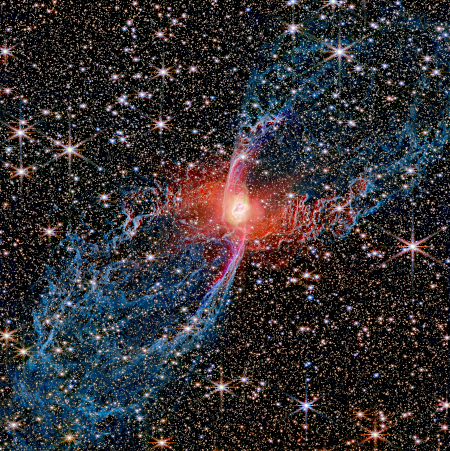
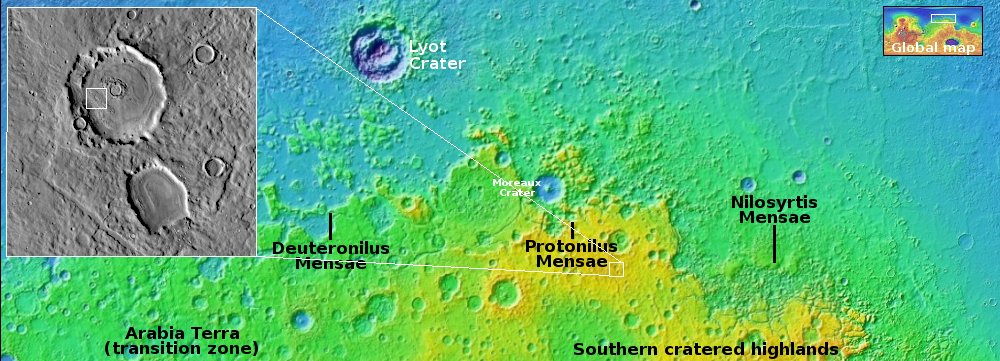
The earliest observations ever of a supernova exploding suggest the blast was bi-polar
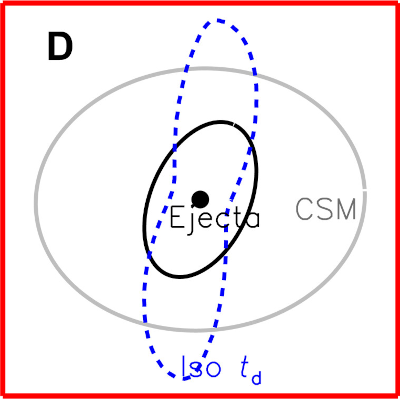
Click for full graphic. CSM stands for the
circumstellar matter that surrounded the star
prior to eruption.
Using the Very Large Telescope in Chile, astronomers were able to observe a supernova in its very earliest moments after eruption, the earliest yet, and determined the eruption did not flow outward in all directions, but appeared to be bi-polar, as indicated by the cartoon to the right.
To capture the snapshot of the April 2024 supernova, astronomers used the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile, which was able to look at the polarization, or orientation, of the supernova’s light. Using a technique called spectropolarimetry, the researchers used the light’s polarization to re-create the explosion’s shape in its first moments. Their results showed that the light emanated not uniformly, like the light from a typical star, but elongated, shaped like an olive.
You can read their paper here. The cartoon comes from Figure 4, and is their “most plausible” interpretation of the data.
This bi-polar shape suggests that in the initial stages of the eruption the material shot out the star’s poles, as seen routinely in planetary nebulae as well as other eruptive stars like Eta Carina. The data also suggests the initial explosion was shaped by the circumstellar material surrounding the star. Such material tends to concentrate at a star’s ecliptic, like our solar system, With less material at the poles, the initial blast favored those directions.
Theorists will now use this data point to better refine the models that attempt to explain how supernovae explode.

Click for full graphic. CSM stands for the
circumstellar matter that surrounded the star
prior to eruption.
Using the Very Large Telescope in Chile, astronomers were able to observe a supernova in its very earliest moments after eruption, the earliest yet, and determined the eruption did not flow outward in all directions, but appeared to be bi-polar, as indicated by the cartoon to the right.
To capture the snapshot of the April 2024 supernova, astronomers used the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile, which was able to look at the polarization, or orientation, of the supernova’s light. Using a technique called spectropolarimetry, the researchers used the light’s polarization to re-create the explosion’s shape in its first moments. Their results showed that the light emanated not uniformly, like the light from a typical star, but elongated, shaped like an olive.
You can read their paper here. The cartoon comes from Figure 4, and is their “most plausible” interpretation of the data.
This bi-polar shape suggests that in the initial stages of the eruption the material shot out the star’s poles, as seen routinely in planetary nebulae as well as other eruptive stars like Eta Carina. The data also suggests the initial explosion was shaped by the circumstellar material surrounding the star. Such material tends to concentrate at a star’s ecliptic, like our solar system, With less material at the poles, the initial blast favored those directions.
Theorists will now use this data point to better refine the models that attempt to explain how supernovae explode.