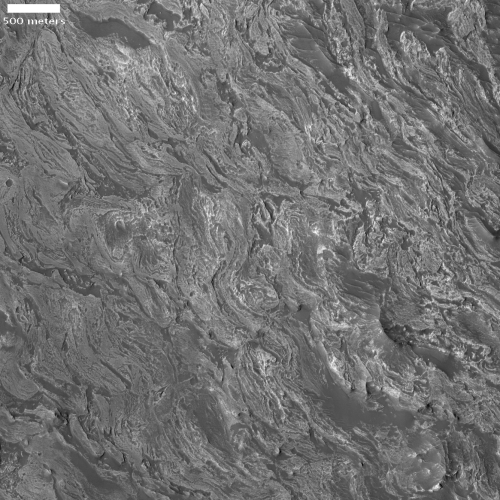
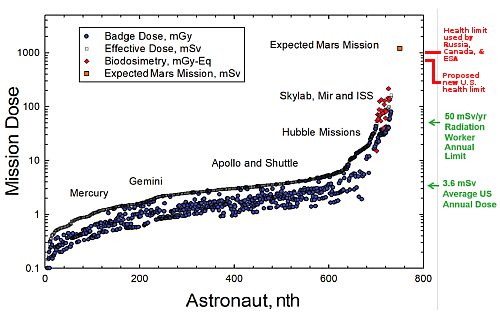
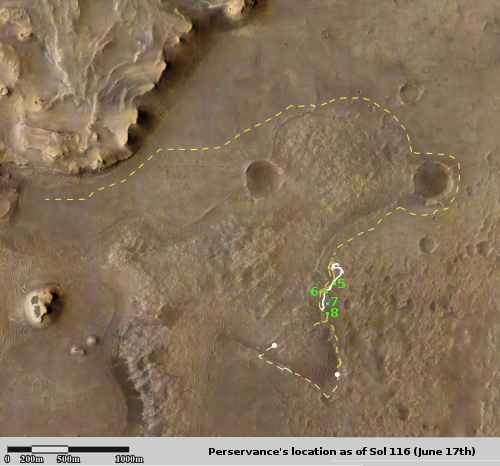
SpaceX successfully launches 88 smallsats, marking a renaissance in rocketry in 2021

First stage landing at Cape Canaveral today
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to place 88 smallsats into orbit, the third rocket launch today.
While Transporter-2 won’t beat the unprecedented number of satellites launched on on Transporter-1 [the first such smallsat launch by SpaceX earlier this year], SpaceX says it will still “launch 88 spacecraft to orbit” and – more importantly – carry more customer mass. In other words, Transporter-2 will carry roughly 50% fewer satellites, each of which will weigh substantially more on average.
Ordering directly through SpaceX, [the price] begins at $1 million for up to 200 kg (~440 lb). … A majority of small satellites weigh significantly less than 200 kilograms but if a customer manages to use all of their allotment, the total cost of a SpaceX rideshare launch could be as low as $5000 per kilogram – incredibly cheap relative to almost any other option. For a [comparable] launch … on a Rocket Lab Electron or Astra Rocket 3.0 rocket using every last gram of available performance, the same customer would end up paying a minimum of $25,000 to $37,500 per kilogram to orbit.
The launch also included a handful of Starlink satellites, adding to SpaceX’s constellation. I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream below the fold. As I write this the satellites have not yet been deployed from the second stage, but that should happen shortly.
The first stage landed successfully, the eighth time this booster has done so. The fairings were also reused, completing their third flight. All told, this was SpaceX’s 20th launch in 2021, 18 of which used reused boosters.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
» Read more

First stage landing at Cape Canaveral today
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully used its Falcon 9 rocket to place 88 smallsats into orbit, the third rocket launch today.
While Transporter-2 won’t beat the unprecedented number of satellites launched on on Transporter-1 [the first such smallsat launch by SpaceX earlier this year], SpaceX says it will still “launch 88 spacecraft to orbit” and – more importantly – carry more customer mass. In other words, Transporter-2 will carry roughly 50% fewer satellites, each of which will weigh substantially more on average.
Ordering directly through SpaceX, [the price] begins at $1 million for up to 200 kg (~440 lb). … A majority of small satellites weigh significantly less than 200 kilograms but if a customer manages to use all of their allotment, the total cost of a SpaceX rideshare launch could be as low as $5000 per kilogram – incredibly cheap relative to almost any other option. For a [comparable] launch … on a Rocket Lab Electron or Astra Rocket 3.0 rocket using every last gram of available performance, the same customer would end up paying a minimum of $25,000 to $37,500 per kilogram to orbit.
The launch also included a handful of Starlink satellites, adding to SpaceX’s constellation. I have embedded SpaceX’s live stream below the fold. As I write this the satellites have not yet been deployed from the second stage, but that should happen shortly.
The first stage landed successfully, the eighth time this booster has done so. The fairings were also reused, completing their third flight. All told, this was SpaceX’s 20th launch in 2021, 18 of which used reused boosters.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
» Read more