Tag: commercial
SpaceX wins competition to build Artemis manned lunar lander, using Starship
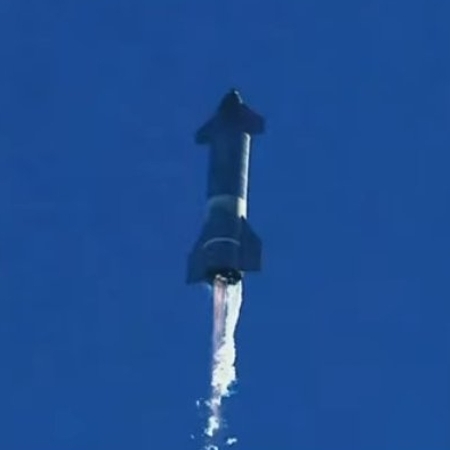

Starship prototype #8 on its first flight test,
December 2020
Capitalism in space: NASA has just announced that it has chosen SpaceX to build the Artemis manned lunar lander, using Starship.
The award, a $2.9 billion fixed price contract, also requires SpaceX to complete an unmanned demo lunar landing with Starship that also returns to Earth, before it lands NASA astronauts on the Moon. The contract also still retains the goal to get this to happen by 2024, though NASA official emphasized that they will only launch when ready.
After these flights the agency says it will open bidding again to the entire industry, which means that others are now being challenged to come up with something that can beat SpaceX in the future.
Nonetheless, the contract award was a surprise, as NASA originally intended to pick two teams to provide redundancy and encourage competition. Instead, the agency completely bypassed lunar landers proposed by Dynetics and a team led by Blue Origin that included Lockheed Martin and Draper.
Even more significantly, though NASA explained in the telecon that they still plan to use SLS and Orion to bring astronauts to Gateway, who will then be picked up by Starship for the landing, this decision is a major rejection of the Space Launch System (SLS), since Starship will not use it to get to the Moon, while the other two landers required it.
In fact, this decision practically makes SLS unnecessary in the Artemis program, as NASA has also awarded SpaceX the contract for supplying cargo to the Lunar Gateway station as well as launching its first two modules, using Dragon capsules and Falcon Heavy. SLS is still slated to launch Orion to Gateway, but Starship can replace Orion as well, since Starship is being designed to carry people from Earth to the Moon. This makes SLS and Orion essentially unneeded, easily abandoned once Starship starts flying.
NASA’s decision also means the Biden administration is willing to use its clout to push for Starship over SLS in Congress, which has favored SLS for years because of the pork it brings to their states and congressional districts. They apparently think that Congress is now ready to risk the end of SLS if it comes with a new program that actually accomplishes something. These developments firmly confirm my sense from February that the political winds are bending away from SLS.
This decision is also a major blow to Blue Origin and the older big space companies that Jeff Bezos’ company partnered with. Their dependence on the very costly and cumbersome SLS rocket meant that their ability to launch on a schedule and cost desired by NASA was severely limited. NASA looked at the numbers, and decided the time was right to go with a more radical system. As was noted by one NASA official during the press teleconference, “NASA is now more open to innovation.”
Based on the details announced during the announcement, NASA was especially drawn to Starship’s payload capability to bring a large payload to the Moon, at the same time it brings humans there as well. It also appears SpaceX’s recent track record of success also added weight to their bid.
Lisa Ferraro & Houston Person – Teach Me Tonight
Sierra Nevada to make its space operations a separate company
Capitalism in space: Sierra Nevada has decided to spin off its space operations involving Dream Chaser and its proposed private space station into a separate company called Sierra Space.
In a message to employees April 14, SNC [Sierra Nevada] Chairwoman and President Eren Ozmen said the company’s Space Systems division will become a standalone company, called Sierra Space, although remain a subsidiary of SNC.
…Ozmen provided few details about how the transition of SNC’s space business to Sierra Space would unfold, but she said it would take several months to complete. Even after the transition, Sierra Space will “continue deep cooperation and synergy” with SNC’s other business areas in aviation and defense.
My guess is that Ozmen does not want the risks of its space-related projects to impact its more reliable aviation and defense holdings. By separating it out, she can better isolate the success or failure of each. This does not necessarily mean that the space holdings are failing, only that they carry a greater financial risk.
Sierra Space’s future strongly hinges on the success of the first Dream Chaser cargo shuttle, Tenacity, whose inaugural flight has been delayed from ’21 to ’22. If that fails, all the other plans of this space division will likely fail as well. If it succeeds however the company’s financial future will be quite promising.
Capitalism in space: Sierra Nevada has decided to spin off its space operations involving Dream Chaser and its proposed private space station into a separate company called Sierra Space.
In a message to employees April 14, SNC [Sierra Nevada] Chairwoman and President Eren Ozmen said the company’s Space Systems division will become a standalone company, called Sierra Space, although remain a subsidiary of SNC.
…Ozmen provided few details about how the transition of SNC’s space business to Sierra Space would unfold, but she said it would take several months to complete. Even after the transition, Sierra Space will “continue deep cooperation and synergy” with SNC’s other business areas in aviation and defense.
My guess is that Ozmen does not want the risks of its space-related projects to impact its more reliable aviation and defense holdings. By separating it out, she can better isolate the success or failure of each. This does not necessarily mean that the space holdings are failing, only that they carry a greater financial risk.
Sierra Space’s future strongly hinges on the success of the first Dream Chaser cargo shuttle, Tenacity, whose inaugural flight has been delayed from ’21 to ’22. If that fails, all the other plans of this space division will likely fail as well. If it succeeds however the company’s financial future will be quite promising.
Phantom Space raises $5 million in investment capital
Rising from the ashes: Phantom Space, the new startup smallsat rocket company created by Jim Cantrell, the former CEO of the smallsat rocket company Vector, has now successfully raised $5 million in seed money to begin development of its rocket, dubbed Daytona.
The expendable Daytona will be powered by eight Hadley engines — seven on the first stage and one on the upper stage. The engines are an example of Phantom Space’s strategy of leveraging externally developed tech; Hadleys are built by Denver-based company Ursa Major Technologies.
According to my sources, the reason Vector never flew and Cantrell and the company parted ways was that the engines they were building for the rocket ended up under-powered. It seems Cantrell has taken a different approach with his new startup by buying engines from an outside source instead of building them in house.
Rising from the ashes: Phantom Space, the new startup smallsat rocket company created by Jim Cantrell, the former CEO of the smallsat rocket company Vector, has now successfully raised $5 million in seed money to begin development of its rocket, dubbed Daytona.
The expendable Daytona will be powered by eight Hadley engines — seven on the first stage and one on the upper stage. The engines are an example of Phantom Space’s strategy of leveraging externally developed tech; Hadleys are built by Denver-based company Ursa Major Technologies.
According to my sources, the reason Vector never flew and Cantrell and the company parted ways was that the engines they were building for the rocket ended up under-powered. It seems Cantrell has taken a different approach with his new startup by buying engines from an outside source instead of building them in house.
Branson sells off more of his Virgin Galactic stock
He’s getting out while the getting is good: In the past three days Richard Branson sold another $150 million worth of his Virgin Galactic stock.
The stock price for these sales was about $27, more than twice the value when the company went public in November 2019.
Including his stock sales in May ’20, Branson has now sold about 30% of his share in the company, leaving him holding only about a 20% share. Essentially, Virgin Galactic is no longer his company.
Meanwhile, Virgin Galactic now says it will not begin tourist flights until ’22. Whether it can survive that long is another question. It certainly hasn’t delivered on any of Branson’s endless grandiose promises, beginning almost two decades ago in 2005.
He’s getting out while the getting is good: In the past three days Richard Branson sold another $150 million worth of his Virgin Galactic stock.
The stock price for these sales was about $27, more than twice the value when the company went public in November 2019.
Including his stock sales in May ’20, Branson has now sold about 30% of his share in the company, leaving him holding only about a 20% share. Essentially, Virgin Galactic is no longer his company.
Meanwhile, Virgin Galactic now says it will not begin tourist flights until ’22. Whether it can survive that long is another question. It certainly hasn’t delivered on any of Branson’s endless grandiose promises, beginning almost two decades ago in 2005.
SpaceX raises another $1.16 billion in private capital
Capitalism in space: In a regulatory filing yesterday SpaceX revealed that it raised another $1.16 billion in private investment capital in just the past two months.
This follows two other recent financing rounds since August of last year in which SpaceX raised almost $3 billion. That makes $4 billion raised in eight months. All told, I think this brings the total private investment capital SpaceX has raised in the past two years to approximately $6 billion, all for building both the Starlink satellite constellation and the Starship/Superheavy rocket.
Not only does this give SpaceX ample cash to build both, it signals the growing faith big money investors have in the company’s plans. They have bought into Elon Musk’s dreams because he has proven that his dreams deliver, not only in exciting space ventures but in profits.
This fund-raising success also tells us that even if Starship does not reach orbit before SLS, it will very soon eclipse it entirely. It has the money now to get built, and the way SpaceX builds things, it will get built fast.
Capitalism in space: In a regulatory filing yesterday SpaceX revealed that it raised another $1.16 billion in private investment capital in just the past two months.
This follows two other recent financing rounds since August of last year in which SpaceX raised almost $3 billion. That makes $4 billion raised in eight months. All told, I think this brings the total private investment capital SpaceX has raised in the past two years to approximately $6 billion, all for building both the Starlink satellite constellation and the Starship/Superheavy rocket.
Not only does this give SpaceX ample cash to build both, it signals the growing faith big money investors have in the company’s plans. They have bought into Elon Musk’s dreams because he has proven that his dreams deliver, not only in exciting space ventures but in profits.
This fund-raising success also tells us that even if Starship does not reach orbit before SLS, it will very soon eclipse it entirely. It has the money now to get built, and the way SpaceX builds things, it will get built fast.
Blue Origin completes another unmanned suborbital test flight of New Shepard
Capitalism in space: Blue Origin today successfully completed another unmanned suborbital test flight of New Shepard, and in doing so also rehearsed the boarding and disembarking procedures they will use when they finally fly this craft with people on board.
Blue Origin personnel rehearsed how customers will board the six-seat crew capsule before Wednesday’s launch. Four employees stood in as astronauts and rode to the launch pad inside a Ford SUV with two support crew members.
After arriving at the pad, the astronaut stand-ins climbed stairs up the launch pad tower and walked across an access gantry leading to the spacecraft sitting atop the already-fueled New Shepard booster. Two employees — Gary Lai, Blue Origin’s New Shepard designer, and Audrey Powers, the company’s vice president of legal and compliance — entered the capsule through the hatch and strapped into seats. … After a few minutes, Lai and Powers exited the spacecraft and the crew evacuated the launch pad before liftoff.
…Blue Origin crews at the West Texas test site also practiced how they will help passengers out of the capsule after landing. Recovery teams quickly converged on the spacecraft after touchdown in the desert, and approached the capsule with mobile stairs and other equipment.
While rehearsing these procedures seems a good idea, there appears to be a bit of blarney in this whole show. Considering that this was their 15th New Shepard flight and the second for this spacecraft, it seems to me that these procedures could have rehearsed during one of those earlier flights, or even during any one of many dress rehearsal countdowns that they should have done previously, not on a flight itself.
Blue Origin has not announced when the first manned suborbital flight will be. In their last prediction in January they had said the first manned flight would happen in April, something that has now clearly not happened.
That flight is now more than five years behind schedule, based on the company’s promises back in 2016. when they flew New Shepard almost every other month and predicted the first manned flights in 2017. Then, Jeff Bezos hired Bob Smith to be Blue Origin’s CEO, and the company’s progress on New Shepard crawled to a stop.
It is now questionable whether this company will even get its first suborbital tourist flight launched before SpaceX completes its first orbital tourist flight in September. At that point why should anyone who can afford to pay for a space flight choose New Shepard and its mere five minutes of weightlessness when they go to orbit with SpaceX and spend days there? It might cost less, but it will still cost a lot, and the cost-benefit analysis sure doesn’t favor Blue Origin’s business model any more.
Capitalism in space: Blue Origin today successfully completed another unmanned suborbital test flight of New Shepard, and in doing so also rehearsed the boarding and disembarking procedures they will use when they finally fly this craft with people on board.
Blue Origin personnel rehearsed how customers will board the six-seat crew capsule before Wednesday’s launch. Four employees stood in as astronauts and rode to the launch pad inside a Ford SUV with two support crew members.
After arriving at the pad, the astronaut stand-ins climbed stairs up the launch pad tower and walked across an access gantry leading to the spacecraft sitting atop the already-fueled New Shepard booster. Two employees — Gary Lai, Blue Origin’s New Shepard designer, and Audrey Powers, the company’s vice president of legal and compliance — entered the capsule through the hatch and strapped into seats. … After a few minutes, Lai and Powers exited the spacecraft and the crew evacuated the launch pad before liftoff.
…Blue Origin crews at the West Texas test site also practiced how they will help passengers out of the capsule after landing. Recovery teams quickly converged on the spacecraft after touchdown in the desert, and approached the capsule with mobile stairs and other equipment.
While rehearsing these procedures seems a good idea, there appears to be a bit of blarney in this whole show. Considering that this was their 15th New Shepard flight and the second for this spacecraft, it seems to me that these procedures could have rehearsed during one of those earlier flights, or even during any one of many dress rehearsal countdowns that they should have done previously, not on a flight itself.
Blue Origin has not announced when the first manned suborbital flight will be. In their last prediction in January they had said the first manned flight would happen in April, something that has now clearly not happened.
That flight is now more than five years behind schedule, based on the company’s promises back in 2016. when they flew New Shepard almost every other month and predicted the first manned flights in 2017. Then, Jeff Bezos hired Bob Smith to be Blue Origin’s CEO, and the company’s progress on New Shepard crawled to a stop.
It is now questionable whether this company will even get its first suborbital tourist flight launched before SpaceX completes its first orbital tourist flight in September. At that point why should anyone who can afford to pay for a space flight choose New Shepard and its mere five minutes of weightlessness when they go to orbit with SpaceX and spend days there? It might cost less, but it will still cost a lot, and the cost-benefit analysis sure doesn’t favor Blue Origin’s business model any more.
More delays to Boeing’s Starliner manned capsule schedule
Capitalism in space: Though no new launch date has been announced, both NASA and Boeing are now likely aiming for a summer launch of the second unmanned Starliner demo mission to ISS.
This is largely due to traffic at the International Space Station rather than the readiness of Starliner itself. Two NASA sources said the vehicle is “close” to being ready, with only a few small tests to certify the spacecraft for flight remaining. Starliner is therefore expected to be ready to fly by early summer.
The primary issue is the availability of space station docking ports fitted with an “international docking adapter,” which are used by SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, Cargo Dragon 2, and Starliner vehicles. There are presently two such ports on the station, and for NASA, the priority for access to these ports are crew rotations followed by supply missions. So the question becomes when the Starliner test flight can find an open slot on station.
It appears that they are now targeting the window of availability for either of those ports in the late July into August time period.
While this might be the main reason for this new delay, it also appears that there might be technical issues as well. In early March Boeing and NASA had announced that they were delaying this demo mission for the same scheduling reasons, but then they said they were targeting a May launch date, during a period after one manned Dragon mission had left in late April and before the next Dragon cargo mission arrived in June.
It now appears they cannot meet that window any longer, and are therefore aiming for the next, in July.
Meanwhile, the first manned Starliner demo mission appears to have also pushed back, from late this year to early next year.
Capitalism in space: Though no new launch date has been announced, both NASA and Boeing are now likely aiming for a summer launch of the second unmanned Starliner demo mission to ISS.
This is largely due to traffic at the International Space Station rather than the readiness of Starliner itself. Two NASA sources said the vehicle is “close” to being ready, with only a few small tests to certify the spacecraft for flight remaining. Starliner is therefore expected to be ready to fly by early summer.
The primary issue is the availability of space station docking ports fitted with an “international docking adapter,” which are used by SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, Cargo Dragon 2, and Starliner vehicles. There are presently two such ports on the station, and for NASA, the priority for access to these ports are crew rotations followed by supply missions. So the question becomes when the Starliner test flight can find an open slot on station.
It appears that they are now targeting the window of availability for either of those ports in the late July into August time period.
While this might be the main reason for this new delay, it also appears that there might be technical issues as well. In early March Boeing and NASA had announced that they were delaying this demo mission for the same scheduling reasons, but then they said they were targeting a May launch date, during a period after one manned Dragon mission had left in late April and before the next Dragon cargo mission arrived in June.
It now appears they cannot meet that window any longer, and are therefore aiming for the next, in July.
Meanwhile, the first manned Starliner demo mission appears to have also pushed back, from late this year to early next year.
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy wins launch contract for VIPER lunar rover
Capitalism in space: Astrobotic, the company building the lander to place NASA’s VIPER lunar rover on the Moon, has picked SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy as the rocket to launch the package.
This mission is part of a fleet of landers being sent to the Moon in the next two years, as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program to hire private companies to do this rather than NASA.
Intuitive Machines, which won CLPS task orders for two lander missions, will launch each on Falcon 9 vehicles late this year and in 2022. Masten Space Systems selected SpaceX to provide launch services for its XL-1 lander mission, which won a CLPS award for a late 2022 mission.
Astrobotic will launch its first CLPS mission, a smaller lunar lander called Peregrine, on the inaugural launch of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan Centaur currently scheduled for late this year. Firefly Aerospace, which won the most recent CLPS award in January, has not selected a launch provider yet for its Blue Ghost lander, but noted the lander is too large to launch on the company’s own Alpha rocket.
That’s five American lunar missions, all built and owned by private companies. Nor will these be the only unmanned lunar missions, when you include the UAE rover targeted for a ’22 launch, along with additional planned Indian, Chinese, and Russian missions. Almost all are aimed at the Moon’s south polar regions.
It is going to get both crowded and busy on the Moon in the next few years.
Capitalism in space: Astrobotic, the company building the lander to place NASA’s VIPER lunar rover on the Moon, has picked SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy as the rocket to launch the package.
This mission is part of a fleet of landers being sent to the Moon in the next two years, as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program to hire private companies to do this rather than NASA.
Intuitive Machines, which won CLPS task orders for two lander missions, will launch each on Falcon 9 vehicles late this year and in 2022. Masten Space Systems selected SpaceX to provide launch services for its XL-1 lander mission, which won a CLPS award for a late 2022 mission.
Astrobotic will launch its first CLPS mission, a smaller lunar lander called Peregrine, on the inaugural launch of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan Centaur currently scheduled for late this year. Firefly Aerospace, which won the most recent CLPS award in January, has not selected a launch provider yet for its Blue Ghost lander, but noted the lander is too large to launch on the company’s own Alpha rocket.
That’s five American lunar missions, all built and owned by private companies. Nor will these be the only unmanned lunar missions, when you include the UAE rover targeted for a ’22 launch, along with additional planned Indian, Chinese, and Russian missions. Almost all are aimed at the Moon’s south polar regions.
It is going to get both crowded and busy on the Moon in the next few years.
UAE hires Japanese company as partner for its ’22 lunar rover mission
Capitalism in space: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has chosen the private Japanese company Ispace to provide the lander bringing its Rashid rover to the Moon in 2022.
ispace’s 240 kg lander is 2.3 meters tall and 2.6 meters wide. It will be launched by SpaceX, Elon Musk’s rocket company, on a Falcon 9 rocket. Once the iSpace lander is placed in the Earth’s orbit, it will travel to the moon on its own, land and unload the rover.
The lander will use solar panels for power, which will also allow the rover to communicate with Earth. It will also carry a solid-state battery made by NGK Spark Plug, which intends to examine its battery’s lunar performance.
This UAE project is similar but a step up from its Al-Amal Mars orbiter. In that case UAE used its money to have the orbiter mostly built by U.S. universities as they taught UAE’s students how to do it. In this case, UAE engineers appear to be building the rover itself, with the purchased help of others to provide the lander..
Capitalism in space: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has chosen the private Japanese company Ispace to provide the lander bringing its Rashid rover to the Moon in 2022.
ispace’s 240 kg lander is 2.3 meters tall and 2.6 meters wide. It will be launched by SpaceX, Elon Musk’s rocket company, on a Falcon 9 rocket. Once the iSpace lander is placed in the Earth’s orbit, it will travel to the moon on its own, land and unload the rover.
The lander will use solar panels for power, which will also allow the rover to communicate with Earth. It will also carry a solid-state battery made by NGK Spark Plug, which intends to examine its battery’s lunar performance.
This UAE project is similar but a step up from its Al-Amal Mars orbiter. In that case UAE used its money to have the orbiter mostly built by U.S. universities as they taught UAE’s students how to do it. In this case, UAE engineers appear to be building the rover itself, with the purchased help of others to provide the lander..
Yes – Round About
New calls for reworking or replacing Outer Space Treaty
Yesterday there were two different public statements calling for the international community to either amend or replace the Outer Space Treaty, one an op-ed in the U.S. and the other a statement by the head of Russia’s space agency.
At first glance these announcements seemed hopeful, especially because the op-ed, written by one of the authors of a just released new study [pdf] by a defense-oriented Washington think tank, made part of its focus the need to encourage commercial activities in space.
» Read more
Yesterday there were two different public statements calling for the international community to either amend or replace the Outer Space Treaty, one an op-ed in the U.S. and the other a statement by the head of Russia’s space agency.
At first glance these announcements seemed hopeful, especially because the op-ed, written by one of the authors of a just released new study [pdf] by a defense-oriented Washington think tank, made part of its focus the need to encourage commercial activities in space.
» Read more
Commerce increases sanctions on Russia impacting space commerce and trade
The Commerce Department last month announced that is increasing the level of sanctions against trade with Russia because it had determined that country had violated international law by using chemical weapons against specific dissidents both in and out of Russia.
On March 4, 2018, the Russia Government deployed a Novichok nerve agent in an attack against former Russian military officer Sergei Skripal and his daughter Yulia Skripal in the United Kingdom. In response, the U.S. Government imposed two sets of sanctions against Russia pursuant to the Chemical and Biological Weapons Control and Warfare Elimination Act of 1991 (CBW Act) in August 2018 and August 2019.
On August 20, 2020, the Russian Government again deployed a Novichok nerve agent, this time against Russian opposition figure Aleksey Navalny, warranting a new determination by the Secretary of State and additional sanctions under the CBW Act.
While this ruling will have a negative impact on any space-related U.S./Russian activities, the full ruling specifically included these waivers:
» Read more
The Commerce Department last month announced that is increasing the level of sanctions against trade with Russia because it had determined that country had violated international law by using chemical weapons against specific dissidents both in and out of Russia.
On March 4, 2018, the Russia Government deployed a Novichok nerve agent in an attack against former Russian military officer Sergei Skripal and his daughter Yulia Skripal in the United Kingdom. In response, the U.S. Government imposed two sets of sanctions against Russia pursuant to the Chemical and Biological Weapons Control and Warfare Elimination Act of 1991 (CBW Act) in August 2018 and August 2019.
On August 20, 2020, the Russian Government again deployed a Novichok nerve agent, this time against Russian opposition figure Aleksey Navalny, warranting a new determination by the Secretary of State and additional sanctions under the CBW Act.
While this ruling will have a negative impact on any space-related U.S./Russian activities, the full ruling specifically included these waivers:
» Read more
Mr. Skeleton – Good Golly Miss Molly
Northrop Grumman’s MEV-2 successfully completes docking to commercial satellite
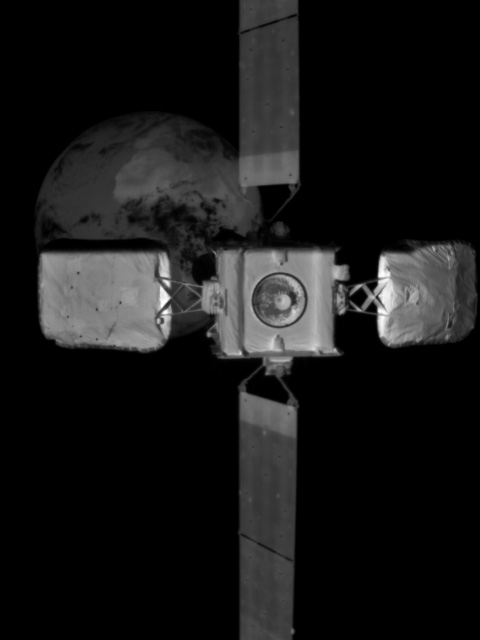

Capitalism in space: Northrop Grumman today announced that its second Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV-2) has successfully docked with an Intelsat geosynchronous communications satellite.
Northrop Grumman is the only provider of flight-proven life extension services for satellites, and this is the second time the company has docked two commercial spacecraft in orbit. The company’s MEV-1 made history when it successfully docked to the Intelsat 901 (IS-901) satellite in February 2020. Unlike MEV-1, which docked above the GEO orbit before moving IS-901 back into service, MEV-2 docked with IS-10-02 directly in its operational GEO orbital location.
…Under the terms of Intelsat’s satellite life-extension servicing contract, MEV-2 will provide five years of service to IS-10-02 before undocking and moving on to provide services for a new mission.
The image, provided by Northrop Grumman, was taken by MEV-2’s infrared wide field of view camera when it was still about 50 feet away from the Intelsat satellite. You can see the Earth in the background. As I understand it, MEV-2 uses the satellite’s own engine nozzle as a docking port, which is the smallest circular feature in the center of the satellite. If you look close you can see the nozzle’s shadow on the right.

Capitalism in space: Northrop Grumman today announced that its second Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV-2) has successfully docked with an Intelsat geosynchronous communications satellite.
Northrop Grumman is the only provider of flight-proven life extension services for satellites, and this is the second time the company has docked two commercial spacecraft in orbit. The company’s MEV-1 made history when it successfully docked to the Intelsat 901 (IS-901) satellite in February 2020. Unlike MEV-1, which docked above the GEO orbit before moving IS-901 back into service, MEV-2 docked with IS-10-02 directly in its operational GEO orbital location.
…Under the terms of Intelsat’s satellite life-extension servicing contract, MEV-2 will provide five years of service to IS-10-02 before undocking and moving on to provide services for a new mission.
The image, provided by Northrop Grumman, was taken by MEV-2’s infrared wide field of view camera when it was still about 50 feet away from the Intelsat satellite. You can see the Earth in the background. As I understand it, MEV-2 uses the satellite’s own engine nozzle as a docking port, which is the smallest circular feature in the center of the satellite. If you look close you can see the nozzle’s shadow on the right.
Bird Box Studio – Streat
Biden administration’s proposed ’22 NASA budget boosts spending in all programs
The just released summary budget by the Biden administration for 2022 includes a $1.5 billion increase in NASA’s budget, with increases for every NASA project across the board.
Maybe the only part of this that is surprising is the $325 million increase to the manned Artemis project to return to the Moon. Democrats have traditionally tried to cut such programs, even as they increased the spending in NASA’s climate budget. Though the Biden administration has shown that its priorities remain in line with this by increasing NASA’s climate budget by a hefty $2.3 billion, it did not cut Artemis but increased its budget also.
This budget proposal is also in line with the general trend in Washington, which is to spend money as if it grows on trees. Trump had also increased NASA’s budget, but tried to counter those increases with cuts in other areas, both in NASA and elsewhere. None of his proposed cuts however were ever really approved, as Congress has no interest in cutting anything.
Now that Biden and the bureaucracy is in power the money to them is going to flow like water from a burst dam. Whether the American people actually benefit from this spending remains to be seen. In general, since the 1960s the payoff from increased federal spending has been poor to terrible. I don’t see any reason to expect otherwise, even if the support of manned space exploration by the Biden administration helps fuel a new commercial renaissance in space. That renaissance cannot last if the country that supports it goes bankrupt.
The just released summary budget by the Biden administration for 2022 includes a $1.5 billion increase in NASA’s budget, with increases for every NASA project across the board.
Maybe the only part of this that is surprising is the $325 million increase to the manned Artemis project to return to the Moon. Democrats have traditionally tried to cut such programs, even as they increased the spending in NASA’s climate budget. Though the Biden administration has shown that its priorities remain in line with this by increasing NASA’s climate budget by a hefty $2.3 billion, it did not cut Artemis but increased its budget also.
This budget proposal is also in line with the general trend in Washington, which is to spend money as if it grows on trees. Trump had also increased NASA’s budget, but tried to counter those increases with cuts in other areas, both in NASA and elsewhere. None of his proposed cuts however were ever really approved, as Congress has no interest in cutting anything.
Now that Biden and the bureaucracy is in power the money to them is going to flow like water from a burst dam. Whether the American people actually benefit from this spending remains to be seen. In general, since the 1960s the payoff from increased federal spending has been poor to terrible. I don’t see any reason to expect otherwise, even if the support of manned space exploration by the Biden administration helps fuel a new commercial renaissance in space. That renaissance cannot last if the country that supports it goes bankrupt.
Starship #11 debris fuels environmentalist opposition
They’re coming for you next: The debris that fell as far as five and a half miles away when SpaceX’s Starship #11 prototype exploded just before landing on March 30th has increased the already vocal opposition from various environmentalist activists of the space project.
Environmental organizations such as the Sierra Club, the Friends of Wildlife Corridor, and concerned citizens in the environmental research field have expressed their dissent about the SpaceX activities at Boca Chica.
Chris Sandoval, a science teacher in Brownsville with degrees in Wildlife and Fisheries and Ecotoxicology, has put forth a research paper explaining the possible effects of SpaceX activity in the surrounding natural habitats and economic consequences as a result of their expansion in the region.
Sandoval says research would show that contamination from rocket fluids would harm wildlife in the surrounding area. “Contaminants such as those of hydrocarbons are able to kill aquatic life, both vertebrate and invertebrate, at very low concentrations, especially when it’s in a semi-enclosed area as the Lagunas are,” explained Sandoval.
And yet, none of these claims seem to apply to the government-run spaceports in Florida and California, both of which are also surrounded by wildlife refuges. Why is that? Why do these environmentalists have a particular opposition to the spaceport of this private company, but none or little opposition to the government’s? Could it be that what they really oppose is private enterprise, and are using the environment as a tool to destroy it?
I should add, according to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service that manages this refuge, SpaceX has been working closely with them on mitigating the damage, which in the end I suspect will be quite minimal. The ecology is far stronger than these environmentalist like to portray it. What SpaceX did hardly compares to the damage a hurricane would cause, and that is not an unusual event at this Gulf coast location.
Whether this environmental opposition to SpaceX will result in any major delays or obstacles remains to be seen. Under a Trump administration I would not be too concerned. Under today’s Democratic Party Biden administration, who knows? The tendency of Democrats is to regulate, and to use their power to squeeze others. So far that has not yet happened aggressively in connection to SpaceX, though there have been signs that the Biden administration is interested in increasing the regulatory roadblocks SpaceX must face. We will only have to wait and see.
Above all this increases the urgency for SpaceX to shift as soon as possible its Starship and Super Heavy test flights to the two oil-rigs it purchased and are refitting as floating launch and landing platforms. Once the bulk of those test flights are far away, out in the ocean, the political clout of these protesters will be minimized.
They’re coming for you next: The debris that fell as far as five and a half miles away when SpaceX’s Starship #11 prototype exploded just before landing on March 30th has increased the already vocal opposition from various environmentalist activists of the space project.
Environmental organizations such as the Sierra Club, the Friends of Wildlife Corridor, and concerned citizens in the environmental research field have expressed their dissent about the SpaceX activities at Boca Chica.
Chris Sandoval, a science teacher in Brownsville with degrees in Wildlife and Fisheries and Ecotoxicology, has put forth a research paper explaining the possible effects of SpaceX activity in the surrounding natural habitats and economic consequences as a result of their expansion in the region.
Sandoval says research would show that contamination from rocket fluids would harm wildlife in the surrounding area. “Contaminants such as those of hydrocarbons are able to kill aquatic life, both vertebrate and invertebrate, at very low concentrations, especially when it’s in a semi-enclosed area as the Lagunas are,” explained Sandoval.
And yet, none of these claims seem to apply to the government-run spaceports in Florida and California, both of which are also surrounded by wildlife refuges. Why is that? Why do these environmentalists have a particular opposition to the spaceport of this private company, but none or little opposition to the government’s? Could it be that what they really oppose is private enterprise, and are using the environment as a tool to destroy it?
I should add, according to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service that manages this refuge, SpaceX has been working closely with them on mitigating the damage, which in the end I suspect will be quite minimal. The ecology is far stronger than these environmentalist like to portray it. What SpaceX did hardly compares to the damage a hurricane would cause, and that is not an unusual event at this Gulf coast location.
Whether this environmental opposition to SpaceX will result in any major delays or obstacles remains to be seen. Under a Trump administration I would not be too concerned. Under today’s Democratic Party Biden administration, who knows? The tendency of Democrats is to regulate, and to use their power to squeeze others. So far that has not yet happened aggressively in connection to SpaceX, though there have been signs that the Biden administration is interested in increasing the regulatory roadblocks SpaceX must face. We will only have to wait and see.
Above all this increases the urgency for SpaceX to shift as soon as possible its Starship and Super Heavy test flights to the two oil-rigs it purchased and are refitting as floating launch and landing platforms. Once the bulk of those test flights are far away, out in the ocean, the political clout of these protesters will be minimized.
Starship and Super Heavy update
Link here. The fifteenth Starship prototype has now been moved to its launchpad, which you can see here, while further work continues on Starship prototypes #16-20, the first Super Heavy prototypes, #1 and #2, and the orbital launchpad.
Starship #15 sports many changes in design from #11, and is expected to do its first test flight sometime in the coming weeks. As for the first Super Heavy prototype, it will be used to test some ground operations as well as the prototype itself, on the ground. Prototype #2 will hopefully make the first Super Heavy hop.
The construction of a full orbital launchpad lends great weight to SpaceX’s goal of making the first orbital flight before the end of the year.
Meanwhile, SpaceX has likely tightened security at this Boca Chica facility after a youtuber sneaked onto the site recently and posted video of himself wandering around the base of Starship #11, unmolested. He has since removed that video, but another youtuber grabbed it and has re-posted it for you to watch.
Link here. The fifteenth Starship prototype has now been moved to its launchpad, which you can see here, while further work continues on Starship prototypes #16-20, the first Super Heavy prototypes, #1 and #2, and the orbital launchpad.
Starship #15 sports many changes in design from #11, and is expected to do its first test flight sometime in the coming weeks. As for the first Super Heavy prototype, it will be used to test some ground operations as well as the prototype itself, on the ground. Prototype #2 will hopefully make the first Super Heavy hop.
The construction of a full orbital launchpad lends great weight to SpaceX’s goal of making the first orbital flight before the end of the year.
Meanwhile, SpaceX has likely tightened security at this Boca Chica facility after a youtuber sneaked onto the site recently and posted video of himself wandering around the base of Starship #11, unmolested. He has since removed that video, but another youtuber grabbed it and has re-posted it for you to watch.
Commercial Japanese company about to test orbital space junk removal
Capitalism in space: The private Japanese company Astroscale has placed in orbit a satellite dubbed ELSA-d to test the use of magnets for capturing and removing space junk from orbit.
ELSA-d was launched March 22nd as part of a Soyuz commercial launch.
The ELSA-d mission will test new technology developed by Astroscale, which consists of two satellites stacked together: a 385-lb. (175 kilograms) “servicer” and a 37-lb. (17 kg) “client.” The servicer is designed to safely remove debris from orbit, while the client spacecraft will serve during the demonstration as a piece of debris to be cleaned up. Once the two satellites separate, they will perform a cosmic game of cat and mouse over the next six months.
…Using a series of maneuvers, Astroscale will test the satellite’s ability to snatch debris and bring it down toward the Earth’s atmosphere, where both servicer and debris will burn up. The servicer is equipped with a magnetic docking plate, as well as GPS technology to estimate the exact position and motion of its target. This debris removal demonstration project is the first of its kind by a commercial satellite operator, according to the statement.
During the trial mission, the company will test whether the servicer can catch the client satellite in three separate demonstrations.
The company’s goal is to convince satellite companies to place its client component on their satellites so that when it comes time to decommission the satellite Astroscale’s servicer can be sent up to remove it.
Capitalism in space: The private Japanese company Astroscale has placed in orbit a satellite dubbed ELSA-d to test the use of magnets for capturing and removing space junk from orbit.
ELSA-d was launched March 22nd as part of a Soyuz commercial launch.
The ELSA-d mission will test new technology developed by Astroscale, which consists of two satellites stacked together: a 385-lb. (175 kilograms) “servicer” and a 37-lb. (17 kg) “client.” The servicer is designed to safely remove debris from orbit, while the client spacecraft will serve during the demonstration as a piece of debris to be cleaned up. Once the two satellites separate, they will perform a cosmic game of cat and mouse over the next six months.
…Using a series of maneuvers, Astroscale will test the satellite’s ability to snatch debris and bring it down toward the Earth’s atmosphere, where both servicer and debris will burn up. The servicer is equipped with a magnetic docking plate, as well as GPS technology to estimate the exact position and motion of its target. This debris removal demonstration project is the first of its kind by a commercial satellite operator, according to the statement.
During the trial mission, the company will test whether the servicer can catch the client satellite in three separate demonstrations.
The company’s goal is to convince satellite companies to place its client component on their satellites so that when it comes time to decommission the satellite Astroscale’s servicer can be sent up to remove it.
Rocket Lab to recover 1st stage on next flight
Capitalism in space: Rocket Lab yesterday announced that in its continuing program to make the first stage of its Electron rocket reusable, it will attempt to recover the stage after splashdown in the ocean during its next launch in May.
While Electron’s second stage delivers the satellites to orbit, Electron’s first stage will undertake a series of complex maneuvers designed to enable the stage to survive the extreme heat and forces of atmospheric re-entry on the way back to Earth.
As the rocket reaches speeds of around eight times the speed of sound on its descent, the air around Electron heats up to 2,400 °C generating an extremely hot plasma that creates a red-orange glow around the re-entering stage. Because Electron will enter the atmosphere engines first, the nine 3D printed Rutherford engines on the first stage will bear the brunt of this extreme heating. To withstand the immense temperatures, this Electron features an evolved heat shield designed to protect the engines and direct the force of the plasma away from the rocket. After entering the atmosphere, Electron will deploy a drogue parachute to help begin the process of slowing the rocket down and stabilizing its descent. Once Electron is at subsonic speeds, a circular parachute is deployed to help further slow the rocket in preparation for a gentle ocean splashdown. A Rocket Lab vessel will then rendezvous with the stage in the splashdown zone, approximately 650 km from Launch Complex 1, and retrieve it for transport back to Rocket Lab’s Production Complex for inspection.
They did the same thing on the previous launch. This second test will be to validate what was learned then.
If all goes as planned, they hope the next recovery attempt will be an in-air snatch by a helicopter, before the stage hits the water. If that is successful that stage will then be capable of re-use.
Capitalism in space: Rocket Lab yesterday announced that in its continuing program to make the first stage of its Electron rocket reusable, it will attempt to recover the stage after splashdown in the ocean during its next launch in May.
While Electron’s second stage delivers the satellites to orbit, Electron’s first stage will undertake a series of complex maneuvers designed to enable the stage to survive the extreme heat and forces of atmospheric re-entry on the way back to Earth.
As the rocket reaches speeds of around eight times the speed of sound on its descent, the air around Electron heats up to 2,400 °C generating an extremely hot plasma that creates a red-orange glow around the re-entering stage. Because Electron will enter the atmosphere engines first, the nine 3D printed Rutherford engines on the first stage will bear the brunt of this extreme heating. To withstand the immense temperatures, this Electron features an evolved heat shield designed to protect the engines and direct the force of the plasma away from the rocket. After entering the atmosphere, Electron will deploy a drogue parachute to help begin the process of slowing the rocket down and stabilizing its descent. Once Electron is at subsonic speeds, a circular parachute is deployed to help further slow the rocket in preparation for a gentle ocean splashdown. A Rocket Lab vessel will then rendezvous with the stage in the splashdown zone, approximately 650 km from Launch Complex 1, and retrieve it for transport back to Rocket Lab’s Production Complex for inspection.
They did the same thing on the previous launch. This second test will be to validate what was learned then.
If all goes as planned, they hope the next recovery attempt will be an in-air snatch by a helicopter, before the stage hits the water. If that is successful that stage will then be capable of re-use.
Soyuz-2 launches three astronauts to ISS
Russia today successfully used its Soyuz-2 rocket to launch three astronauts to ISS.
Because this flight is occurring three days before the 60th anniversary of Yuri Gagarin’s first human flight in space, the Russians gave the Soyuz capsule his name to honor him and the event. The spacecraft docked with ISS only two orbits later.
The crew also included an American, Mark Vande Hei, who is flying as part of the new barter agreement with Russia, whereby Americans fly in Soyuz in exchange for Russians flying in American commercial capsule. This was the first time NASA paid nothing for a flight on Soyuz since the shuttle retired a decade ago.
The return to Earth of Vande Hei and his fellow crew member Pyotr Dubrov will be on the next Soyuz capsule to launch in October, MS-19, in order to accommodate a short visit by a Russian movie director and actress.
Roscosmos will launch Soyuz MS-19 no earlier than October 5 with Commander Anton Shkaplerov and two civilian spaceflight participants. Russian film director Klim Shipenko and a Russian actress, who is yet to be named, will film a movie called “The Challenge” and spend approximately a week aboard the ISS before returning to Earth aboard Soyuz MS-18 with Novitsky.
With this commercial manned flight there will be two such flights in the fall, the Dragon Inspiration4 flight that will not dock with ISS and this Russian one. Both will then be followed by the Axiom commercial tourist flight on a Dragon capsule early in ’22. Expect such commercial manned flights to become somewhat routine in the coming years.
UPDATE: China also launched an Earth observation satellite yesterday, using its Long March 4B rocket
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
10 SpaceX
8 China
6 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. still leads China 14 to 8 in the national rankings.
Russia today successfully used its Soyuz-2 rocket to launch three astronauts to ISS.
Because this flight is occurring three days before the 60th anniversary of Yuri Gagarin’s first human flight in space, the Russians gave the Soyuz capsule his name to honor him and the event. The spacecraft docked with ISS only two orbits later.
The crew also included an American, Mark Vande Hei, who is flying as part of the new barter agreement with Russia, whereby Americans fly in Soyuz in exchange for Russians flying in American commercial capsule. This was the first time NASA paid nothing for a flight on Soyuz since the shuttle retired a decade ago.
The return to Earth of Vande Hei and his fellow crew member Pyotr Dubrov will be on the next Soyuz capsule to launch in October, MS-19, in order to accommodate a short visit by a Russian movie director and actress.
Roscosmos will launch Soyuz MS-19 no earlier than October 5 with Commander Anton Shkaplerov and two civilian spaceflight participants. Russian film director Klim Shipenko and a Russian actress, who is yet to be named, will film a movie called “The Challenge” and spend approximately a week aboard the ISS before returning to Earth aboard Soyuz MS-18 with Novitsky.
With this commercial manned flight there will be two such flights in the fall, the Dragon Inspiration4 flight that will not dock with ISS and this Russian one. Both will then be followed by the Axiom commercial tourist flight on a Dragon capsule early in ’22. Expect such commercial manned flights to become somewhat routine in the coming years.
UPDATE: China also launched an Earth observation satellite yesterday, using its Long March 4B rocket
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
10 SpaceX
8 China
6 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. still leads China 14 to 8 in the national rankings.
Cat Stevens – Moonshadow
An evening pause: A lovely song, performed live in 1971 before he became a overzealous Islamist.
Hat tip Roland.
Jolie Môme – C’est Si Bon
SpaceX successfully launches another sixty Starlink satellites
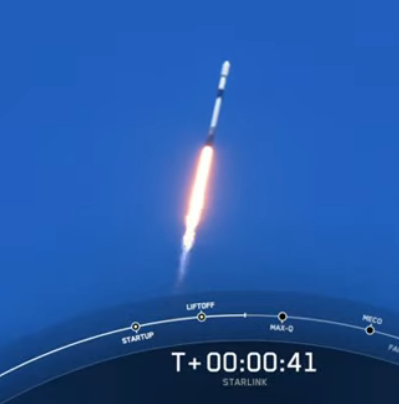
SpaceX this morning successfully launched another 60 Starlink satellites, bringing the total number in orbit to more than 1,500.
The first stage, on its seventh flight, successfully landed on the drone ship. During SpaceX’s live stream they noted that every launch by the company this year has used a previously flown first stage. Both fairings on this flight were also reused.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
10 SpaceX
7 China
5 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 14 to 7 in the national rankings.
I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream below the fold. Because of the clear weather this was a particularly beautiful launch. The video during the landing of the first stage was especially spectacular, with the camera on the booster showing the entire landing.
» Read more

SpaceX this morning successfully launched another 60 Starlink satellites, bringing the total number in orbit to more than 1,500.
The first stage, on its seventh flight, successfully landed on the drone ship. During SpaceX’s live stream they noted that every launch by the company this year has used a previously flown first stage. Both fairings on this flight were also reused.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
10 SpaceX
7 China
5 Russia
2 Rocket Lab
The U.S. now leads China 14 to 7 in the national rankings.
I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream below the fold. Because of the clear weather this was a particularly beautiful launch. The video during the landing of the first stage was especially spectacular, with the camera on the booster showing the entire landing.
» Read more
The Carol Burnett Show – The Hitman
SpaceX’s decision to build launchpad with Starship tanks proves the rocket will be cheapest ever built
Capitalism in space: The decision by SpaceX’s to build the tank farm for its Starship/Super Heavy launchpad at Boca Chica using Starship tanks, rather than inexpensive off-the-shelf storage tanks, strongly suggests that the company’s manufacturing facility for building those tanks makes them very inexpensive, and also suggests that the final rocket will be as cheap to launch as SpaceX has promised.
SpaceX is effectively taking identical rocket parts, slightly tweaking a handful of those parts, and turning what could have been a rocket into a propellant storage tank. This is significant because relative to all other rockets in history, even including SpaceX’s own Falcon 9 and Heavy, building storage tanks with unchanged rocket parts on a rocket assembly line would be roughly akin to hiring Vincent van Gogh to paint lane lines.
Ever since Elon Musk made the radical decision to switch from composite structures to stainless steel, Starship has always aimed to be radically different than any large rocket before it. Crucially, by using commodity steel, the CEO imagined SpaceX would be able to build Starships fairly easily and for pennies on the dollar next to even SpaceX’s exceptionally affordable Falcon 9. In the last 18 months, it’s become apparent that SpaceX has built a factory capable of churning out one or two massive steel rockets per month and is willing to consign at least four or five of those Starship prototypes to all-but-guaranteed failures for the sake of data-gathering and iterative improvement.
Technically, the most logical conclusion would be that Musk was right and that SpaceX has quickly developed the ability to build steel rockets larger than any other launch vehicle on Earth for perhaps just $5M or less apiece.
The analysis at the link is detailed and worth reading. If correct, this decision by SpaceX proves that Starship and Super Heavy will be the cheapest rocket ever flown, even though it will be the largest ever flown, and also completely reusable.
Capitalism in space: The decision by SpaceX’s to build the tank farm for its Starship/Super Heavy launchpad at Boca Chica using Starship tanks, rather than inexpensive off-the-shelf storage tanks, strongly suggests that the company’s manufacturing facility for building those tanks makes them very inexpensive, and also suggests that the final rocket will be as cheap to launch as SpaceX has promised.
SpaceX is effectively taking identical rocket parts, slightly tweaking a handful of those parts, and turning what could have been a rocket into a propellant storage tank. This is significant because relative to all other rockets in history, even including SpaceX’s own Falcon 9 and Heavy, building storage tanks with unchanged rocket parts on a rocket assembly line would be roughly akin to hiring Vincent van Gogh to paint lane lines.
Ever since Elon Musk made the radical decision to switch from composite structures to stainless steel, Starship has always aimed to be radically different than any large rocket before it. Crucially, by using commodity steel, the CEO imagined SpaceX would be able to build Starships fairly easily and for pennies on the dollar next to even SpaceX’s exceptionally affordable Falcon 9. In the last 18 months, it’s become apparent that SpaceX has built a factory capable of churning out one or two massive steel rockets per month and is willing to consign at least four or five of those Starship prototypes to all-but-guaranteed failures for the sake of data-gathering and iterative improvement.
Technically, the most logical conclusion would be that Musk was right and that SpaceX has quickly developed the ability to build steel rockets larger than any other launch vehicle on Earth for perhaps just $5M or less apiece.
The analysis at the link is detailed and worth reading. If correct, this decision by SpaceX proves that Starship and Super Heavy will be the cheapest rocket ever flown, even though it will be the largest ever flown, and also completely reusable.
Rocket startup ABL Space gets giant Lockheed Martin launch contract
Capitalism in space: Smallsat rocket startup ABL Space, which has yet to launch its first test rocket, has won a gigantic launch contract from Lockheed Martin for as many as 58 launches through 2029.
Under terms of the block-buy agreement between ABL Space Systems and Lockheed, the aerospace giant will purchase “up to” 26 launches through 2026 and as many as 32 additional launches through 2029. If the terms are fulfilled, this would come to 58 launches over the next eight years for ABL Space. In an industry where even a single launch contract often produces a news release, a contract for five dozen launches is unprecedented for a private company.
…The partnership will allow Lockheed, which builds large numbers of satellites for commercial customers, frequent and low-cost access to space. It is perhaps not a surprise that Lockheed selected ABL Space for its small launch needs, as Lockhead was an early investor in the launch company during a seed phase in 2019 and has continued to participate in additional rounds of fundraising. ABL has raised a total of $219 million to date.
Though Lockheed Martin is not ABL’s biggest investor, by being an early investor it has been involved in the development of ABL’s RS1 rocket from the start, which also means that Lockheed Martin was essentially buying its own rocket company to place the satellites it makes into orbit.
In fact, this decision falls into line with what appears to be Lockheed Martin’s long term corporate strategy. In 2017 the company opened its satellite-making factory with the satellites designed with standardized structures so that customers could pick and choose the design of their liking.
In 2018 it was revealed that the company was a key investor in Rocket Lab, while also participating in the creation of the United Kingdom’s first spaceport in Sutherland, Scotland.
It then decided to become a major investor in ABL, probably taking advantage of what it learned from Rocket Lab to improve the design. Now it plans to use that new rocket to launch a large number of the smallsats it is building in its factory.
Lockheed Martin is essentially copying SpaceX’s vertical integration strategy, whereby it owns or builds all aspects of its launch business. This allows it to reduce costs while controlling construction entirely. You cut out the middle man, and make your satellites cheaper to sell to others.
The first launch of ABL’s RS1 rocket was originally scheduled for the first half of this year, but has now been pushed back to the third quarter. If successful the company says it will follow it with two more launches before the end of the year, and very ambitious schedule.
Capitalism in space: Smallsat rocket startup ABL Space, which has yet to launch its first test rocket, has won a gigantic launch contract from Lockheed Martin for as many as 58 launches through 2029.
Under terms of the block-buy agreement between ABL Space Systems and Lockheed, the aerospace giant will purchase “up to” 26 launches through 2026 and as many as 32 additional launches through 2029. If the terms are fulfilled, this would come to 58 launches over the next eight years for ABL Space. In an industry where even a single launch contract often produces a news release, a contract for five dozen launches is unprecedented for a private company.
…The partnership will allow Lockheed, which builds large numbers of satellites for commercial customers, frequent and low-cost access to space. It is perhaps not a surprise that Lockheed selected ABL Space for its small launch needs, as Lockhead was an early investor in the launch company during a seed phase in 2019 and has continued to participate in additional rounds of fundraising. ABL has raised a total of $219 million to date.
Though Lockheed Martin is not ABL’s biggest investor, by being an early investor it has been involved in the development of ABL’s RS1 rocket from the start, which also means that Lockheed Martin was essentially buying its own rocket company to place the satellites it makes into orbit.
In fact, this decision falls into line with what appears to be Lockheed Martin’s long term corporate strategy. In 2017 the company opened its satellite-making factory with the satellites designed with standardized structures so that customers could pick and choose the design of their liking.
In 2018 it was revealed that the company was a key investor in Rocket Lab, while also participating in the creation of the United Kingdom’s first spaceport in Sutherland, Scotland.
It then decided to become a major investor in ABL, probably taking advantage of what it learned from Rocket Lab to improve the design. Now it plans to use that new rocket to launch a large number of the smallsats it is building in its factory.
Lockheed Martin is essentially copying SpaceX’s vertical integration strategy, whereby it owns or builds all aspects of its launch business. This allows it to reduce costs while controlling construction entirely. You cut out the middle man, and make your satellites cheaper to sell to others.
The first launch of ABL’s RS1 rocket was originally scheduled for the first half of this year, but has now been pushed back to the third quarter. If successful the company says it will follow it with two more launches before the end of the year, and very ambitious schedule.
Melanie Oesch – From a Jack to a King
An evening pause: Hat tip from Jim Mallamace, who adds that she is singing “with her father, mother, and two brothers. So wholesome.” And from Switzerland no less.
