is already spending slightly less than $10 million this year on this work.
The bottom line is that it appears SpaceX already has at least one real customer for its giant rocket. And if the military is that interested now, it likely means many more private customers are beginning to line up.