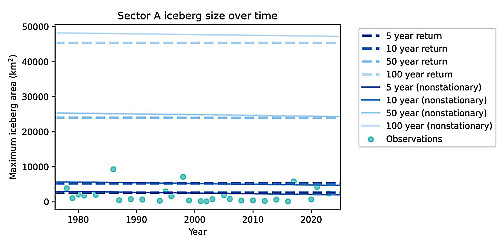
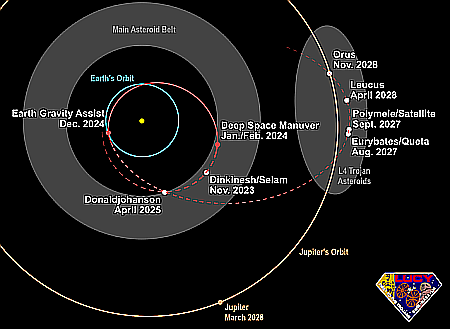
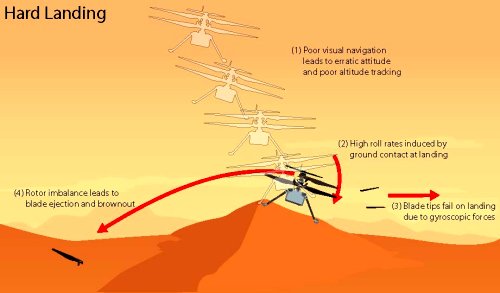
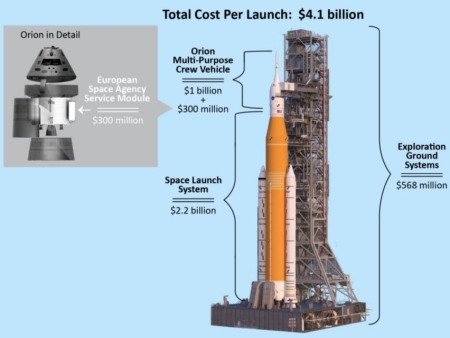
SpaceX requests special election to make Starbase at Boca Chica a city
In a letter [pdf] sent yesterday to a local judge, SpaceX requested that a special election be held in Cameron County on whether its Starbase facilities in Boca Chica should be incorporated as a city.
To continue growing the workforce necessary to rapidly develop and manufacture Starship, we need the ability to grow Starbase as a community. That is why we are requesting that Cameron County call an election to enable the incorporation of Starbase as the newest city in the Rio Grande Valley.
Incorporating Starbase will streamline the processes required to build the amenities necessary to make the area a world class place to live—for the hundreds already calling it home, as well as for prospective workers eager to help build humanity’s future in space. As you know, through agreements with the County, SpaceX currently performs several civil functions around Starbase due to its remote location, including management of the roads, utilities, and the provision of schooling and medical care for the residents. Incorporation would move the management of some of these functions to a more appropriate public body.
The letter went on to list the many other things SpaceX is already doing to benefit the area, including many of the environmental requirements imposed on it by the FAA and Fish & Wildlife.
At this moment there has been no response from the judge or Cameron County. I suspect there will be no objection, and this vote will take place in the near future. I also expect it will pass, because SpaceX employees now make up almost the entire population of Boca Chica.
In a letter [pdf] sent yesterday to a local judge, SpaceX requested that a special election be held in Cameron County on whether its Starbase facilities in Boca Chica should be incorporated as a city.
To continue growing the workforce necessary to rapidly develop and manufacture Starship, we need the ability to grow Starbase as a community. That is why we are requesting that Cameron County call an election to enable the incorporation of Starbase as the newest city in the Rio Grande Valley.
Incorporating Starbase will streamline the processes required to build the amenities necessary to make the area a world class place to live—for the hundreds already calling it home, as well as for prospective workers eager to help build humanity’s future in space. As you know, through agreements with the County, SpaceX currently performs several civil functions around Starbase due to its remote location, including management of the roads, utilities, and the provision of schooling and medical care for the residents. Incorporation would move the management of some of these functions to a more appropriate public body.
The letter went on to list the many other things SpaceX is already doing to benefit the area, including many of the environmental requirements imposed on it by the FAA and Fish & Wildlife.
At this moment there has been no response from the judge or Cameron County. I suspect there will be no objection, and this vote will take place in the near future. I also expect it will pass, because SpaceX employees now make up almost the entire population of Boca Chica.