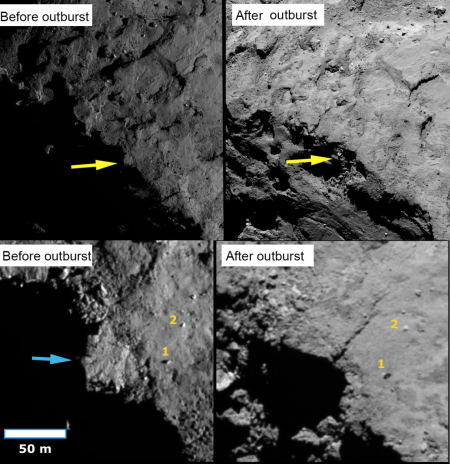
A Jupiter Trojan asteroid spouts a tail
The ATLAS telescope has discovered the first Jupiter Trojan asteroid to spout a tail like a comet.
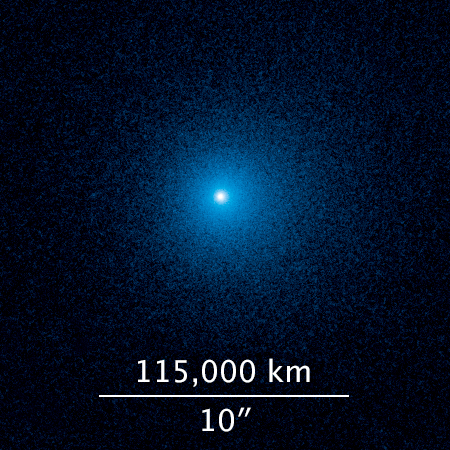
Early in June 2019, ATLAS reported what seemed to be a faint asteroid near the orbit of Jupiter. The Minor Planet Center designated the new discovery as 2019 LD2. Inspection of ATLAS images taken on June 10 by collaborators Alan Fitzsimmons and David Young at Queen’s University Belfast revealed its probable cometary nature. Follow-up observations by the University of Hawaiʻi’s J.D. Armstrong and his student Sidney Moss on June 11 and 13 using the Las Cumbres Observatory (LCO) global telescope network confirmed the cometary nature of this body.
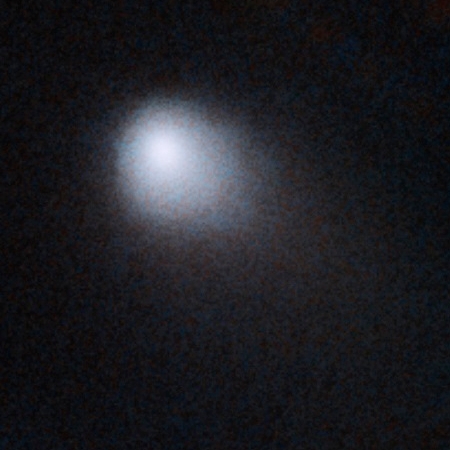
Later, in July 2019, new ATLAS images caught 2019 LD2 again – now truly looking like a comet, with a faint tail made of dust or gas. The asteroid passed behind the Sun and was not observable from the Earth in late 2019 and early 2020, but upon its reappearance in the night sky in April of 2020, routine ATLAS observations confirmed that it still looks like a comet. These observations showed that 2019 LD2 has probably been continuously active for almost a year.
While ATLAS has discovered more than 40 comets, what makes this object extraordinary is its orbit. The early indication that it was an asteroid near Jupiter’s orbit have now been confirmed through precise measurements from many different observatories. In fact, 2019 LD2 is a special kind of asteroid called a Jupiter Trojan – and no object of this type has ever before been seen to spew out dust and gas like a comet.
There are a number of mysteries here. First, why should it have suddenly become active, since its orbit is relatively circular (similar to Jupiter’s)? Second, it had been assumed that the Jupiter Trojans had been in their orbits for a long time and had long ago vented any ice on their surfaces. This discovery proves that assumption false. It suggests that either this asteroid is a comet that was recently captured, or that things can happen on these asteroids to bring some buried volatiles up to the surface, where they can then vent.
Above all, this asteroid shows that it is dangerous to assume all Jupiter Trojan asteroids are the same. I guarantee when we finally get a close look at a bunch, when the Lucy mission arrives beginning in 2027, the variety will be quite spectacular.
The ATLAS telescope has discovered the first Jupiter Trojan asteroid to spout a tail like a comet.
Early in June 2019, ATLAS reported what seemed to be a faint asteroid near the orbit of Jupiter. The Minor Planet Center designated the new discovery as 2019 LD2. Inspection of ATLAS images taken on June 10 by collaborators Alan Fitzsimmons and David Young at Queen’s University Belfast revealed its probable cometary nature. Follow-up observations by the University of Hawaiʻi’s J.D. Armstrong and his student Sidney Moss on June 11 and 13 using the Las Cumbres Observatory (LCO) global telescope network confirmed the cometary nature of this body.
Later, in July 2019, new ATLAS images caught 2019 LD2 again – now truly looking like a comet, with a faint tail made of dust or gas. The asteroid passed behind the Sun and was not observable from the Earth in late 2019 and early 2020, but upon its reappearance in the night sky in April of 2020, routine ATLAS observations confirmed that it still looks like a comet. These observations showed that 2019 LD2 has probably been continuously active for almost a year.
While ATLAS has discovered more than 40 comets, what makes this object extraordinary is its orbit. The early indication that it was an asteroid near Jupiter’s orbit have now been confirmed through precise measurements from many different observatories. In fact, 2019 LD2 is a special kind of asteroid called a Jupiter Trojan – and no object of this type has ever before been seen to spew out dust and gas like a comet.
There are a number of mysteries here. First, why should it have suddenly become active, since its orbit is relatively circular (similar to Jupiter’s)? Second, it had been assumed that the Jupiter Trojans had been in their orbits for a long time and had long ago vented any ice on their surfaces. This discovery proves that assumption false. It suggests that either this asteroid is a comet that was recently captured, or that things can happen on these asteroids to bring some buried volatiles up to the surface, where they can then vent.
Above all, this asteroid shows that it is dangerous to assume all Jupiter Trojan asteroids are the same. I guarantee when we finally get a close look at a bunch, when the Lucy mission arrives beginning in 2027, the variety will be quite spectacular.