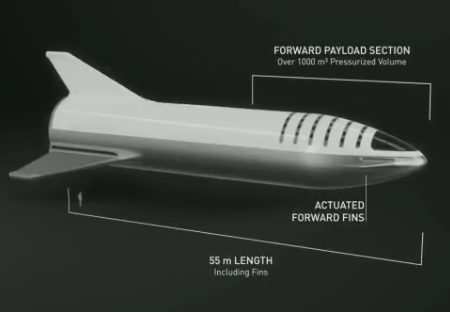
SpaceX turned down government money to build Falcon Heavy
Capitalism in space: In a presentation yesterday in Europe, one of SpaceX’s executives, Hans Koenigsmann, made it clear that SpaceX paid entirely for the development of Falcon Heavy, and in fact turned down an offer of government funding.
According to the SpaceX executive, the company was actually approached by “the government”, with the unknown agency or agencies stating – in Hans’ words – that they wanted to be a part of the rocket’s development. According to Hans, SpaceX responded in an extremely unorthodox fashion: “we said, ‘Nope! We just wanna build it, you can buy it when it’s ready and we’ll charge you for the service.’” He noted in the next sentence that funding was the primary lever on the table: “It’s a great position to do this, you gotta find the money, you gotta know people that have money and are willing to invest in your company, and [SpaceX has] been lucky enough to know some of those people.”
In other words, when given an opportunity to either rely on government funding or some other source of capital for a given R&D project, SpaceX – or at least Hans Koenigsmann, VP of Reliability – would apparently recommend the latter option in almost all cases. Again, without being prompted, he elaborated on his feelings about funding sources, culminating in a statement that is simply profound coming from an executive in the aerospace industry. The following quote is unabridged and straight from Hans himself:
“You need to [try to not] get money from the government, otherwise the government will tell you what to build and how to build it… they will tell you how to build this and that’s just not always – I mean for some things it’s the best to do, but in others it’s actually not.”
In other words, don’t let the government run your business. Use the government as an eventual customer, but build your product in a way that will not make them your only customer.
You can watch his entire presentation in the embedded video below the fold. Koenigsmann also noted that this Sunday’s first attempt to land a first stage at Vandenberg will likely produce a spectacular show for anyone who watches.
» Read more
Capitalism in space: In a presentation yesterday in Europe, one of SpaceX’s executives, Hans Koenigsmann, made it clear that SpaceX paid entirely for the development of Falcon Heavy, and in fact turned down an offer of government funding.
According to the SpaceX executive, the company was actually approached by “the government”, with the unknown agency or agencies stating – in Hans’ words – that they wanted to be a part of the rocket’s development. According to Hans, SpaceX responded in an extremely unorthodox fashion: “we said, ‘Nope! We just wanna build it, you can buy it when it’s ready and we’ll charge you for the service.’” He noted in the next sentence that funding was the primary lever on the table: “It’s a great position to do this, you gotta find the money, you gotta know people that have money and are willing to invest in your company, and [SpaceX has] been lucky enough to know some of those people.”
In other words, when given an opportunity to either rely on government funding or some other source of capital for a given R&D project, SpaceX – or at least Hans Koenigsmann, VP of Reliability – would apparently recommend the latter option in almost all cases. Again, without being prompted, he elaborated on his feelings about funding sources, culminating in a statement that is simply profound coming from an executive in the aerospace industry. The following quote is unabridged and straight from Hans himself:
“You need to [try to not] get money from the government, otherwise the government will tell you what to build and how to build it… they will tell you how to build this and that’s just not always – I mean for some things it’s the best to do, but in others it’s actually not.”
In other words, don’t let the government run your business. Use the government as an eventual customer, but build your product in a way that will not make them your only customer.
You can watch his entire presentation in the embedded video below the fold. Koenigsmann also noted that this Sunday’s first attempt to land a first stage at Vandenberg will likely produce a spectacular show for anyone who watches.
» Read more