Modern Journalism: Retyping press releases
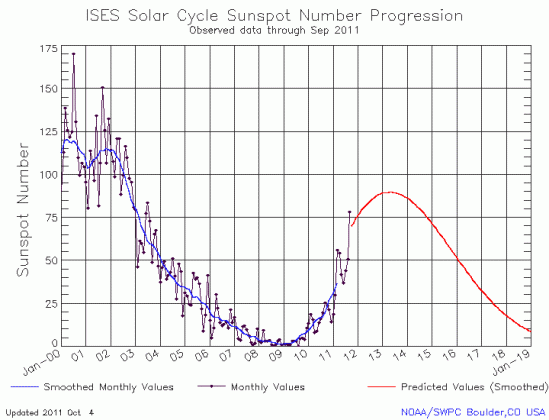
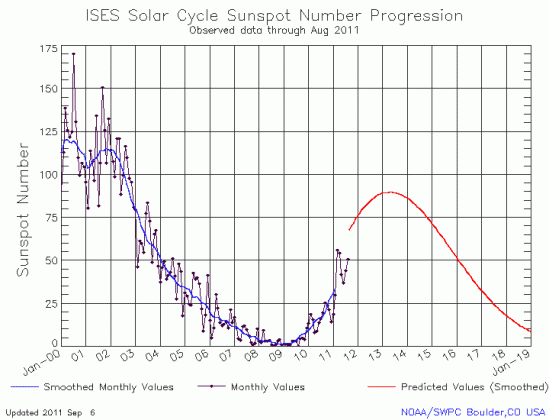
This post is really about the monthly NOAA update of the solar cycle, but before I do that, I must note some really bad science journalism in connection with that solar minimum.
This week NASA released a poorly written press release describing how the Sun’s magnetic field flips whenever it goes through solar maximum, the period when sunspot activity reaches its maximum. The article gave the incorrect impression that this “flip” will be some grand singular and spectacular event and when it happens the consequences to Earth could be significant. Then it buried this most important little detail to the article’s final paragraphs:
» Read more