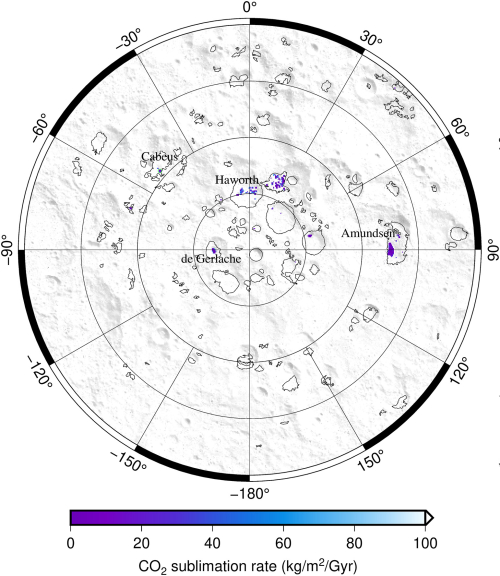
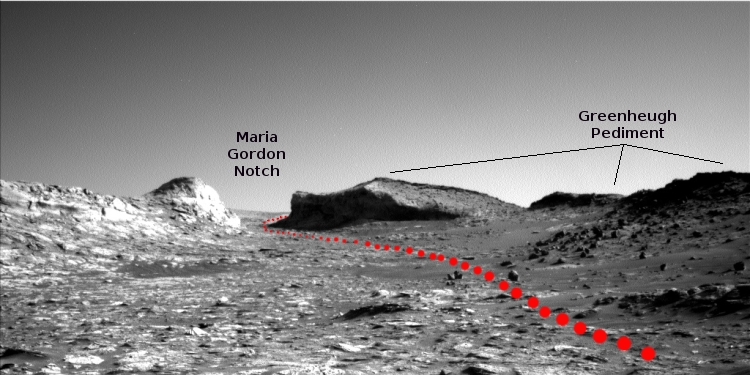
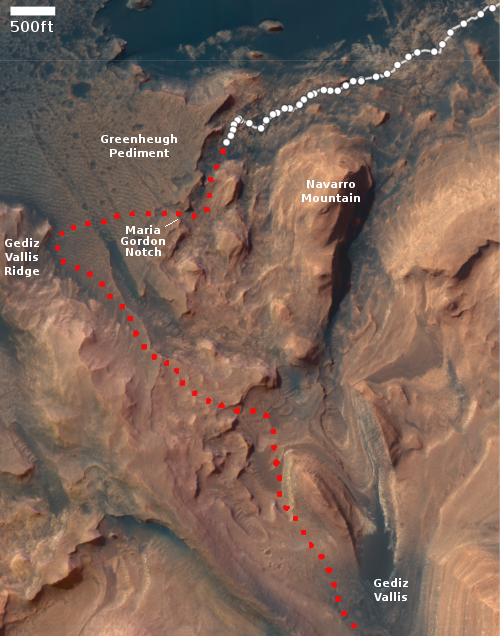
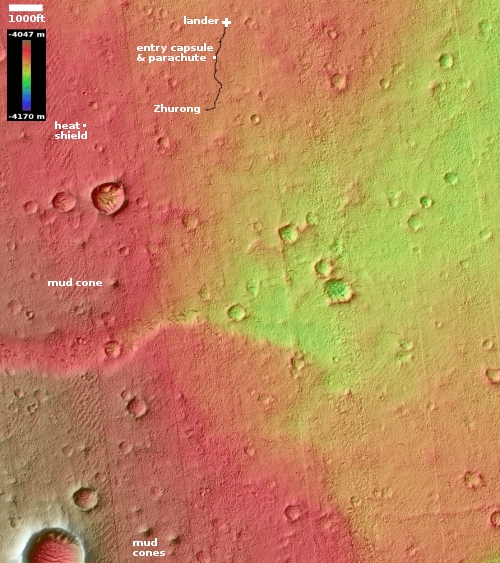
Hubble still in safe mode
NASA released a new but relatively terse update on November 1st describing the status of the Hubble Space Telescope, which has been in safe mode since October 25th.
Hubble’s science instruments issued error codes at 1:46 a.m. EDT Oct. 23, indicating the loss of a specific synchronization message. This message provides timing information the instruments use to correctly respond to data requests and commands. The mission team reset the instruments, resuming science operations the following morning.
At 2:38 a.m. EDT, Oct. 25, the science instruments again issued error codes indicating multiple losses of synchronization messages. As a result, the science instruments autonomously entered safe mode states as programmed.
Mission team members are evaluating spacecraft data and system diagrams to better understand the synchronization issue and how to address it. They also are developing and testing procedures to collect additional data from the spacecraft. These activities are expected to take at least one week.
In other words, the engineers presently do not understand the problem, and are working at pinpointing its cause.
This is not a “glitch”. If used properly that word really refers to something that is akin to a short burp in operations. Hubble has been shut down now for ten days, and will remain so for at least one more week. This is a serious problem that remains unsolved.
NASA released a new but relatively terse update on November 1st describing the status of the Hubble Space Telescope, which has been in safe mode since October 25th.
Hubble’s science instruments issued error codes at 1:46 a.m. EDT Oct. 23, indicating the loss of a specific synchronization message. This message provides timing information the instruments use to correctly respond to data requests and commands. The mission team reset the instruments, resuming science operations the following morning.
At 2:38 a.m. EDT, Oct. 25, the science instruments again issued error codes indicating multiple losses of synchronization messages. As a result, the science instruments autonomously entered safe mode states as programmed.
Mission team members are evaluating spacecraft data and system diagrams to better understand the synchronization issue and how to address it. They also are developing and testing procedures to collect additional data from the spacecraft. These activities are expected to take at least one week.
In other words, the engineers presently do not understand the problem, and are working at pinpointing its cause.
This is not a “glitch”. If used properly that word really refers to something that is akin to a short burp in operations. Hubble has been shut down now for ten days, and will remain so for at least one more week. This is a serious problem that remains unsolved.