Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter takes another look at the non-face on Mars
In 2007, shortly after it began science operations in Mars orbit, the science team for Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) pointed its high resolution camera at the so-called “Face on Mars”, taking a picture that confirmed (as had Mars Global Surveyor several years earlier) that this “face” was a non-face, simply a mesa whose features made it appear roughly facelike in low resolution imagery.
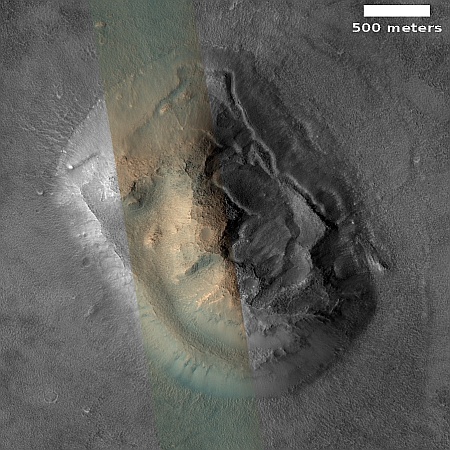
Now, more than sixteen years later, scientists have used MRO to take a new picture of the non-face mesa. That picture is to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. Compared to the 2007 photo the new photo has far better lighting conditions, revealing many details on the mesa’s eastern half that were mostly obscured by shadows previously.
In fact, these new details strongly suggest that the depression on the mesa’s eastern slopes harbors a decaying glacier. At least, that is what the features there resemble.
» Read more
In 2007, shortly after it began science operations in Mars orbit, the science team for Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) pointed its high resolution camera at the so-called “Face on Mars”, taking a picture that confirmed (as had Mars Global Surveyor several years earlier) that this “face” was a non-face, simply a mesa whose features made it appear roughly facelike in low resolution imagery.
Now, more than sixteen years later, scientists have used MRO to take a new picture of the non-face mesa. That picture is to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. Compared to the 2007 photo the new photo has far better lighting conditions, revealing many details on the mesa’s eastern half that were mostly obscured by shadows previously.
In fact, these new details strongly suggest that the depression on the mesa’s eastern slopes harbors a decaying glacier. At least, that is what the features there resemble.
» Read more