Could weird lunar crater be the crash site for Lunar Orbiter 2?
Could this weird lunar crater be the crash site for Lunar Orbiter 2?
Could this weird lunar crater be the crash site for Lunar Orbiter 2?
Could this weird lunar crater be the crash site for Lunar Orbiter 2?
In a piece today at the Huffington Post, science journalist Seth Borenstein declares the wonders of NASA’s next mission: to send astronauts to an asteroid by 2025, as declared by President Obama.
If you believe this is going to happen, then I have a bridge I want to sell you. To do it we need a spaceship in which people can live for at least a year, and a rocket to get that ship into orbit. Not only do we not yet know how to build such a spaceship, we no longer have the capability of putting it into orbit. In case you’re unaware (Borenstein acts like he is), the space shuttle no longer exists. And under this administration and Congress, any replacement we get isn’t going to be able to launch such an interplanetary spaceship anywhere in the near future, especially faced as we are with the present federal debt.
The disgraceful thing about this article, however, is the lack of skepticism shown by Borenstein.
» Read more
A public test of privately built moon lander has been delayed by gyro problem. Key quote:
One customer has already bought a ticket with Moon Express, asking them to deposit a small telescope on the dark side of the Moon. Jain says the company will also offer low cost ways for anyone to use the moon as a kind of time capsule. “If something goes to the moon it stays there forever, people will pay to sends things like photos, or maybe your hair or DNA.”
Bumped: I posted this essay last July 20th on the anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing on the moon. I think it is worth rereading again, even as the shuttle is about to return to Earth for the last time.
Today, July 20th, is the anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing on the Moon, the first time ever that a human being arrived on another planet. Americans love to celebrate this event, as it symbolizes one of the finest moments in our history, when we set out to achieve something truly great and noble and succeeded far better than we could have imagined. Not only did we get to the Moon as promised, over the next three and a half years we sent another five missions, each with increasingly sophisticated equipment, each sent to explore some increasingly alien terrain. Forty-plus years later, no one has come close to matching this achievement, a fact that emphasizes how difficult it was for the United States to accomplish it.
There is one small but very important detail about the Apollo 11 mission, however, that most Americans are unaware of. In mounting the American flag, the astronauts found the lunar surface much harder than expected. They had a great deal of trouble getting the flagpole into the ground. As Andrew Chaikin wrote in his book, A Man on the Moon, “For a moment it seemed the flag would fall over in front of a worldwide audience, but at last the men managed to steady it.” Then Armstrong took what has become one of the world’s iconic images, that of Buzz Aldrin standing on the lunar surface saluting the flag of the United States of America.

What people don’t know, however, is that when Armstrong and Aldrin blasted off from the lunar surface, the blast wave from the Lunar Module’s rocket knocked the flag over. As Chaikin also wrote, “Outside, a spray of gold foil and debris from the descent stage flew away in all directions. The flag toppled to the dust.”
Thus, for the last four decades this American flag, shown so proudly unfurled on the surface of the Moon, has actually been lying unceremoniously on the ground, in the lunar dust.
It might actually be possible to see this, though the photos at this time remain unclear and quite blurry.
» Read more
Hubble has discovered a fourth moon orbiting Pluto.
The second ARTEMIS space probe will enter lunar orbit on Sunday.
“With two spacecraft orbiting in opposite directions, we can acquire a full 3-D view of the structure of the magnetic fields near the moon and on the lunar surface,” said Vassilis Angelopoulos, principal investigator for the THEMIS and ARTEMIS missions and a professor of space physics at UCLA. “ARTEMIS will be doing totally new science, as well as reusing existing spacecraft to save a lot of taxpayer money.”
Confessions of a moon rock thief.
And in a related story: Fish captain fights to keep long-missing moon rock.

Since the 1990s, scientists have suspected that water-ice might be hidden in the forever-dark floors of the polar craters on the Moon. If so, these locations become valuable real estate, as they not only would provide future settlers water for drinking, the water itself can be processed to provide oxygen and fuel.
Moreover, the high points near these craters, including the crater rims, are hoped to be high enough so that the sun would never set or be blocked by other mountains as it made its circuit low along the horizon each day. If such a place existed, solar panels could be mounted there to generate electricity continuously, even during the long 14-day lunar night.
Below the fold is a six minute video, produced from images taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) from February 6, 2010 to February 6, 2011, in an effort to find out if such a place actually exists. It shows how the sunlight hits the south pole across an entire year.
» Read more
Mining the moon for water and fuel.
Texas-based Shackleton Energy Company has already begun operations aimed at mining the Moon within the next few years. The company’s plans for mining and refining operations would involve melting the ice and purifying the water, converting the water into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen, and then condensing the gases into liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, all potential rocket fuels.
Shackleton CEO Dale Tietz says the water extracted would be used almost exclusively as rocket fuel to power operations both within Low Earth Orbit (LEO) – such as space tourism and the removal of space-debris – on the Moon, and further out into space. ‘We are a for-profit business enterprise moving forward, and so we are only going there really for one reason and that is to mine, prospect mine and harvest water for rocket propellant production,’ says Tietz.
The first of two ARTEMIS spacecraft has successfully entered lunar orbit.
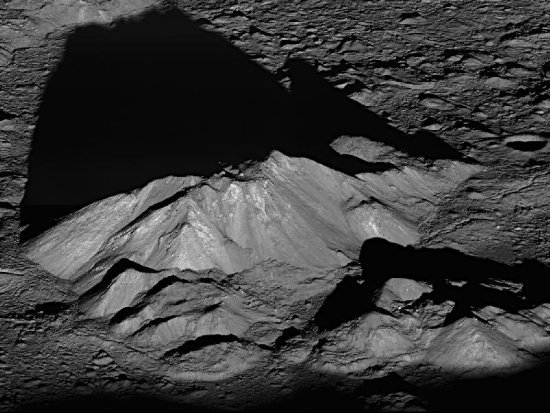
Another astonishing space photograph, this time from lunar orbit, taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter on June 11, 2011.
The image looks down at the central peak of Tycho crater, with enough detail to make out individual boulders at the summit. Go the link to see some closeups.

China’s second lunar probe, Chang’e 2, has been boosted out of lunar orbit and beyond.
A new analysis of a moon rock brought back by Apollo 17 has suggested that the water content of lunar magma is 100 times higher than previously thought.

Fifty years ago today, John Kennedy stood before Congress and the nation and declared that the United States was going to the Moon. Amazingly, though this is by far the most remembered speech Kennedy ever gave, very few people remember why he gave the speech, and what he was actually trying to achieve by making it.
Above all, going to the Moon and exploring space was not his primary goal.
For Kennedy — whose presidential campaign included an aggressive anti-communist stance against the Soviet Union — the months before the speech had not gone well. Five weeks earlier, for instance, the CIA-led attempt to invade Cuba and overthrow Castro’s communist government had ended in total failure. When Kennedy refused to lend direct military support to the Bay of Pigs invasion, the 1,200 man rebel force was quickly overcome. “How could I have been so stupid as to let them go ahead?” Kennedy complained privately to his advisors.
In Berlin, the tensions between the East and the West were continuing to escalate, and would lead in only a few short months to Khrushchev’s decision to build the Berlin Wall, sealing off East Berlin and the citizens of East Germany from the rest of the world.
In the race to beat the Soviets in space, things were going badly as well. NASA had announced the United States’ intention to put the first man into space sometime in the spring of 1961. The agency hoped that this flight would prove that the leader of the capitalist world still dominated the fields of technology, science, and exploration.
Originally scheduled for a March 6, 1961 launch, the short fifteen minute sub-orbital flight was repeatedly delayed. The Mercury capsule’s first test flight in January, with a chimpanzee as test pilot, rose forty miles higher than intended, overshot its landing by a hundred and thirty miles, and when the capsule was recovered three hours later it had begun leaking and was actually sinking. Then in March another test of the Mercury capsule included the premature firing of the escape rocket on top of the capsule, the unplanned release of the backup parachutes during descent, and the discovery of dents on the capsule itself.
These difficulties caused NASA to postpone repeatedly its first manned mission. First the agency rescheduled the launch to late March. Then early April. Then mid-April. And then it was too late.
» Read more
The next Moon mission, launching this summer.
A review of India’s troubled GSLV rocket has put a hold on its next moon probe.
Space Adventures and tourists to the Moon.
After consultation with Rocket Space Corporation Energia, modifications to the Soyuz TMA configuration have been agreed upon. The most important of which is the addition of a second habitation module to the Soyuz TMA lunar complex. The additional module would launch with the Block DM propulsion module and rendezvous with the Soyuz spacecraft in low-Earth orbit.
“Space Adventures will once again grace the pages of aerospace history, when the first private circumlunar mission launches. We have sold one of the two seats for this flight and anticipate that the launch will occur in 2015,” said Richard Garriott, Vice-Chairman of Space Adventures. “Having flown on the Soyuz, I can attest to how comfortable the spacecraft is, but the addition of the second habitation module will only make the flight that more enjoyable.”
Did a microbe survive 2.5 years attached to Surveyor 3 on the Moon, and then come home on Apollo 12? New research says no.
Confirmed: one of two tickets for a lunar flyby on a Soyuz has been sold. More here.
Software engineers to the Moon!
Crazy? Absolutely! Impossible? Probably not! There are a growing number of people who believe that with federal funding for our space program getting scarce, the future lies in private-public partnerships. Entrepreneur Elon Musk’s third job (after leading electric car company Tesla and acting as the Chairman of solar installer SolarCity) is heading up SpaceX, which was the first private company to successfully launch, orbit and recover a rocketship. Virgin’s Richard Branson has a similar private space venture.
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter website recently announced a new way to tour the Moon. The website, called QuickMap, allows a user with any home computer to zoom into any spot on the lunar surface and see the high resolution images being taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Using QuickMap, I spent a few hours this past weekend strolling about on the northern half of the floor of the crater Copernicus. It is in this area, annotated in the image on the right, that NASA engineer James Fincannon has already located a slew of collapse features and possible caves, the images of which I have posted previously on behindtheblack. (Click on the image or here to see a larger version of this updated index map.)
(You also can go sightseeing there if you wish. Go to QuickMap and zoom in on 10.1 latitude and -20.1 longitude to get to the floor of Copernicus. Or pick your own spot on the lunar surface and do some of your own exploring!)
What I found in the northern half of Copernicus’s floor was a plethora of possible caves and collapse features. Literally, the crater floor is littered with what appear to be pits, fissures, rills, and sinks. More significantly, sometimes the cave entrances line up with long straight collapse features, suggesting strongly the existence of extensive underground passages beyond the initial entrance pits.
» Read more
The winners of the 18th annual Great Moonbuggy Race.
China’s second lunar orbiter, Chang’e 2: still in operation after 180 days.
Unfortunately, little of its scientific results have been released.
No, the “supermoon” didn’t cause the Japanese earthquake.
29 teams, one purchased ride, and one mystery for the Google Lunar X Prize.
The discovery of new caves on the Moon keep coming. Today I have two new stories. The first is a discovery by professional scientists of a giant lava tube cave in the Oceanus Procellarum or Ocean of Storms. The second is the detection of a plethora of caves and sinks on the floor of the crater Copernicus, found by a NASA engineer who likes to explore the gobs of data being accumulated by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and made available to all on the web.
The image below of the Moon’s near side, taken by India’s Cartosat-2A satellite and taken from the science paper, shows the location of lava tube in Oceanus Procellarum (indicated by the red dot) and the crater Copernicus.
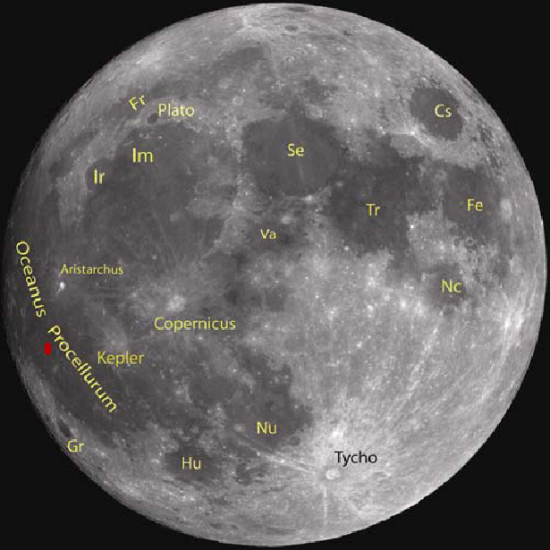
First the professional discovery. Yesterday, the Times of India reported the discovery of lava tube more than a mile long on the Moon. I did not post a link to the article because I didn’t think the news story provided enough information to make it worth passing along. Today however, fellow caver Mark Minton emailed me the link where the actual research paper could be downloaded [pdf]. This I find definitely worth describing.
» Read more
The Google Lunar X Prize has announced the final roster of teams competing for its $30 Million prize.