Russia and India agree to orbit their space stations in the same inclination, the same as ISS
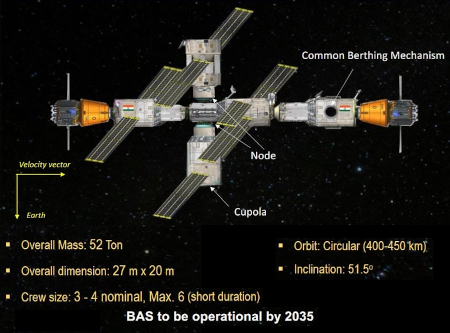
India’s Bharatiya Antariksh Station as outlined in 2024.
Click for original image.
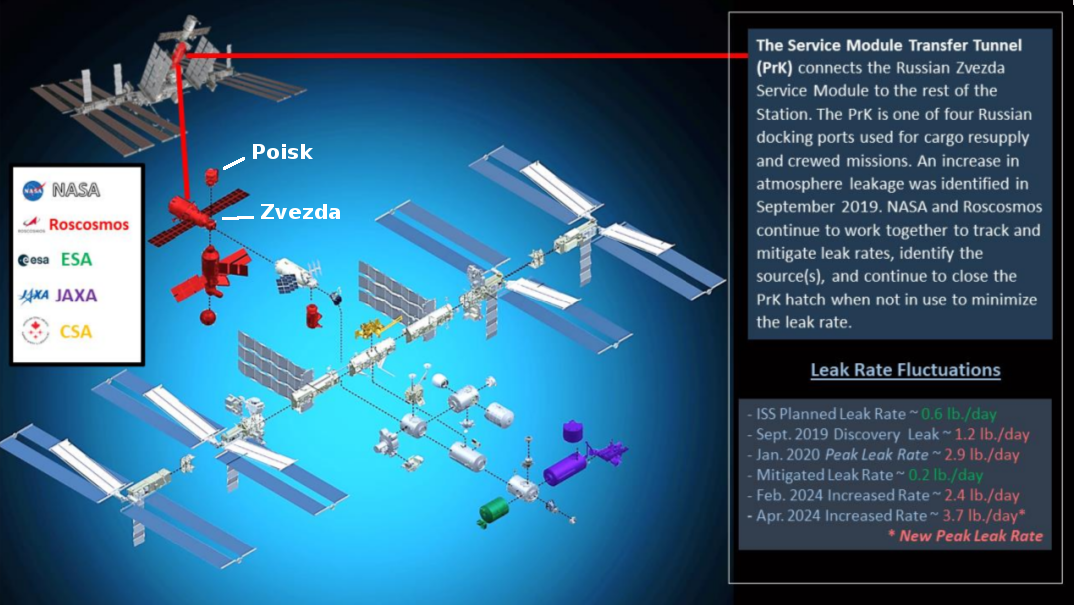
According to statements made by Roscosmos head Dmitry Bakanov at a conference in New Delhi this week, Russia and India have agreed to orbit their planned new space stations in the same inclination as ISS, 51.6 degrees, and coordinate their operations at both stations.
By choosing the same orbital geometry for ROS [Russian Orbital Station] and BAS [Bharatiya Antariksh Station], Moscow and New Delhi are effectively planning a continuous “replacement belt” in low Earth orbit. After the ISS is retired, crewed spacecraft launched from Russia and India would still be able to reach a major laboratory complex without radically changing launch trajectories or infrastructure, and—crucially—could, in principle, travel between the two stations with relatively modest maneuvers compared with a full plane-change.
Bakanov’s New Delhi comments build on a broader Roscosmos–ISRO understanding that the two stations should be able to support cross-visits, resource sharing and coordinated operations once both are flying.
This high inclination is required because spacecraft launching from Russia’s high latitudes can’t reach lower inclinations practically. India could put its station at a lower inclination (being at a lower latitude), but if this story is true, it apparently has decided there are advantages using an orbit that will allow cross-missions with Russia, including launches from Russia.
India plans to launch the first module of its station in 2028, and have the entire station operational by 2035. Russia says it will launch is station’s first module by 2027, with full operations beginning by 2030. While both schedules are likely to see delays, we should expect India to get its station built, while Russia will likely struggle to launch even one module.
In fact, I suspect this deal is Russia’s effort to find some partner that can carry it in the future, when its own station gets delayed.
» Read more

India’s Bharatiya Antariksh Station as outlined in 2024.
Click for original image.
According to statements made by Roscosmos head Dmitry Bakanov at a conference in New Delhi this week, Russia and India have agreed to orbit their planned new space stations in the same inclination as ISS, 51.6 degrees, and coordinate their operations at both stations.
By choosing the same orbital geometry for ROS [Russian Orbital Station] and BAS [Bharatiya Antariksh Station], Moscow and New Delhi are effectively planning a continuous “replacement belt” in low Earth orbit. After the ISS is retired, crewed spacecraft launched from Russia and India would still be able to reach a major laboratory complex without radically changing launch trajectories or infrastructure, and—crucially—could, in principle, travel between the two stations with relatively modest maneuvers compared with a full plane-change.
Bakanov’s New Delhi comments build on a broader Roscosmos–ISRO understanding that the two stations should be able to support cross-visits, resource sharing and coordinated operations once both are flying.
This high inclination is required because spacecraft launching from Russia’s high latitudes can’t reach lower inclinations practically. India could put its station at a lower inclination (being at a lower latitude), but if this story is true, it apparently has decided there are advantages using an orbit that will allow cross-missions with Russia, including launches from Russia.
India plans to launch the first module of its station in 2028, and have the entire station operational by 2035. Russia says it will launch is station’s first module by 2027, with full operations beginning by 2030. While both schedules are likely to see delays, we should expect India to get its station built, while Russia will likely struggle to launch even one module.
In fact, I suspect this deal is Russia’s effort to find some partner that can carry it in the future, when its own station gets delayed.
» Read more