The precipitous decline in sunspots continues. While November 2017 remains the most inactive month for sunspots since the middle of 2009, December was a very close second.
Below is my annotated version of NOAA’s monthly update of the solar cycle, covering sunspot activity for December, which they posted on Sunday.
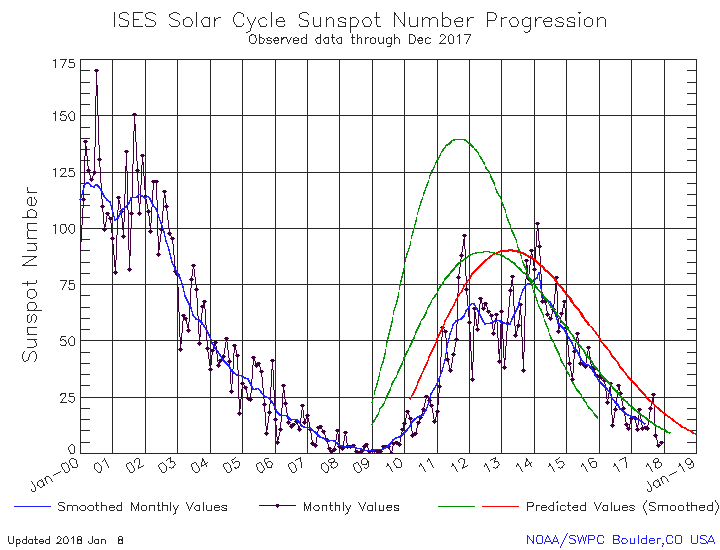
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.
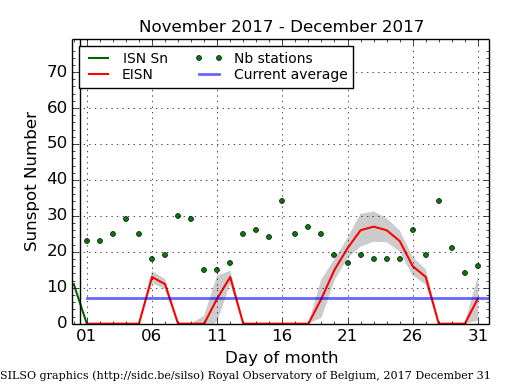
The graph on the right, produced by SILSO (Sunspot Index and Long-term Solar Observations) on December 31, shows only 14 days during the month when there were sunspots active on the Sun’s visible hemisphere. This is only four more days then seen in November. And like November, the few sunspots were weak, resulting in tiny sunspot numbers total.
The first graph above illustrates how weak this on-going sunspot cycle has been. While the curve most closely matches the 2007 weak prediction of half the solar science community, it has one very notable difference. The actual ramp up to solar maximum started two years later than predicted, even though it appears to be ending when that prediction expected. The result is a very very short solar cycle, something that has historically always been associated with very active and intense sunspot activity. Instead, this short cycle has only seen weak activity, generally below all the predictions.
All signs continue to point to an early arrival of solar minimum. They also suggest that the next maximum will also be weak, and might even not come at all, as some solar scientists have proposed. Instead, we might be heading toward another Grand Minimum, with no significant sunspots for decades.
So, is it cold outside right now? Well, that’s weather, not climate. Nonetheless, there is a lot of circumstantial evidence that few sunspots correspond with a cooling climate on Earth. (The last grand minimum occurred in the 1600s, during what was called the Little Ice Age.) There is even some preliminary evidence to suggest that cosmic rays might be a cause. (Watch the video at the end of this link.).
Whether any of this will happen however remains unknown. We will need to wait to find out.


