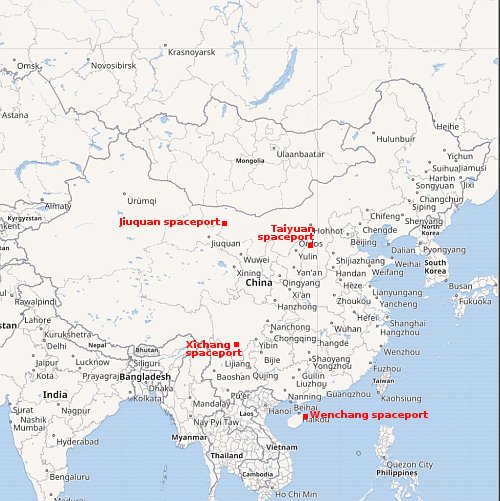
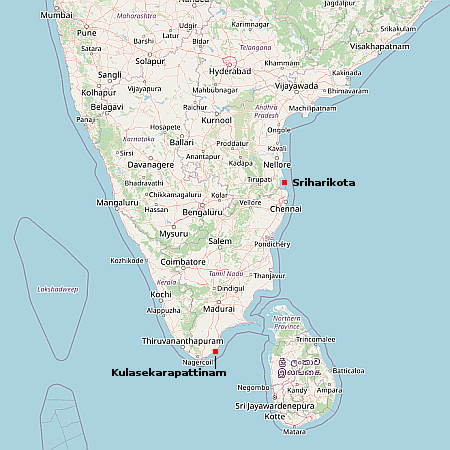
Intuitive Machines sets mid-November launch date for its Nova-C lunar lander
Intuitive Machines announced yesterday that the launch of its lunar lander, Nova-C, is now targeting a November 15-20, 2023 window, lifting off on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
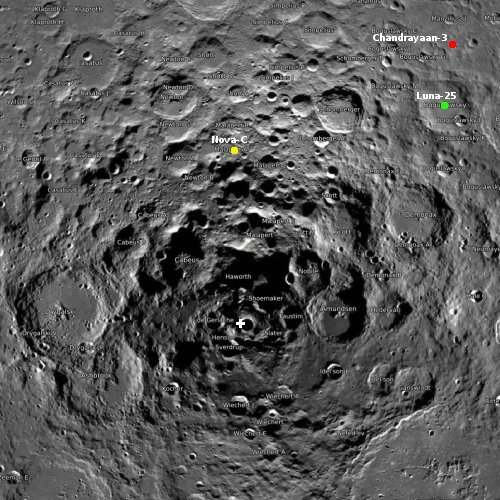
The yellow dot on the map to the right indicates the landing site, Malapert A, in the southern latitudes of the Moon. The white cross indicates the south pole.
The lander had originally planned to launch in 2021, but delays in construction pushed the launch back two years. A second company, Astrobotics, has its own lander, Peregrine, that though also delayed two years, has been ready to launch since early this year. It won’t launch until the end of this year at the earliest, however, due to delays in readying its rocket, ULA’s Vulcan on its first flight.
Both India’s Chandrayaan-3 and Russia’s Luna-3 are right now on their way to the Moon, with each planning a landing next week.
Intuitive Machines announced yesterday that the launch of its lunar lander, Nova-C, is now targeting a November 15-20, 2023 window, lifting off on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
The yellow dot on the map to the right indicates the landing site, Malapert A, in the southern latitudes of the Moon. The white cross indicates the south pole.
The lander had originally planned to launch in 2021, but delays in construction pushed the launch back two years. A second company, Astrobotics, has its own lander, Peregrine, that though also delayed two years, has been ready to launch since early this year. It won’t launch until the end of this year at the earliest, however, due to delays in readying its rocket, ULA’s Vulcan on its first flight.
Both India’s Chandrayaan-3 and Russia’s Luna-3 are right now on their way to the Moon, with each planning a landing next week.