Scientists propose new theory to explain mysterious slope streaks on Mars
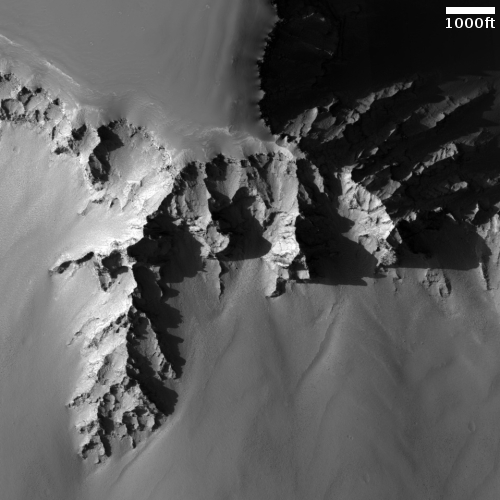
In a paper published earlier this month, scientists have proposed a new theory to explain the the origin of slope streaks on Mars, a unique Martian geological feature that at first glance look like a stainlike avalanches which also appear to do nothing to change the surface topography. (See earlier posts here and here for a description of this strange Martian phenomenon.)
Essentially, data from the orbiters suggests that carbon dioxide frost develops just under the surface during the night. In equatorial regions this frost mixes with dust (allowing it to exist even in these warmer climates). When the morning light hits the frost it causes it to sublimate away, which in turn causes the appearance of slope streaks as the dust is released from the frost.
At sunrise, sublimation-driven winds within the regolith are occasionally strong enough to displace individual dust grains, initiating and sustaining dust avalanches on steep slopes, forming ground features known as slope streaks. This model suggests that the CO2 frost cycle is an active geomorphological agent at all latitudes and not just at high or polar latitudes, and possibly a key factor maintaining mobile dust reservoirs at the surface.
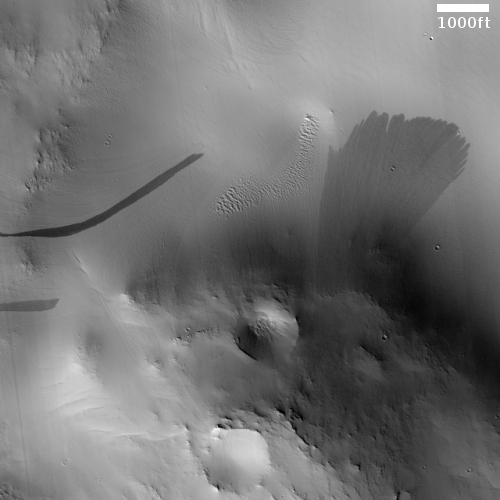
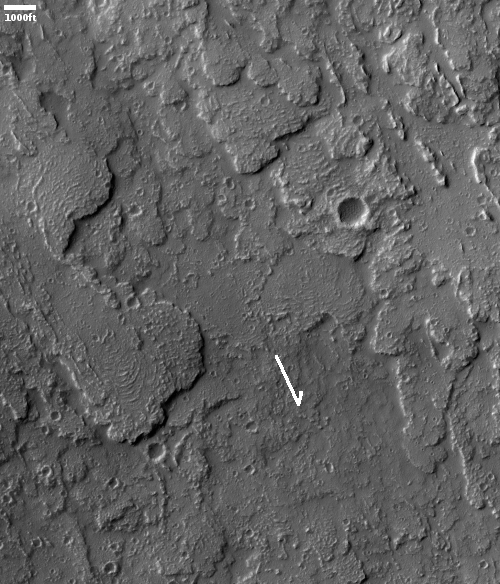
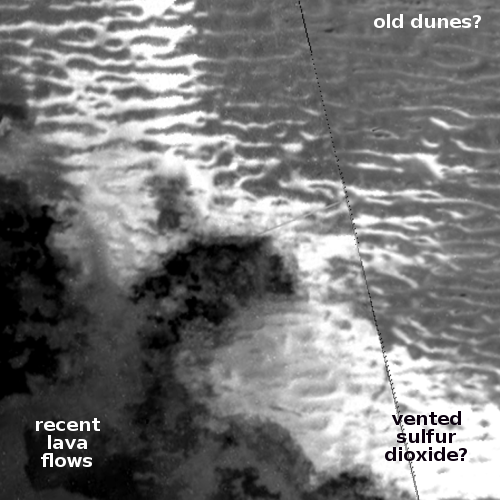
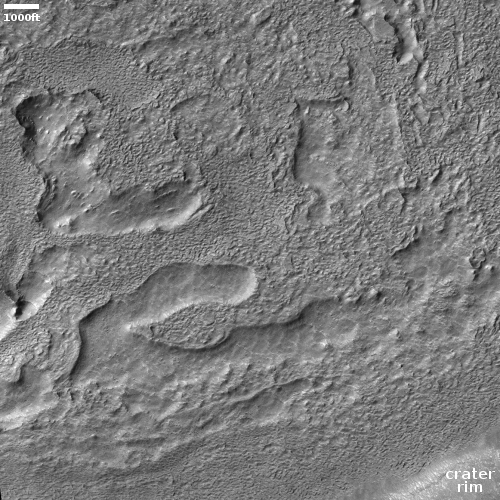
The cool image above, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on October 28, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and shows an excellent example of two very spectacular large slope streaks, one long and narrow and another short and wide. Located at 23 degrees, this is an area where no ice has yet been found near the surface.
This new theory joins two other popular theories attempting to explain slope streaks. The others postulate that the streaks are either dust avalanches of a different type or the percolation of a brine of chloride and/or perchlorate in a thin layer several inches thick close to the surface.
None have been proven. None likely fit all the known data at this point.
In a paper published earlier this month, scientists have proposed a new theory to explain the the origin of slope streaks on Mars, a unique Martian geological feature that at first glance look like a stainlike avalanches which also appear to do nothing to change the surface topography. (See earlier posts here and here for a description of this strange Martian phenomenon.)
Essentially, data from the orbiters suggests that carbon dioxide frost develops just under the surface during the night. In equatorial regions this frost mixes with dust (allowing it to exist even in these warmer climates). When the morning light hits the frost it causes it to sublimate away, which in turn causes the appearance of slope streaks as the dust is released from the frost.
At sunrise, sublimation-driven winds within the regolith are occasionally strong enough to displace individual dust grains, initiating and sustaining dust avalanches on steep slopes, forming ground features known as slope streaks. This model suggests that the CO2 frost cycle is an active geomorphological agent at all latitudes and not just at high or polar latitudes, and possibly a key factor maintaining mobile dust reservoirs at the surface.
The cool image above, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on October 28, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and shows an excellent example of two very spectacular large slope streaks, one long and narrow and another short and wide. Located at 23 degrees, this is an area where no ice has yet been found near the surface.
This new theory joins two other popular theories attempting to explain slope streaks. The others postulate that the streaks are either dust avalanches of a different type or the percolation of a brine of chloride and/or perchlorate in a thin layer several inches thick close to the surface.
None have been proven. None likely fit all the known data at this point.