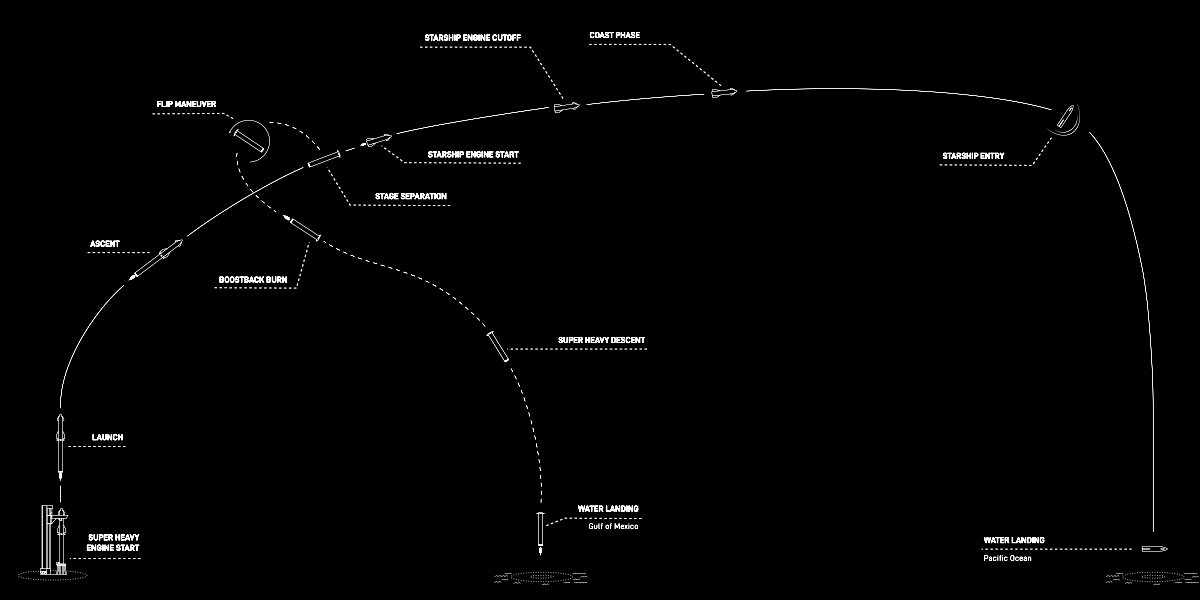
FAA announces it has rubber-stamped SpaceX’s investigation of the November Starship/Superheavy test launch
The FAA yesterday announced that it has completed its review of SpaceX’s investigation of the November Starship/Superheavy test launch and has approved the company’s conclusions.
The Federal Aviation Administration has concluded its review of SpaceX’s investigation of the second Starship launch in November, with the regulator saying Monday that it accepted the “root causes and 17 corrective actions” identified by the company.
While this means the investigation is now closed, SpaceX must implement all the corrective actions and apply for a modified launch license before it can fly Starship again. “The FAA is evaluating SpaceX’s license modification request and expects SpaceX to submit additional required information before a final determination can be made,” the regulator said in a statement Monday.
You can read a SpaceX update of its investigation here. As previously reported, when Starship vented the extra oxygen carried to better simulate a payload it caused “a combustion event” and fires that cut off communications.
This resulted in a commanded shut down of all six engines prior to completion of the ascent burn, followed by the Autonomous Flight Safety System detecting a mission rule violation and activating the flight termination system, leading to vehicle breakup. The flight test’s conclusion came when the spacecraft was as at an altitude of ~150 km and a velocity of ~24,000 km/h, becoming the first Starship to reach outer space.
Despite SpaceX’s report, which states the company “has implemented hardware changes” to prevent a reoccurance, the FAA has still not yet issued a launch license. Based on these updates and Elon Musk’s own prediction, it appears a license will be forthcoming in the next two weeks, matching my December prediction of a March launch. Expect SpaceX to quickly launch, as it has “more Starships ready to fly,” and it wants to fly them fast in order to refine the engineering so as to move to operational flights.
It is also possible that the FAA will continue to slow-walk its approvals, and SpaceX might be left hanging for more than two weeks. Had the government not been involved, all signs suggested that SpaceX would have done its third test flight in January, and would have now been gearing up for its fourth flight. That was the kind of pace SpaceX set when it was doing its first Starship test flights during the Trump administration. The government under Joe Biden’s presidency however is not allowing that kind of launch pace.
The FAA yesterday announced that it has completed its review of SpaceX’s investigation of the November Starship/Superheavy test launch and has approved the company’s conclusions.
The Federal Aviation Administration has concluded its review of SpaceX’s investigation of the second Starship launch in November, with the regulator saying Monday that it accepted the “root causes and 17 corrective actions” identified by the company.
While this means the investigation is now closed, SpaceX must implement all the corrective actions and apply for a modified launch license before it can fly Starship again. “The FAA is evaluating SpaceX’s license modification request and expects SpaceX to submit additional required information before a final determination can be made,” the regulator said in a statement Monday.
You can read a SpaceX update of its investigation here. As previously reported, when Starship vented the extra oxygen carried to better simulate a payload it caused “a combustion event” and fires that cut off communications.
This resulted in a commanded shut down of all six engines prior to completion of the ascent burn, followed by the Autonomous Flight Safety System detecting a mission rule violation and activating the flight termination system, leading to vehicle breakup. The flight test’s conclusion came when the spacecraft was as at an altitude of ~150 km and a velocity of ~24,000 km/h, becoming the first Starship to reach outer space.
Despite SpaceX’s report, which states the company “has implemented hardware changes” to prevent a reoccurance, the FAA has still not yet issued a launch license. Based on these updates and Elon Musk’s own prediction, it appears a license will be forthcoming in the next two weeks, matching my December prediction of a March launch. Expect SpaceX to quickly launch, as it has “more Starships ready to fly,” and it wants to fly them fast in order to refine the engineering so as to move to operational flights.
It is also possible that the FAA will continue to slow-walk its approvals, and SpaceX might be left hanging for more than two weeks. Had the government not been involved, all signs suggested that SpaceX would have done its third test flight in January, and would have now been gearing up for its fourth flight. That was the kind of pace SpaceX set when it was doing its first Starship test flights during the Trump administration. The government under Joe Biden’s presidency however is not allowing that kind of launch pace.