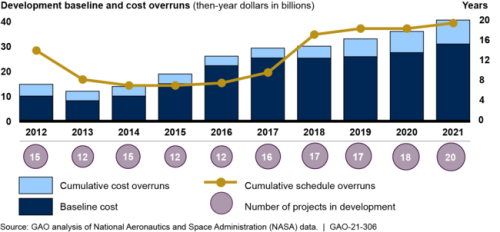
According to a new NASA inspector general report released today [pdf], because of numerous technical, budgetary, and management issues, the planned Artemis manned lunar landing now set for 2025 is likely to be delayed several years beyond that date. From the report’s summary:
NASA’s three initial Artemis missions, designed to culminate in a crewed lunar landing, face varying degrees of technical difficulties and delays heightened by the COVID-19 pandemic and weather events that will push launch schedules from months to years past the Agency’s current goals. With Artemis I mission elements now being integrated and tested at Kennedy Space Center, we estimate NASA will be ready to launch by summer 2022 rather than November 2021 as planned. Although Artemis II is scheduled to launch in late 2023, we project that it will be delayed until at least mid-2024 due to the mission’s reuse of Orion components from Artemis I. … Given the time needed to develop and fully test [SpaceX’s Starship lunar lander] and new spacesuits, we project NASA will exceed its current timetable for landing humans on the Moon in late 2024 by several years. [emphasis mine]
Gosh, it sure didn’t long for my prediction from last week — that the new target date of ’25 was garbage — to come true.
Today’s report also states that it does not expect the first test launch of SLS to occur in February ’22, as NASA presently predicts, but later, in the summer of ’22. It then notes that the next SLS launch, meant to be the first manned launch of SLS and Orion and presently scheduled for late ’23, will almost certainly be delayed to mid-’24. And that’s assuming all goes well on the first unmanned test flight.
While the report lauds SpaceX’s fast development pace, it also does not have strong confidence in SpaceX’s ability to get its Starship lunar lander ready on time, and believes that NASA could see its completion occurring from three to four years later than planned.
The report also confirms an August 2021 inspector general report about NASA’s failed program to develop lunar spacesuits, stating that its delays make a ’24 lunar landing impossible.
The report states that Gateway is well behind schedule, and will likely not be operational until ’26, at the earliest. While the present plan for that first manned lunar landing does not require Gateway, Gateway’s delays and cost overruns impact the overall program.
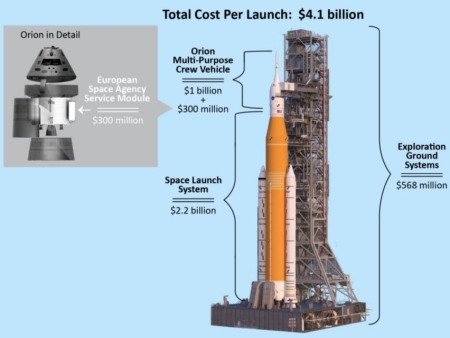
Finally, the report firmly states that the per launch cost of SLS is $4.1 billion, a price that will make any robust lunar exploration program utterly unsustainable.
Before the arrival of Trump, NASA’s original plan for SLS and Gateway called for a manned lunar landing in 2028. The Trump administration attempted to push NASA to get it done by ’24. This inspector general report suggests to me that this push effort was largely wasted, that NASA’s Artemis program will likely continue to have repeated delays, announced piecemeal in small chunks. This has been the public relations strategy of NASA throughout its entire SLS program. They announce a target date and then slowly over time delay it in small amounts to hide the fact that the real delay is many years.
Expect this same pattern with the manned lunar landing mission. They announce a delay of one year from ’24 to ’25. After a year they will then announce another delay to ’26. A year later another delay to ’27. And so forth.