A pimple on Mars
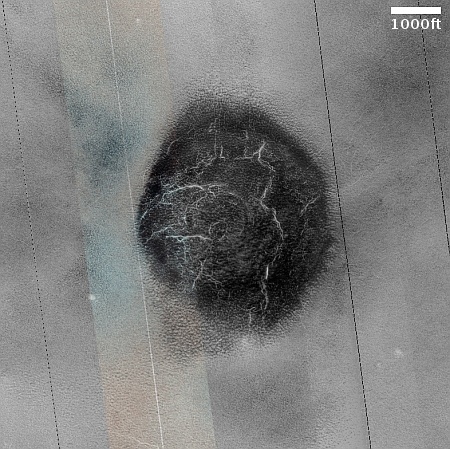
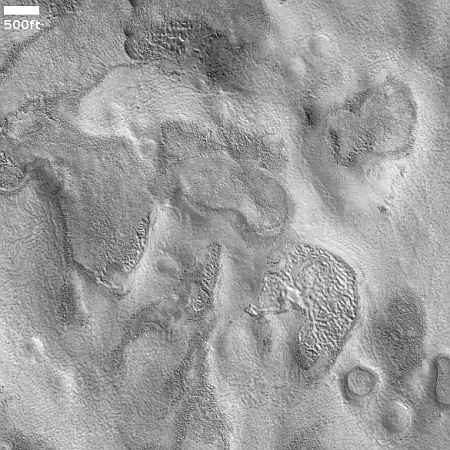
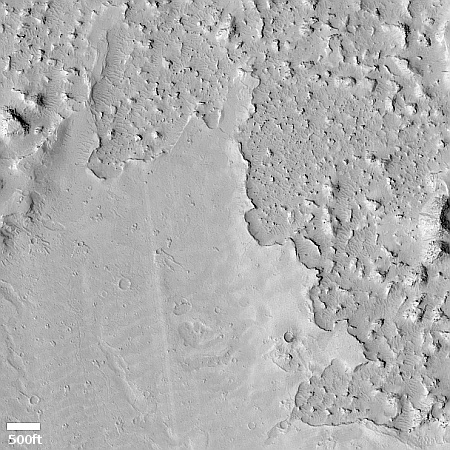
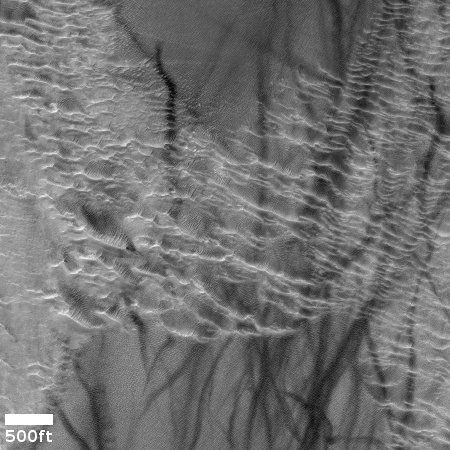
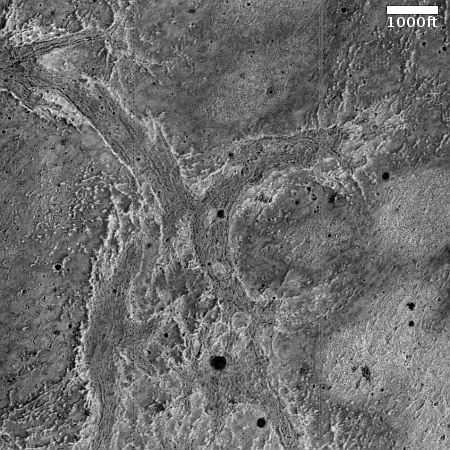
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on November 1, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Labeled simply as a “terrain sample,” it was likely not taken as part of any specific research project, but to fill a gap in the camera’s schedule in order to maintain its proper temperature. When the camera team does this they try to pick something interesting, and sometimes succeed.
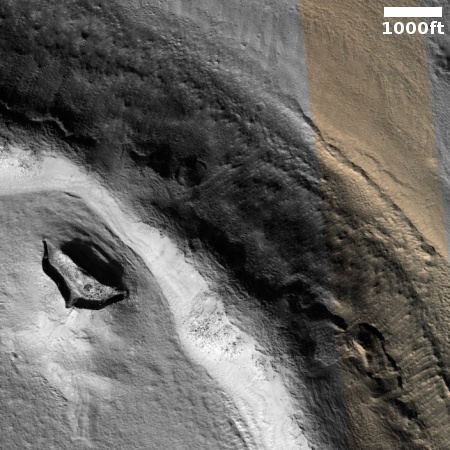
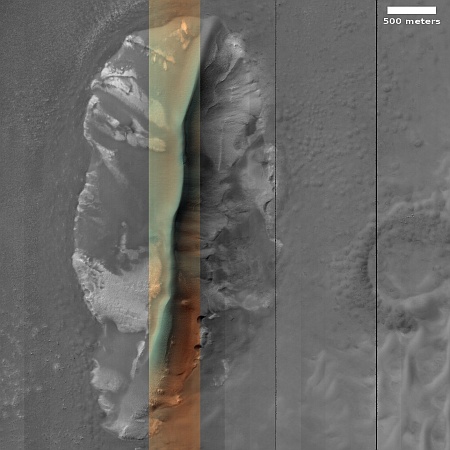
I think they succeeded in this case. At first glance this appears to be a crater, but on closer inspection it is instead a small mound. The picture was taken in the winter, at the high latitude of 55 degrees north. The featureless white surface surrounding this dark mound is almost certainly the mantle of dry ice that falls as snow and covers the poles during the winter. If not that, it is then likely to be a water ice sheet that orbital data suggests covers much of Mars’ high latitudes.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on November 1, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Labeled simply as a “terrain sample,” it was likely not taken as part of any specific research project, but to fill a gap in the camera’s schedule in order to maintain its proper temperature. When the camera team does this they try to pick something interesting, and sometimes succeed.
I think they succeeded in this case. At first glance this appears to be a crater, but on closer inspection it is instead a small mound. The picture was taken in the winter, at the high latitude of 55 degrees north. The featureless white surface surrounding this dark mound is almost certainly the mantle of dry ice that falls as snow and covers the poles during the winter. If not that, it is then likely to be a water ice sheet that orbital data suggests covers much of Mars’ high latitudes.
» Read more