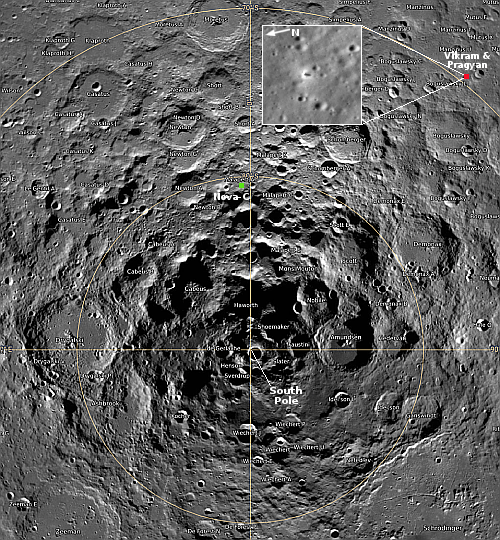
Repeating moonquakes on Moon found to be caused by remaining sections of Apollo 17’s LM
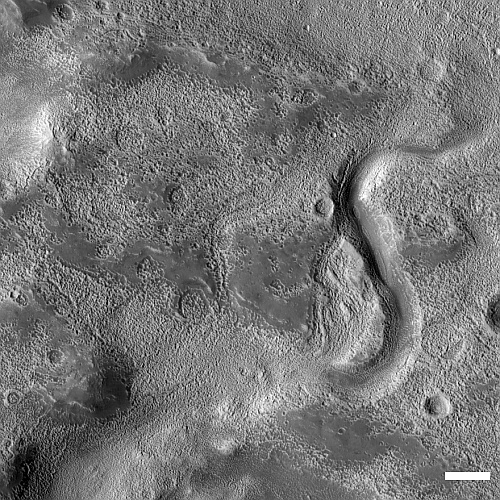
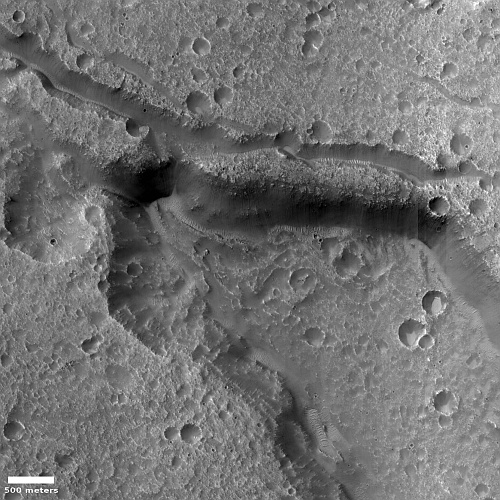
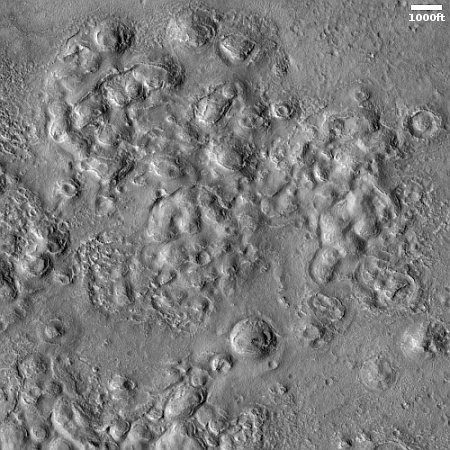
Scientists reviewing the archive seismic data produced by the seismometers placed on the Moon by the Apollo missions have discovered that repeating small moonquakes in that data were actually caused by base of Apollo 17’s Lunar Module (LM) that provided a launchpad for the part of the LM that lifted the astronauts off the Moon.
Triangulating the origin of the mystery quakes, researchers surprisingly realized they came from the Apollo 17 lunar lander base, which expands and vibrates each morning as it becomes heated by the sun.
“Every lunar morning when the sun hits the lander, it starts popping off,” Allen Husker, a Caltech research professor of geophysics who worked on the project, said in a statement. “Every five to six minutes another one, over a period of five to seven Earth hours. They were incredibly regular and repeating.”
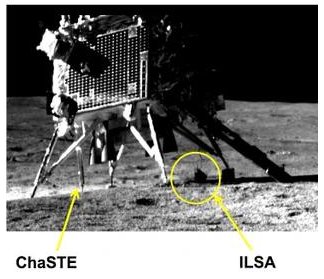
That the extreme range of temperatures experienced by the LM could cause detectable quakes as the LM base expanded suggests strongly how difficult it is for a spacecraft to survive the lunar night lasting 14 Earth days. For all we know, that base has now literally fallen apart due to these stresses. This in turn suggests it is highly unlikely that India’s Pragyan rover will come back to life when the sun rises on September 22, 2023.
Scientists reviewing the archive seismic data produced by the seismometers placed on the Moon by the Apollo missions have discovered that repeating small moonquakes in that data were actually caused by base of Apollo 17’s Lunar Module (LM) that provided a launchpad for the part of the LM that lifted the astronauts off the Moon.
Triangulating the origin of the mystery quakes, researchers surprisingly realized they came from the Apollo 17 lunar lander base, which expands and vibrates each morning as it becomes heated by the sun.
“Every lunar morning when the sun hits the lander, it starts popping off,” Allen Husker, a Caltech research professor of geophysics who worked on the project, said in a statement. “Every five to six minutes another one, over a period of five to seven Earth hours. They were incredibly regular and repeating.”
That the extreme range of temperatures experienced by the LM could cause detectable quakes as the LM base expanded suggests strongly how difficult it is for a spacecraft to survive the lunar night lasting 14 Earth days. For all we know, that base has now literally fallen apart due to these stresses. This in turn suggests it is highly unlikely that India’s Pragyan rover will come back to life when the sun rises on September 22, 2023.