Frozen lava flows around Martian hills
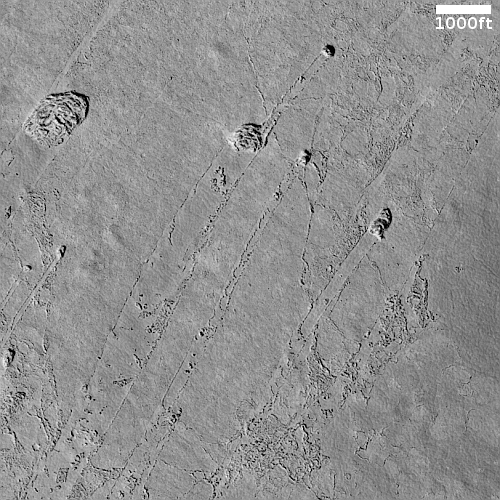
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on August 24, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows the westernmost edge of the Athabasca flood lava plain, thought to be the youngest lava flow on Mars, having covered the area of Great Britain in a matter of weeks 600 million years ago.
This image was a captioned feature yesterday by the MRO science team. As they note:
Although you can’t sail a boat on a sea of lava, hills and craters that stick up higher than the lava flow act like barriers. When a boat is driven through the water, there is a bow wave at the front of the boat, and a wake that trails off behind that indicates which way the boat is moving. In a lava flow, when a hill sticks up, the lava piles up on the upstream side (just like a bow wave) and can leave a wake on the downstream side, so we can tell which way the lava was moving against the stationary hill.
As you can see, every hill has a pile of lava on its northeast slopes, and a wake to its southeast. As the main vent of the Athabasca eruption is to the northeast, about 500 miles away (as shown on the overview map below), the flow direction suggested by the wakes fit the general geography.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on August 24, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows the westernmost edge of the Athabasca flood lava plain, thought to be the youngest lava flow on Mars, having covered the area of Great Britain in a matter of weeks 600 million years ago.
This image was a captioned feature yesterday by the MRO science team. As they note:
Although you can’t sail a boat on a sea of lava, hills and craters that stick up higher than the lava flow act like barriers. When a boat is driven through the water, there is a bow wave at the front of the boat, and a wake that trails off behind that indicates which way the boat is moving. In a lava flow, when a hill sticks up, the lava piles up on the upstream side (just like a bow wave) and can leave a wake on the downstream side, so we can tell which way the lava was moving against the stationary hill.
As you can see, every hill has a pile of lava on its northeast slopes, and a wake to its southeast. As the main vent of the Athabasca eruption is to the northeast, about 500 miles away (as shown on the overview map below), the flow direction suggested by the wakes fit the general geography.
» Read more