The Sun continues to fizzle
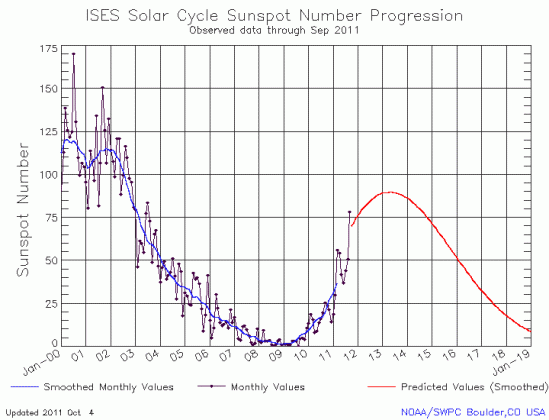
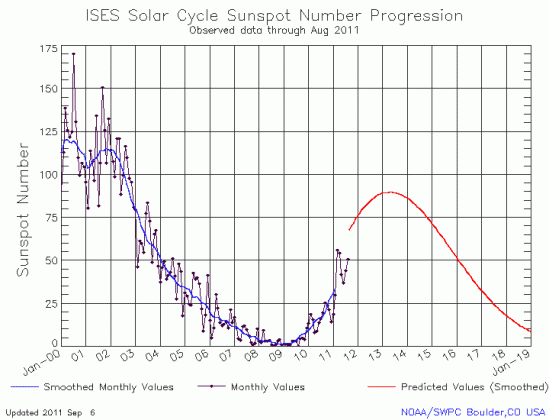
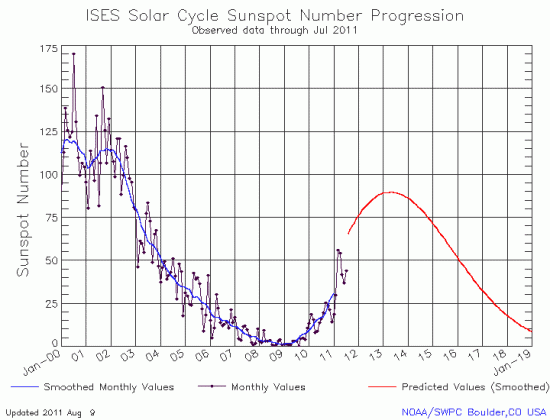
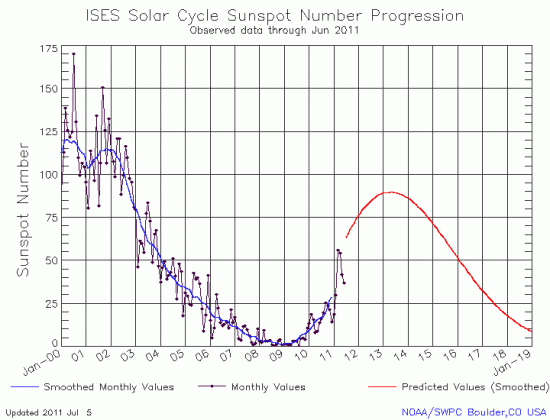
Yesterday NOAA posted its monthly update of the ongoing sunspot cycle of the Sun. You can see this latest graph, covering the month of July, below the fold.
As we have seen now for almost four years, the Sun continues to under-perform the predictions of solar scientists when it comes to the number of sunspots it is producing. In fact, that the sunspot number did not rise in July is surprising, as July had appeared to be a very active month for sunspots, with some of the strongest solar flares and coronal mass ejections seen in years. Instead, the number declined ever so slightly.
» Read more