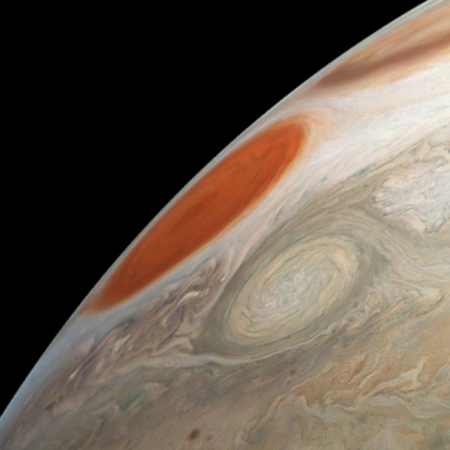
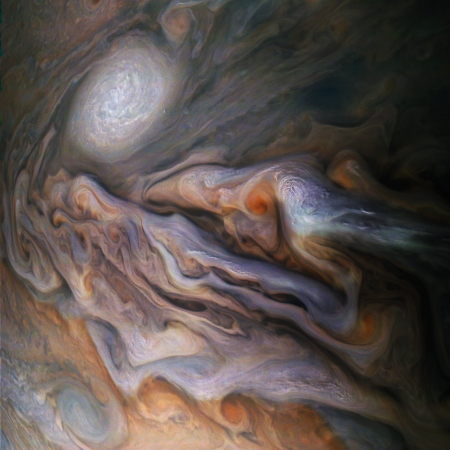
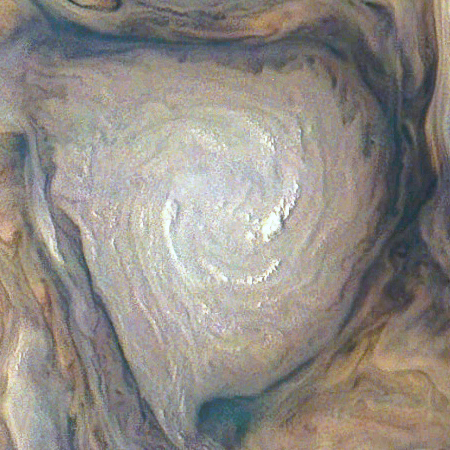
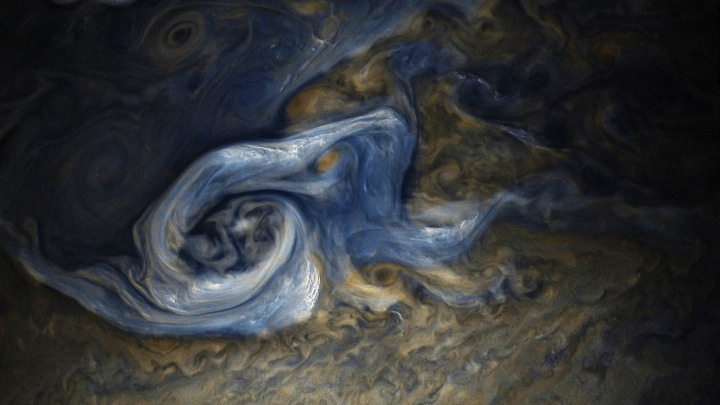
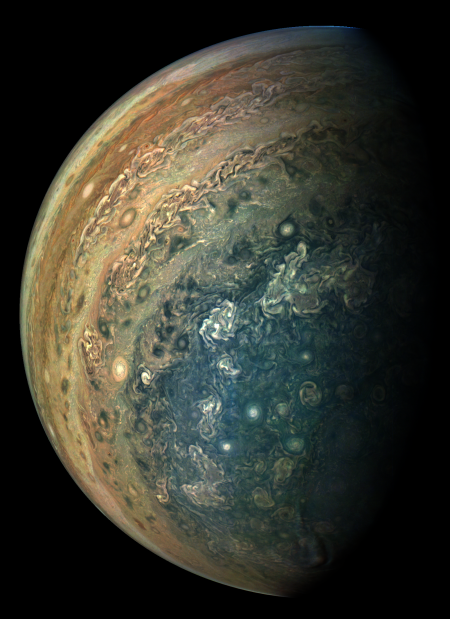
The uncertainty of science: New results from Juno reveal that the jet-stream-type bands visible on the surface extend down to 1,900 miles, deeper than expected. Below that,
…the planet rotates nearly as a rigid body.”This is really an amazing result, and future measurements by Juno will help us understand how the transition works between the weather layer and the rigid body below,” said Tristan Guillot, a Juno co-investigator from the Université Côte d’Azur, Nice, France, and lead author of the paper on Jupiter’s deep interior. “Juno’s discovery has implications for other worlds in our solar system and beyond. Our results imply that the outer differentially-rotating region should be at least three times deeper in Saturn and shallower in massive giant planets and brown dwarf stars.”
Scientists had not expected the atmosphere go that deep.
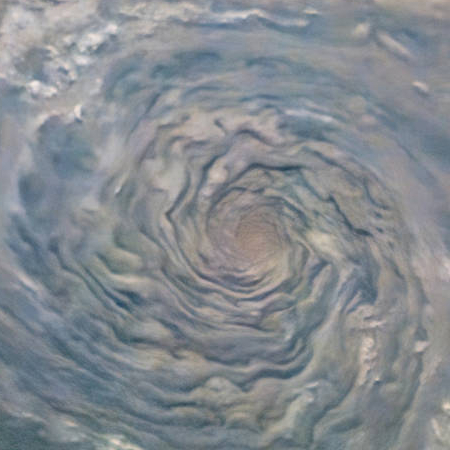
Other results show that that the gas giant’s complex polar regions are surprising as well.
Its north pole is dominated by a central cyclone surrounded by eight circumpolar cyclones with diameters ranging from 2,500 to 2,900 miles (4,000 to 4,600 kilometers) across. Jupiter’s south pole also contains a central cyclone, but it is surrounded by five cyclones with diameters ranging from 3,500 to 4,300 miles (5,600 to 7,000 kilometers) in diameter. Almost all the polar cyclones, at both poles, are so densely packed that their spiral arms come in contact with adjacent cyclones. However, as tightly spaced as the cyclones are, they have remained distinct, with individual morphologies over the seven months of observations detailed in the paper.
“The question is, why do they not merge?” said Adriani. “We know with Cassini data that Saturn has a single cyclonic vortex at each pole. We are beginning to realize that not all gas giants are created equal.”
I am always baffled when scientists are surprised at the infinite variety of the universe. It is absurd to assume Jupiter and Saturn would be alike, especially considering the history of solar system exploration since the dawn of the space age. Since the first probe got a close look at the Moon, every single new object observed has been completely different from every other previously observed object. Every object has been unique. None have been the same.
Jupiter should be no different. And I guarantee that the next fifty gas giants we finally get a close look at out there among the stars will be as different from each other as they are from Jupiter. It is going to take a lot of exploration for us to finally get a handle on the overall patterns of planetary formation.