SpaceX is now targeting January 13, 2025 for 7th Starship/Superheavy test launch
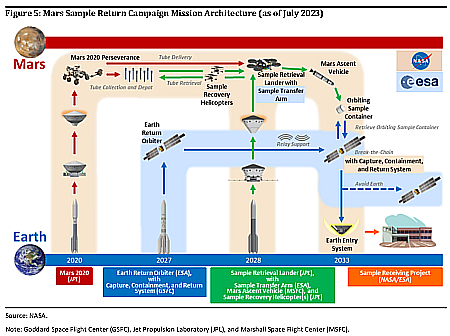
In a tweet yesterday, SpaceX announced that it now intends to fly the seventh test orbital launch of Starship/Superheavy no earlier than January 13, 2025, with a launch window opening at 4 pm (Central).
The launch will test numerous new systems. Superheavy will test the reuse of one of the engines used on the fifth flight, brought back successfully when the booster was successfully caught by the tower chopsticks. It will also test improvements to the launch tower as another chopstick catch will be attempted. As for this Starship prototype, which the company calls Version 2, the upgrades and tests are extensive:
- New avionics
- Redesigns in the propulsion system
- The flaps have been shrunk and shifted in position to prevent heat damage
- The tiled heat shield system has been further upgraded
- Deployment test of 10 dummy Starlink satellites
- An in-orbit Raptor-2 engine relight
The last test is critical for future orbital test flights. On this test Starship will follow the same orbital flight path as the previous flights, low enough that the atmosphere will force it down without action over the Indian Ocean. SpaceX needs to prove that Starship’s Raptor-2 engines can reliably be restarted before it can go to full orbits that will require such a relight to accurately bring the spacecraft down at the right place.
In a tweet yesterday, SpaceX announced that it now intends to fly the seventh test orbital launch of Starship/Superheavy no earlier than January 13, 2025, with a launch window opening at 4 pm (Central).
The launch will test numerous new systems. Superheavy will test the reuse of one of the engines used on the fifth flight, brought back successfully when the booster was successfully caught by the tower chopsticks. It will also test improvements to the launch tower as another chopstick catch will be attempted. As for this Starship prototype, which the company calls Version 2, the upgrades and tests are extensive:
- New avionics
- Redesigns in the propulsion system
- The flaps have been shrunk and shifted in position to prevent heat damage
- The tiled heat shield system has been further upgraded
- Deployment test of 10 dummy Starlink satellites
- An in-orbit Raptor-2 engine relight
The last test is critical for future orbital test flights. On this test Starship will follow the same orbital flight path as the previous flights, low enough that the atmosphere will force it down without action over the Indian Ocean. SpaceX needs to prove that Starship’s Raptor-2 engines can reliably be restarted before it can go to full orbits that will require such a relight to accurately bring the spacecraft down at the right place.