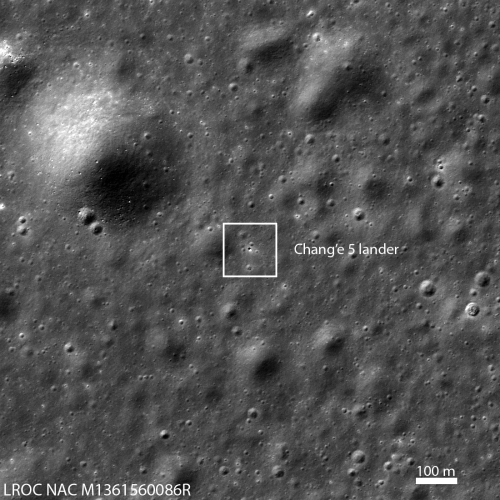
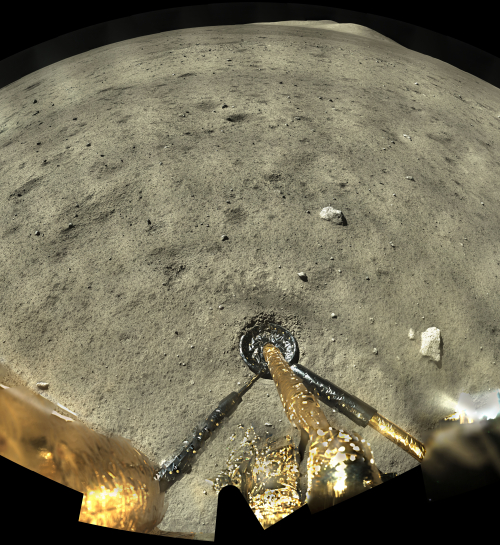
Chang’e-5’s lunar samples less dense than expected
Because the lunar samples retrieved by China’s Chang’e-5 probe were less dense than expected, it ended up recovering only 3.8 pounds of material rather than the targeted 4.4 pounds.
The probe had estimated the lunar rocks to have a density of 1.6 grams per cubic millimetre, based on data from past missions by other countries, said Pei Zhaoyu, the mission spokesman. Going by that figure, the probe stopped taking samples after just 12 hours, apparently assessing that the target had been reached. “However, from tests, the actual density might not be that high,” Pei told reporters.
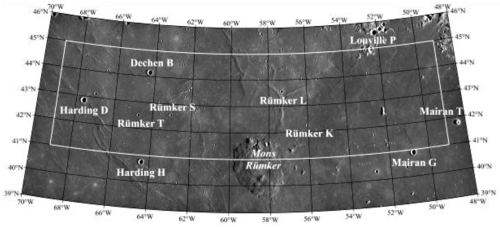
This is not a failure, but a discovery. In order to make sure the lander did not recover too much material, weighing too much, they needed to set limits based on the expected weight of the material recovered. That these samples taken from the Mons Rümker volcano complex are lighter than expected reveals something about them. It suggests the lava here was different than lava samples taken elsewhere.
Because the lunar samples retrieved by China’s Chang’e-5 probe were less dense than expected, it ended up recovering only 3.8 pounds of material rather than the targeted 4.4 pounds.
The probe had estimated the lunar rocks to have a density of 1.6 grams per cubic millimetre, based on data from past missions by other countries, said Pei Zhaoyu, the mission spokesman. Going by that figure, the probe stopped taking samples after just 12 hours, apparently assessing that the target had been reached. “However, from tests, the actual density might not be that high,” Pei told reporters.
This is not a failure, but a discovery. In order to make sure the lander did not recover too much material, weighing too much, they needed to set limits based on the expected weight of the material recovered. That these samples taken from the Mons Rümker volcano complex are lighter than expected reveals something about them. It suggests the lava here was different than lava samples taken elsewhere.