Italian rocket company Avio wins two launch contracts valued at $117 million total
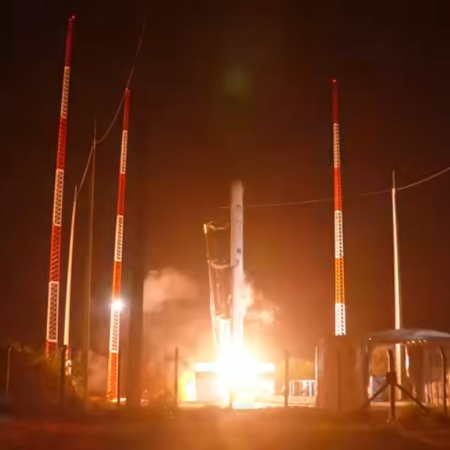
Last week the Italian rocket company Avio announced that it has signed launch contracts for its Vega-C rocket with two different unnamed satellite customers, the value of the contracts equaling $117 million total.
The satellites to be launched will be used for Earth observation, environmental monitoring and resource management purposes for civil and scientific applications, providing high-resolution imagery as well as best-in-class geolocation accuracy. The passengers will feature a mass ranging from more than 400 to more than 1,000 kilograms and will be deployed into a ~500 km Sun-synchronous orbit.
These contracts totally secure over EUR 100 million for launch services to be scheduled between 2028 and 2031.
Though the customers remain unnamed, the Avio release indicated that one was from Europe and the other was non-European. That latter contract deal could be linked to Avio’s announcement at about the same time that it is spending $500 million to build a rocket facility in Virginia. If the non-European customer was American and its satellites were for the Pentagon, having a U.S.-based facility made that contract award far more likely.
Last week the Italian rocket company Avio announced that it has signed launch contracts for its Vega-C rocket with two different unnamed satellite customers, the value of the contracts equaling $117 million total.
The satellites to be launched will be used for Earth observation, environmental monitoring and resource management purposes for civil and scientific applications, providing high-resolution imagery as well as best-in-class geolocation accuracy. The passengers will feature a mass ranging from more than 400 to more than 1,000 kilograms and will be deployed into a ~500 km Sun-synchronous orbit.
These contracts totally secure over EUR 100 million for launch services to be scheduled between 2028 and 2031.
Though the customers remain unnamed, the Avio release indicated that one was from Europe and the other was non-European. That latter contract deal could be linked to Avio’s announcement at about the same time that it is spending $500 million to build a rocket facility in Virginia. If the non-European customer was American and its satellites were for the Pentagon, having a U.S.-based facility made that contract award far more likely.