For only 7th time, searchers find meteorite immediately after fall
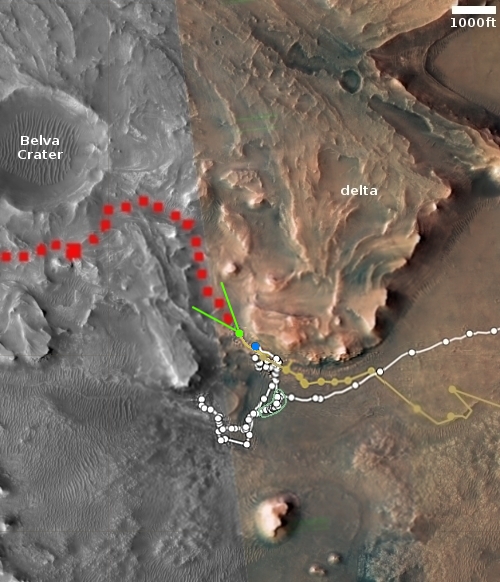
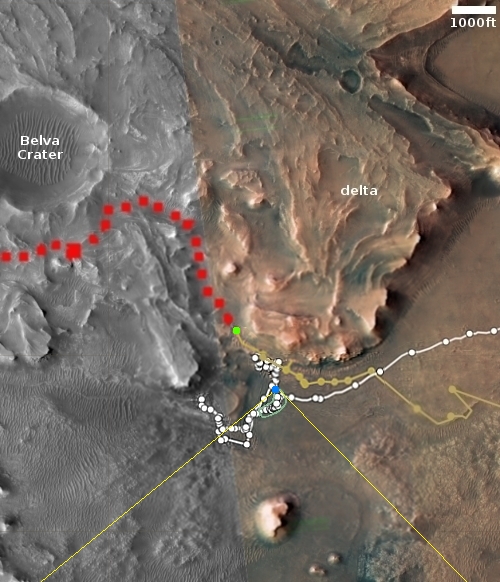
For only 7th time, searchers on February 15th found a fragment of a meteorite that had only fallen to Earth three days before, and was furthermore only discovered mere hours before it entered the Earth’s atmosphere.
From the tweet of the discoverers:
FRIPON/Vigie-Ciel finds a fragment of asteroid 2023CX1 in Seine Maritime!!! The discovery was made by Loïs Leblanc, an 18-year-old student, part of the field research team.
Vigie-Ciel (“Sky Watchers”) and FRIPON are a volunteer project that searches for meteorites. The asteroid itself was discovered by Hungarian astronomer Krisztián Sárneczky while doing routine survey scan for near Earth asteroids.
The find was the second time Sárneczky has spotted an asteroid just hours before it broke apart in Earth’s atmosphere as a fireball, following an incredible find in March 2022.
By finding meteorites this quickly after arrival scientists get a more pristine sample, since the asteroid has not been exposed to the Earth’s environment for any extended length of time.
For only 7th time, searchers on February 15th found a fragment of a meteorite that had only fallen to Earth three days before, and was furthermore only discovered mere hours before it entered the Earth’s atmosphere.
From the tweet of the discoverers:
FRIPON/Vigie-Ciel finds a fragment of asteroid 2023CX1 in Seine Maritime!!! The discovery was made by Loïs Leblanc, an 18-year-old student, part of the field research team.
Vigie-Ciel (“Sky Watchers”) and FRIPON are a volunteer project that searches for meteorites. The asteroid itself was discovered by Hungarian astronomer Krisztián Sárneczky while doing routine survey scan for near Earth asteroids.
The find was the second time Sárneczky has spotted an asteroid just hours before it broke apart in Earth’s atmosphere as a fireball, following an incredible find in March 2022.
By finding meteorites this quickly after arrival scientists get a more pristine sample, since the asteroid has not been exposed to the Earth’s environment for any extended length of time.