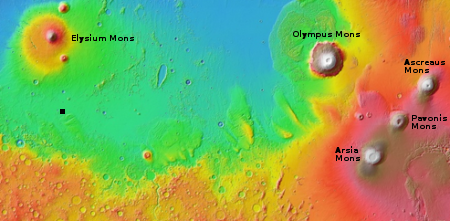
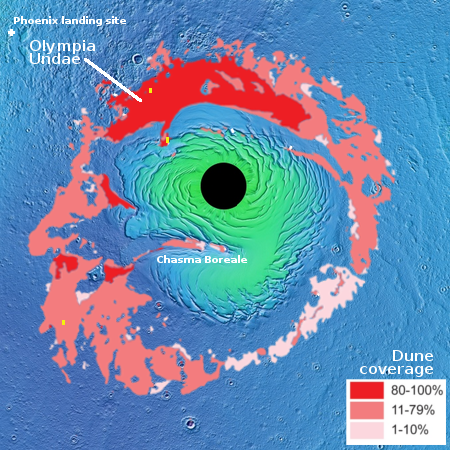
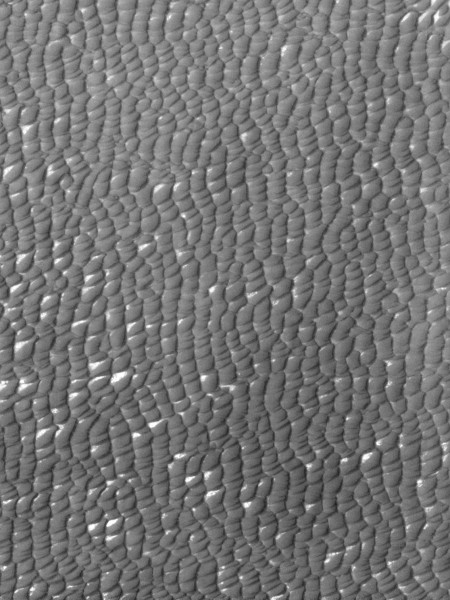
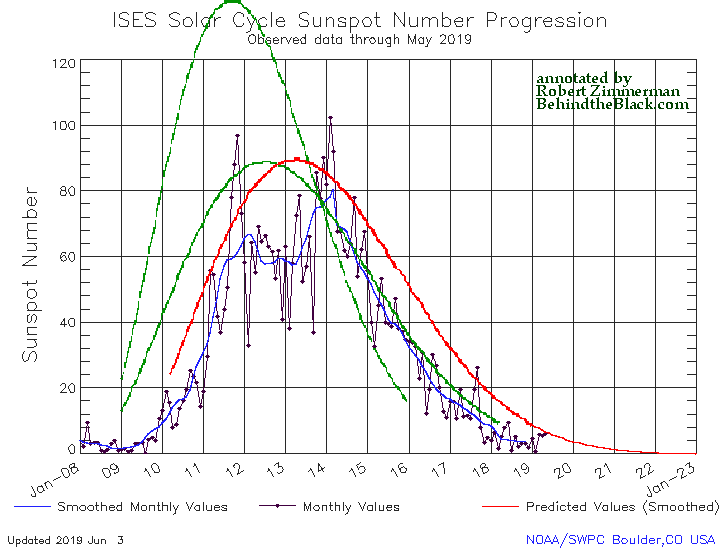
Two Earthlike planets possibly found around neaby red dwarf star
The uncertainty of science: Astronomers think they may have detected evidence of two Earth-sized planets orbiting a tiny red dwarf star only twelve light years away.
Ribas and his colleagues are currently searching for planets orbiting 342 small stars, so they aimed the CARMENES instrument, located at Spain’s Calar Alto Observatory, at the mini-star.
CARMENES observed Teegarden’s star over three years, watching for the wiggles and tugs produced by any orbiting planets. In the end, more than 200 measurements suggested that two small worlds are jostling the star, each weighing in at approximately 1.1 times Earth’s mass. The team calculates that one of the planets, called Teegarden’s star b, completed an orbit in a mere 4.9 Earth-days; the other world, Teegarden’s star c, has an orbit of just 11.4 days.
There is great uncertainty in these results, as the article correctly notes. However, if confirmed these planets could be the home of a very ancient civilization, considering that the red dwarf star is already twice as old as our Sun. There also could be no life there at all, as red dwarf stars tend to be very lacking in many of the materials needed for life.
The uncertainty of science: Astronomers think they may have detected evidence of two Earth-sized planets orbiting a tiny red dwarf star only twelve light years away.
Ribas and his colleagues are currently searching for planets orbiting 342 small stars, so they aimed the CARMENES instrument, located at Spain’s Calar Alto Observatory, at the mini-star.
CARMENES observed Teegarden’s star over three years, watching for the wiggles and tugs produced by any orbiting planets. In the end, more than 200 measurements suggested that two small worlds are jostling the star, each weighing in at approximately 1.1 times Earth’s mass. The team calculates that one of the planets, called Teegarden’s star b, completed an orbit in a mere 4.9 Earth-days; the other world, Teegarden’s star c, has an orbit of just 11.4 days.
There is great uncertainty in these results, as the article correctly notes. However, if confirmed these planets could be the home of a very ancient civilization, considering that the red dwarf star is already twice as old as our Sun. There also could be no life there at all, as red dwarf stars tend to be very lacking in many of the materials needed for life.