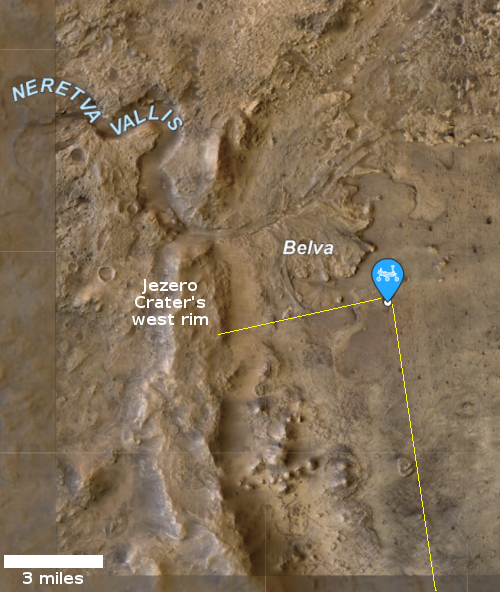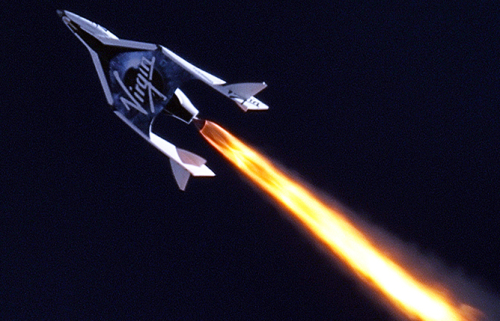
Capitalism in space: Virgin Galactic today announced that it is now planning its first passenger flight of its VSS Unity suborbital spacecraft on July 11th, and that flight will carry Richard Branson as one of its passengers.
[Aleanna Crane, vice president of communications for Virgin Galactic] said that the last flight had been so flawless that the team had decided to test the cabin experience. “Who better to test the full cabin experience than Richard Branson?” she said. “He is flying as a mission specialist, and he has a role like the rest of the crew.” The craft will carry three other Virgin Galactic employees in the cabin seats in addition to the two pilots up front.
…The company plans to broadcast the flight beginning at 9 a.m. Eastern time on July 11. The SpaceShipTwo rocket, named Unity, will be carried under an airplane named White Knight Two to an altitude of 50,000 feet before being dropped. Unity’s engine will then ignite, taking it up to higher than 50 miles. At the top of the arc, passengers will float for about four minutes before the space plane re-enters the atmosphere and glides to a runway landing.
By flying on July 11th, Virgin Galactic — and Branson — will beat Blue Origin — and Jeff Bezos — by nine days in accomplishing the first passenger suborbital flight. Blue Origin’s July 20th flight however will be carrying the first paying customer, while Virgin Galactic’s flight will not.
For Branson making this flight ahead of Bezos is almost essential. He has been promising this flight now for more than fourteen years, always declaring it was only months from happening. It never did, and the years dragged on and on with no achievement or Virgin Galactic suborbital tourist flights. To get beaten now would be quite embarrassing, to put it mildly. Yet, to only win this race by mere days remains embarrassing as well, since Virgin Galactic was supposed to do this more than a decade ago and did not.
Regardless, both flights are stunts intended to garner publicity and encourage ticket sales for future suborbital flights. And while there appears to be some market interest in these suborbital flights, both are mere pipsqueaks to the coming orbital tourist flights by SpaceX, Axiom, and the Russians, with Boeing to follow shortly thereafter.