The hits keep coming! A report [pdf] issued today by NASA’s Inspector General strongly criticizes the construction by NASA of two SLS test stands at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
This is going to sound familiar, but the report found that the construction of both test stands took much longer than scheduled and went significantly over budget, almost doubling. Worse, this was caused by some basic managerial decisions that should not have happened. From the report’s conclusion:
To meet its ambitious schedule of an initial SLS launch in December 2017, NASA designed and initiated construction on Test Stands 4693 and 4697 based on preliminary testing specifications and before test stand requirements and capabilities were fully understood. As a result, the cost of the stands increased by $35.5 million from an original estimated cost of $40.5 million. …Finally, NASA failed to establish adequate funding reserves to cover anticipated contract and requirement changes or adequately document consideration of alternative sites for the testing. In short, rushing the decision regarding the test stands to support a December 2017 first flight raised the cost of constructing the stands by tens of millions of dollars.[emphasis mine]
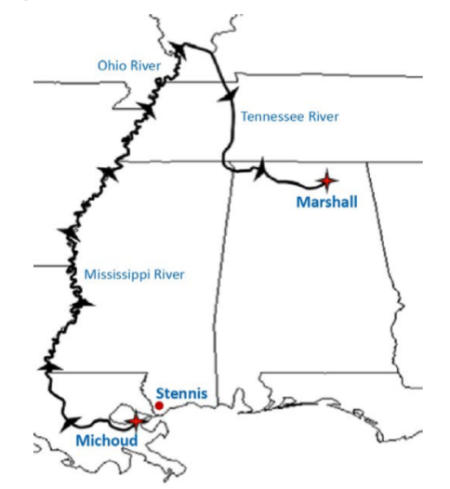
The report strongly criticized the agency for deciding to build the stands at the Marshall Space Flight Center. NASA could have chosen to build them at the Stennis Space Center in Mississippi, but did not consider that location in its decision.
Similarly, of three possible construction sites – one at Stennis and two at Marshall – NASA officially considered only the two Marshall locations for testing the structural integrity of the SLS’s liquid hydrogen tank. Although teams from both Marshall and Stennis proposed designs for possible test stands, only the Marshall designs were reviewed and listed as possible alternatives at the final decision review. [emphasis mine]
The map on the right is figure 6 on page 16 of the IG report, and shows the absurdity of choosing Marshall over Stennis. As the report continued,
As a result, we question whether such costs as transporting the tanks to Marshall from Michoud were adequately considered as part of the Agency’s analysis. This approximately 1,240-mile trip will entail shipment by barge along the Mississippi River, the Ohio River, and finally the Tennessee River; take about 2 weeks; and cost approximately $500,000 per tank (see Figure 6 below). Because each tank will need to be transported separately and the barge will need to return to Michoud between loads, the total transportation time for both tanks is 6 weeks. In contrast, transporting a tank from Michoud to Stennis would take less than one week and cost approximately $200,000.
You can wonder whether the influence of porkmaster Senator Richard Shelby (R-Alabama) had anything to do with NASA’s decision to favor Marshall but I personally have no doubt.
Overall, this IG report, as well as yesterday’s GAO audit, show us a government agency that has no idea how do to things in an efficient and expedient manner.
The timing of the release of these reports is interesting. They describe bad managerial decisions made during the Obama administration. Yet, during that administration it had been my impression that audits by GAO and NASA’s IG tended to pussy-foot around NASA’s problems. Their reports noted delays and cost issues, but always couched their criticisms with care. Now that Obama has left office, however, it appears they feel free to state their conclusions more bluntly, which is that none of the upper management in the Obama administration, either at NASA or at the White House, was ever willing to take a hard look at how NASA was doing things.
However, this isn’t just the Obama administration. These kinds of bad managerial decisions in the federal government have been going on now for decades. This has been a clearly bi-partisan failure, by presidents from both parties in Washington. Based on these reports, a lot of heads should roll, throughout the executive branch. The question remains whether there is anyone in Washington, including the present president, willing to do this.
Moreover, the problems are not just in the executive branch. Elected officials, such as Shelby, have been micromanaging NASA’s effort foolishly now for decades. Worse, their micromanagement has done little to serve the needs of the nation, and in fact, has done us great harm. For example, for the past decade Congress has squeezed commercial space in order to throw more money to SLS, and as a result the country’s inability to launch its own astronauts into space has stretched out far longer than necessary, the longest ever since the dawn of the space age.
The last few elections have suggested that the public recognizes this, and wants Congress to change. Unfortunately, I see little indication so far that Congress recognizes this.

