Movie of Juno’s September 1 fly-by of Jupiter
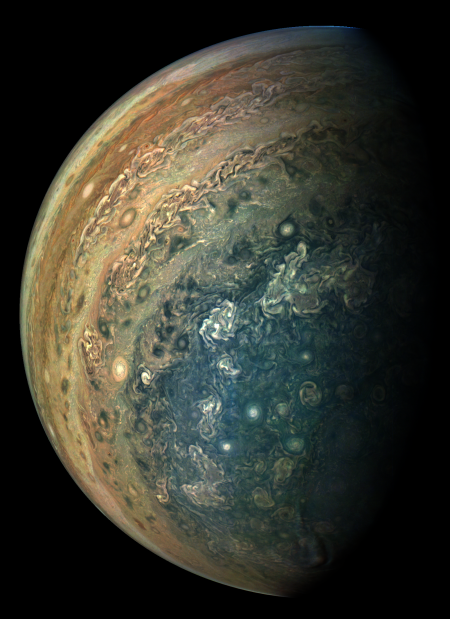
Citizen scientist Gerald Eichstädt has done it again, assembling and enhancing the images taken by Juno in its September 1, 2017 fly-by of Jupiter to produce a spectacular movie, embedded below.
In his words,
This animation reconstructs the two and a half hours from 2017-09-01T20:45:00 to 2017-09-01T23:15:00 in 125-fold time-lapse with 25 frames per second, using 20 raw JunoCam images. JunoCam is Juno’s optical and near infrared Education and Public Outreach camera.
Trajectory data are retrieved from SPICE kernels via the NAIF spy.exe tool. The NAIF/SPICE environment is the way NASA provides spacecraft navigation data.
The movie shows Jupiter in a heavily enhanced way, in order to reveal detail.
Some of the raw images cover only part of the area required to render a still of the movie. In these cases, you’ll see the border of the raw image.
Each image is rendered into a short scene. The scences overlap and are blended.
Rendering the movie took about five days. Any shortcomings of the movie are a result of imperfect image processing.
Citizen scientist Gerald Eichstädt has done it again, assembling and enhancing the images taken by Juno in its September 1, 2017 fly-by of Jupiter to produce a spectacular movie, embedded below.
In his words,
This animation reconstructs the two and a half hours from 2017-09-01T20:45:00 to 2017-09-01T23:15:00 in 125-fold time-lapse with 25 frames per second, using 20 raw JunoCam images. JunoCam is Juno’s optical and near infrared Education and Public Outreach camera.
Trajectory data are retrieved from SPICE kernels via the NAIF spy.exe tool. The NAIF/SPICE environment is the way NASA provides spacecraft navigation data.
The movie shows Jupiter in a heavily enhanced way, in order to reveal detail.
Some of the raw images cover only part of the area required to render a still of the movie. In these cases, you’ll see the border of the raw image.
Each image is rendered into a short scene. The scences overlap and are blended.
Rendering the movie took about five days. Any shortcomings of the movie are a result of imperfect image processing.