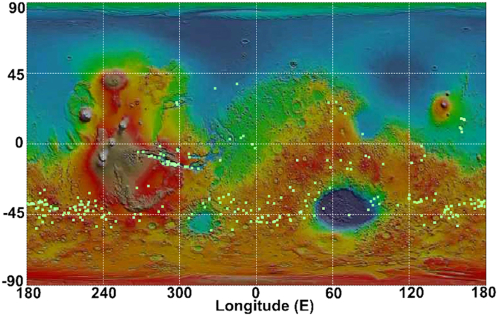
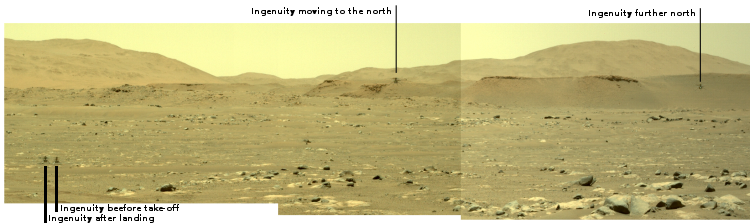
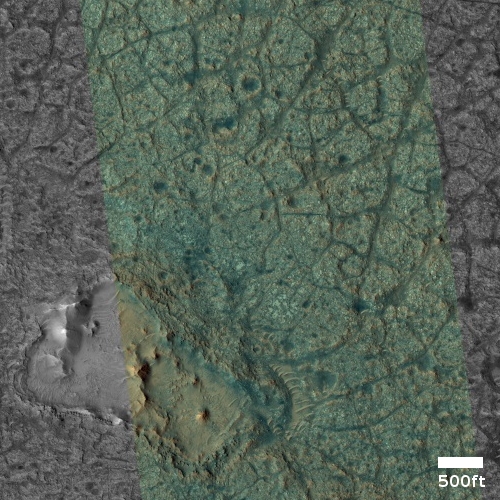
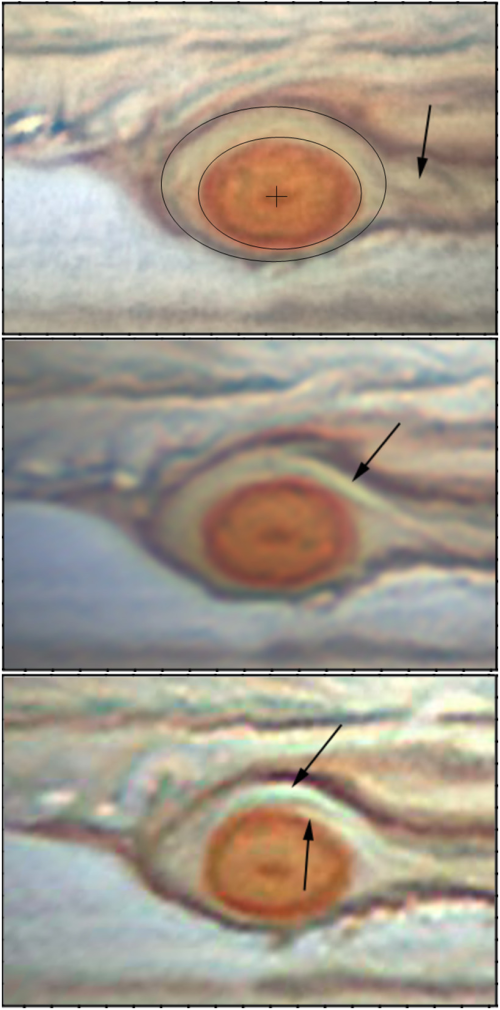
SpaceX leases bigger space at LA port for processing Falcon 9 boosters after launch
Capitalism in space: According to the mayor of Los Angeles, SpaceX has signed a new lease for more space at the city’s port, taking over the facilities no longer used by Sea Launch’s floating launch platform that is now in Russia.
News of the port lease broke on April 26th with a tweet from the mayor of Long Beach, California after the Port of Long Beach (POLB) Commission voted to approve SpaceX’s 24-month sublease with an effective start date of May 1st, 2021. From 2014 to 2020, a massive floating rocket launch complex and associated service ships once used by SeaLaunch called POLB’s Pier 16 home while mothballed and the company left behind a decent amount of infrastructure when it vacated the facility last year.
That includes a ~5600 square meter (~65,000 sq ft) warehouse and office space formerly used to process SeaLaunch payloads and Ukrainian Zenit rockets, as well as a pier and dock space generally optimized for loading and unloading large rockets from rocket transport ships. In other words, Pier 16 is a perfect fit for SpaceX’s needs.
SpaceX has twice before signed similar leases and then canceled them. Now it appears the deal is more firm, as the company appears to be gearing up for regular Starlink satellite launches from Vandenberg, requiring a bigger need in LA for processing Falcon 9 first stage boosters after launch.
I wonder too if this deal might be in connection with Starship and the two used floating oil rigs that SpaceX now owns and is refitting as Superheavy/Starship launch and landing pads. This LA facility would be ideal for these ocean platforms before and after launch.
Capitalism in space: According to the mayor of Los Angeles, SpaceX has signed a new lease for more space at the city’s port, taking over the facilities no longer used by Sea Launch’s floating launch platform that is now in Russia.
News of the port lease broke on April 26th with a tweet from the mayor of Long Beach, California after the Port of Long Beach (POLB) Commission voted to approve SpaceX’s 24-month sublease with an effective start date of May 1st, 2021. From 2014 to 2020, a massive floating rocket launch complex and associated service ships once used by SeaLaunch called POLB’s Pier 16 home while mothballed and the company left behind a decent amount of infrastructure when it vacated the facility last year.
That includes a ~5600 square meter (~65,000 sq ft) warehouse and office space formerly used to process SeaLaunch payloads and Ukrainian Zenit rockets, as well as a pier and dock space generally optimized for loading and unloading large rockets from rocket transport ships. In other words, Pier 16 is a perfect fit for SpaceX’s needs.
SpaceX has twice before signed similar leases and then canceled them. Now it appears the deal is more firm, as the company appears to be gearing up for regular Starlink satellite launches from Vandenberg, requiring a bigger need in LA for processing Falcon 9 first stage boosters after launch.
I wonder too if this deal might be in connection with Starship and the two used floating oil rigs that SpaceX now owns and is refitting as Superheavy/Starship launch and landing pads. This LA facility would be ideal for these ocean platforms before and after launch.