ISRO completes launch rehearsal for Chandrayaan-3’s launch on July 14th
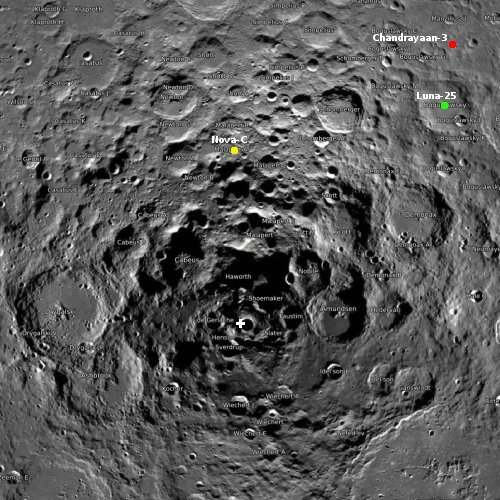
India’s space agency ISRO yesterday completed a full launch dress rehearsal of its Launch Vehicle Mark-3 rocket (LV-M3), in preparation for its July 14, 2023 launch that will put Chandrayaan-3 on its way to the Moon, India’s second attempt to soft land on another world.
More information here. The spacecraft will not reach the Moon until mid-August, and if all goes as planned, the lander Vikram will attempt its landing on August 23rd. If successful, the Pragyan rover will roll off the lander and begin exploration lasting about two weeks, or one lunar day. It is not designed to survive the long lunar night.
The LV-M3 rocket is simply the most powerful variation of India’s Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rocket, capable of putting large payloads into space or sending probes to other planets.
India’s space agency ISRO yesterday completed a full launch dress rehearsal of its Launch Vehicle Mark-3 rocket (LV-M3), in preparation for its July 14, 2023 launch that will put Chandrayaan-3 on its way to the Moon, India’s second attempt to soft land on another world.
More information here. The spacecraft will not reach the Moon until mid-August, and if all goes as planned, the lander Vikram will attempt its landing on August 23rd. If successful, the Pragyan rover will roll off the lander and begin exploration lasting about two weeks, or one lunar day. It is not designed to survive the long lunar night.
The LV-M3 rocket is simply the most powerful variation of India’s Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rocket, capable of putting large payloads into space or sending probes to other planets.