India targets Nov 2020 for new lunar lander mission
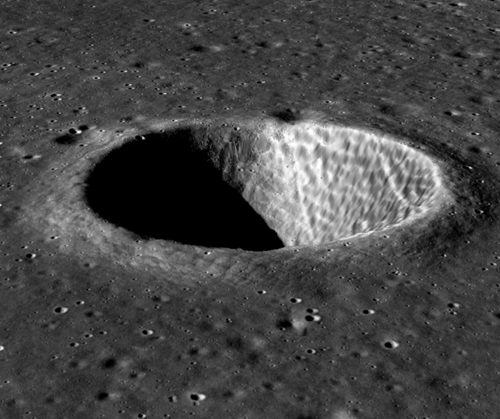
The new colonial movement: Sources inside India’s space agency ISRO yesterday revealed that they are now working to build and fly another lunar lander/rover, dubbed Chandrayaan-3, with a target launch date of November 2020, only one year from now.
Isro has formed multiple committees — an overall panel and three sub-committees — and held at least four high-level meetings since October. The new mission will include only a lander and rover, as the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter is functioning well. On Tuesday, the overview committee met with the agenda of reviewing the configuration of Chandrayaan-3. It also looked into the recommendations of various sub-committees on propulsion, sensors, overall engineering, navigation and guidance.
The Chandrayaan-2 orbiter had provided the propulsion capabilities to get the Vikram lander (with rover) to lunar orbit earlier this year, only to have the lander fail shortly before touchdown. To do this new mission without an orbiter will require adding a propulsion unit to the rover/lander. They are also looking at strengthening the lander’s legs to better resist a high velocity landing.
Kudos to ISRO for moving so quickly. There is no reason a replacement lander/rover should take years to build. They already know what to do, they need only do it again, with upgrades designed to avoid the failure in September.
The new colonial movement: Sources inside India’s space agency ISRO yesterday revealed that they are now working to build and fly another lunar lander/rover, dubbed Chandrayaan-3, with a target launch date of November 2020, only one year from now.
Isro has formed multiple committees — an overall panel and three sub-committees — and held at least four high-level meetings since October. The new mission will include only a lander and rover, as the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter is functioning well. On Tuesday, the overview committee met with the agenda of reviewing the configuration of Chandrayaan-3. It also looked into the recommendations of various sub-committees on propulsion, sensors, overall engineering, navigation and guidance.
The Chandrayaan-2 orbiter had provided the propulsion capabilities to get the Vikram lander (with rover) to lunar orbit earlier this year, only to have the lander fail shortly before touchdown. To do this new mission without an orbiter will require adding a propulsion unit to the rover/lander. They are also looking at strengthening the lander’s legs to better resist a high velocity landing.
Kudos to ISRO for moving so quickly. There is no reason a replacement lander/rover should take years to build. They already know what to do, they need only do it again, with upgrades designed to avoid the failure in September.