Rocket startup Stoke Space raises an additional $350 million in private investment capital
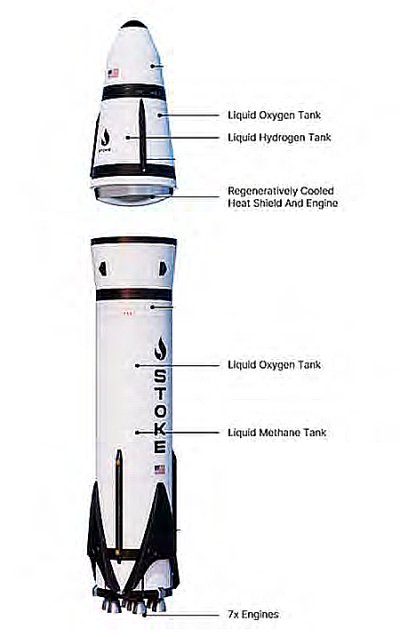

Stoke’s Nova rocket, designed to be
completely reusable.
The rocket startup Stoke Space yesterday announced that its most recent fund-raising round has raised an additional $350 million in private investment capital above the original target of $510 million.
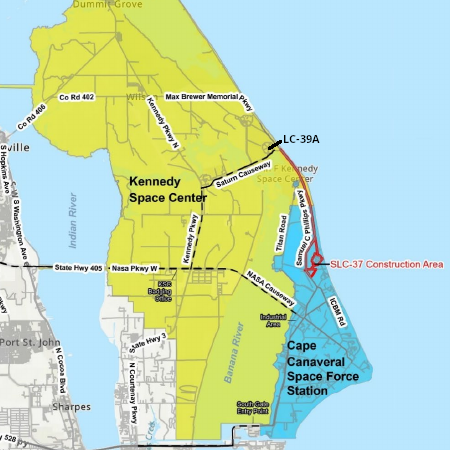
Stoke Space Technologies, the rocket company developing fully and rapidly reusable medium-lift launch vehicles, announced today an extension of its previous Series D financing, bringing the total amount raised in the round to $860 million. The round was initially announced in October 2025 at $510 million. That funding focused on completing activation of Launch Complex 14 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Fla., and expanding production capacity for the Nova launch vehicle. Stoke will use the additional capital to accelerate future elements of its product roadmap.
In total the company has now raises $1.34 billion. Though it has been moving steadily towards the first test launch of its totally reusable Nova rocket, it has so far refused to announce any launch dates. Based on all accounts, it appears that launch could occur before the end of this year, but nothing is confirmed.
Stoke’s ability to raise so much capital contrasts sharply with the failure of the British rocket startup Orbex, as noted in my previous post. Investors know that when Stoke is ready to launch from Florida, it will be able to do so, and so they have confidence in the company. With Orbex no one was willing to invest because the investors recognized that red tape was handicapping the company.

Stoke’s Nova rocket, designed to be
completely reusable.
The rocket startup Stoke Space yesterday announced that its most recent fund-raising round has raised an additional $350 million in private investment capital above the original target of $510 million.
Stoke Space Technologies, the rocket company developing fully and rapidly reusable medium-lift launch vehicles, announced today an extension of its previous Series D financing, bringing the total amount raised in the round to $860 million. The round was initially announced in October 2025 at $510 million. That funding focused on completing activation of Launch Complex 14 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Fla., and expanding production capacity for the Nova launch vehicle. Stoke will use the additional capital to accelerate future elements of its product roadmap.
In total the company has now raises $1.34 billion. Though it has been moving steadily towards the first test launch of its totally reusable Nova rocket, it has so far refused to announce any launch dates. Based on all accounts, it appears that launch could occur before the end of this year, but nothing is confirmed.
Stoke’s ability to raise so much capital contrasts sharply with the failure of the British rocket startup Orbex, as noted in my previous post. Investors know that when Stoke is ready to launch from Florida, it will be able to do so, and so they have confidence in the company. With Orbex no one was willing to invest because the investors recognized that red tape was handicapping the company.