Click for original image.
UPDATE: Launch scrubbed. To get to new links for watching the live stream in the second launch attempt, now scheduled for April 20, 2023, go here.
Original post:
————-
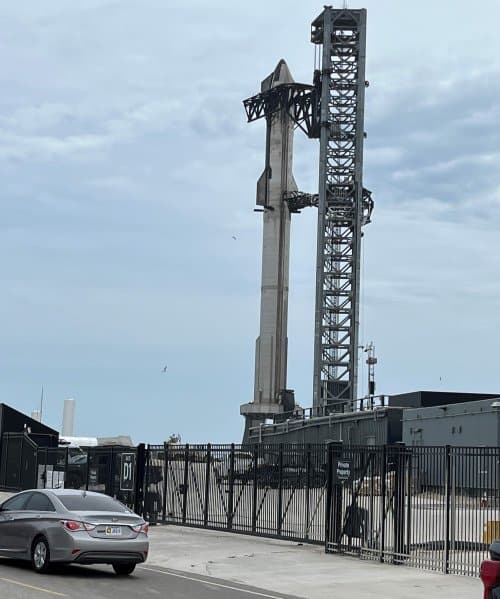
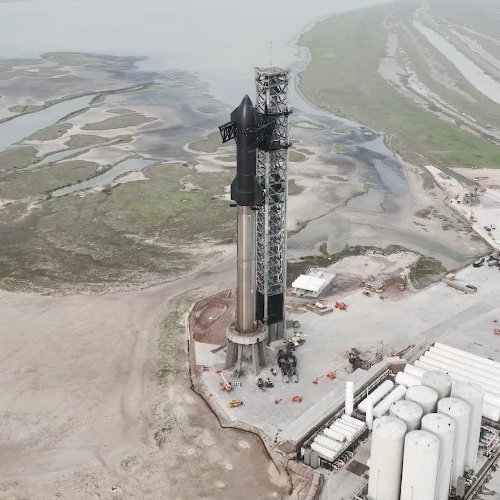
The first orbital test launch of SpaceX’s massive Superheavy first stage with its orbital Starship spacecraft stacked on top is now scheduled for a launch in a two-and-a-half hour long launch window beginning at 8 am (Central) on Monday, April 17, 2023.
I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream of that launch below, which will begin around 7 am (Central). You can also see an independent 24/7 live stream from LabPadre, showing the launchpad from many different angles and available here. NasaSpaceFlight.com also has a 24/7 live stream showing multiple angles here. Though both of these independent live streams provide alternative view angles of the launch, both will rely on SpaceX’s main live stream, embedded below, for actual updates on the countdown status.
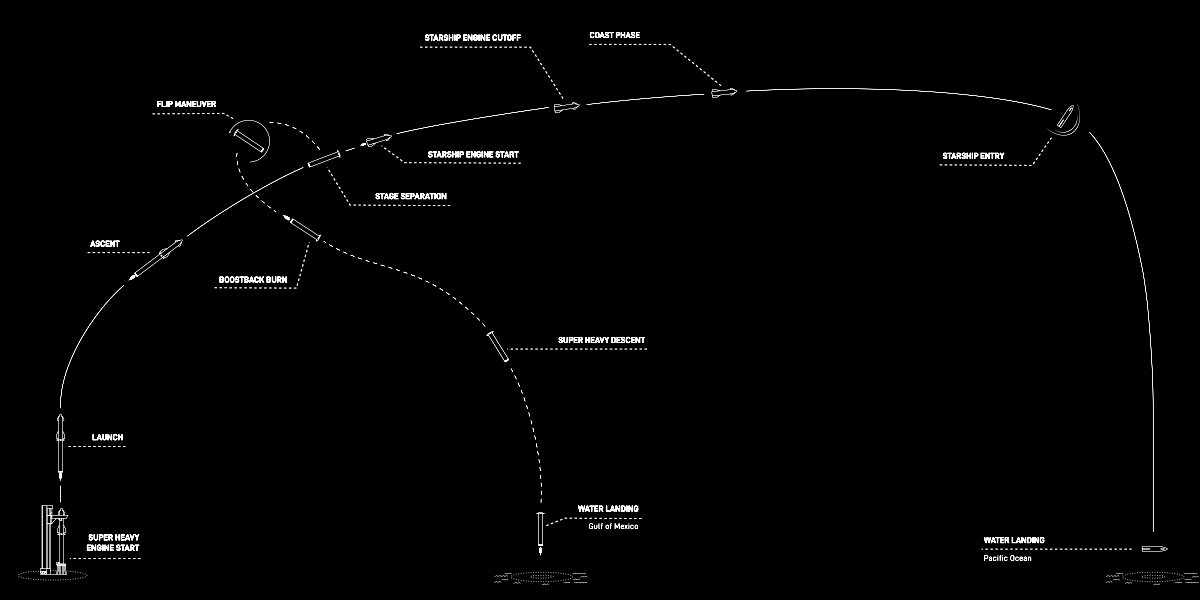
If the launch is scrubbed on April 17th, SpacX has backup dates on April 18th and 19th. The flight plan and time line is shown in the graphic above.
The monumental significance of this rocket cannot be overstated. It is the most powerful rocket ever built, capable of putting more mass into orbit than either the Saturn-5 or NASA’s new SLS rocket.
It took less than seven years from concept to launch. Compare that to SLS, which was proposed in 2004 and only launched last year, two decades later.
It has been been entirely developed with private funds. Though SpaceX does have a NASA contract for building a Starship lunar lander, little of that contract’s funds have yet been distributed to the company. From private funds SpaceX has raised about $10 billion, most of which has been channeled into this rocket’s development, with a small unknown amount used to develop Starlink. Compare that once again to SLS, which has cost about $60 billion to build.
Finally, it is being designed to be completely reusable, thus reducing the cost exponentially for putting large 100-ton payloads into orbit. If successful, Starship/Superheavy will very quickly make the human exploration and colonization of the solar system possible.
And it will do so not as a government project that is part of a government program, but as a private sector product, conceived by individual Americans freely following their dreams, and developed for profit, quickly and efficiently.
Let freedom ring!
» Read more





